Content Menu
● What is a Pick and Place SMD Machine?
● The Role of Pick and Place Machines in PCB Assembly
>> Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Foundation
>> Automation and Precision
● How Pick and Place SMD Machines Improve PCB Assembly Efficiency
>> 1. Increased Speed and Throughput
>> 2. Enhanced Accuracy and Quality
>> 3. Versatility and Flexibility
>> 4. Cost Efficiency
>> 5. Improved PCB Design Integration
● Key Features of Pick and Place SMD Machines
>> Robotic Arms and Nozzles
>> Vision Systems
>> Component Feeders
>> Software and Programming
● Common Challenges and Maintenance
● Future Trends in Pick and Place SMD Machines
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the primary function of a pick and place SMD machine?
>> 2. How does a pick and place machine improve PCB assembly quality?
>> 3. Can pick and place machines handle different component sizes and types?
>> 4. What maintenance is required for pick and place SMD machines?
>> 5. How does PCB design affect pick and place machine efficiency?
In the fast-evolving electronics manufacturing industry, the demand for high-quality, reliable, and cost-effective printed circuit boards (PCBs) has never been greater. Central to meeting this demand is the use of advanced automation technologies, among which the pick and place SMD machine stands out as a transformative tool. This article explores how a pick and place SMD machine significantly improves PCB assembly efficiency, detailing its working principles, benefits, and impact on modern electronics production.
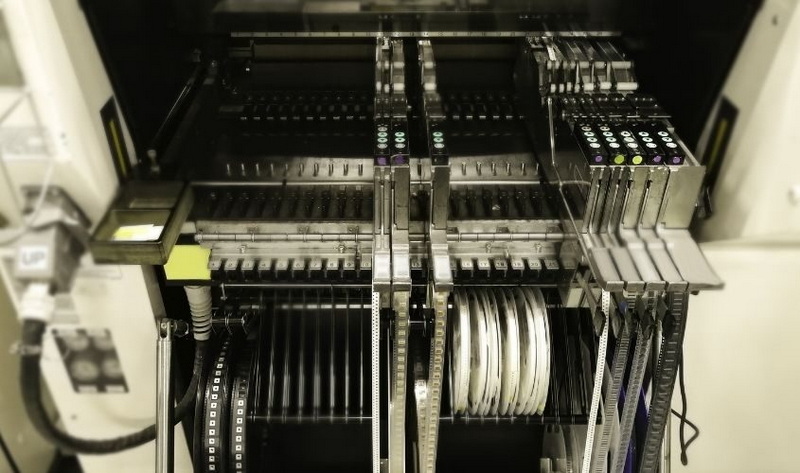

What is a Pick and Place SMD Machine?
A pick and place SMD (Surface Mount Device) machine is an automated robotic system designed to accurately pick electronic components from feeders and place them onto the surface of PCBs during the assembly process. Unlike traditional manual assembly, which is labor-intensive and prone to errors, these machines use precision robotics, vision systems, and programmable software to handle thousands of components per hour with exceptional accuracy.
The pick and place machine is a cornerstone of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) assembly lines, enabling manufacturers to meet the increasing complexity and miniaturization of modern electronic devices.
The Role of Pick and Place Machines in PCB Assembly
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Foundation
Surface Mount Technology revolutionized PCB assembly by allowing components to be mounted directly on the PCB surface rather than through holes. This enables higher component density, faster assembly, and improved electrical performance. Pick and place SMD machines are specifically engineered to handle SMT components, making them indispensable in modern PCB manufacturing.
Automation and Precision
Pick and place machines automate the placement of components, drastically reducing human error and increasing repeatability. Equipped with robotic arms, vacuum nozzles, and vision systems, these machines can identify, pick, and place components with micron-level precision, ensuring each part is positioned exactly as per design specifications.
How Pick and Place SMD Machines Improve PCB Assembly Efficiency
1. Increased Speed and Throughput
One of the most significant advantages of pick and place SMD machines is their speed. These machines can place hundreds to thousands of components per minute, far surpassing manual assembly rates. This rapid placement capability enables manufacturers to meet high-volume production demands and shorten time-to-market for electronic products.
For example, high-end pick and place machines can place up to 60,000 components per hour, which is impossible to achieve manually. This speed is critical for industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications, where rapid product cycles are the norm.
2. Enhanced Accuracy and Quality
The precision of pick and place machines minimizes placement errors, such as misalignment or incorrect orientation, which are common in manual assembly. Advanced vision systems verify component placement in real-time, reducing defects and improving overall product quality. This leads to fewer reworks and higher yield rates.
Accurate placement is especially important for fine-pitch components and complex packages like BGAs (Ball Grid Arrays), where even a slight misalignment can cause functional failures. The machine's ability to detect and correct errors during placement ensures consistent quality.
3. Versatility and Flexibility
Pick and place SMD machines can handle a wide variety of component types and sizes, including resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and ball grid arrays (BGAs). Their programmable nature allows quick changeovers between different PCB designs, supporting both small batch prototyping and large-scale production runs.
This flexibility is essential for manufacturers who produce multiple product lines or prototypes, as it reduces downtime and setup costs. Modern machines also support mixed technology assembly, combining SMT and through-hole components in one line.
4. Cost Efficiency
Although the initial investment in pick and place machines can be substantial, the long-term cost savings are significant. Automation reduces labor costs, minimizes material waste, and decreases the likelihood of costly errors. The increased throughput and quality also contribute to better return on investment.
By reducing manual labor, manufacturers can allocate human resources to more complex tasks such as quality control and process optimization. Additionally, the reduction in defective boards lowers scrap rates and warranty claims, further improving profitability.
5. Improved PCB Design Integration
Modern pick and place machines integrate seamlessly with PCB design software, allowing direct import of design files. This integration ensures that component placement is optimized for manufacturability, reducing assembly time and improving yield. Designers can also apply best practices to facilitate smoother pick and place operations, such as logical component arrangement and proper fiducial placement.
This synergy between design and manufacturing helps avoid common pitfalls like component crowding or insufficient fiducials, which can slow down the assembly process or cause errors.
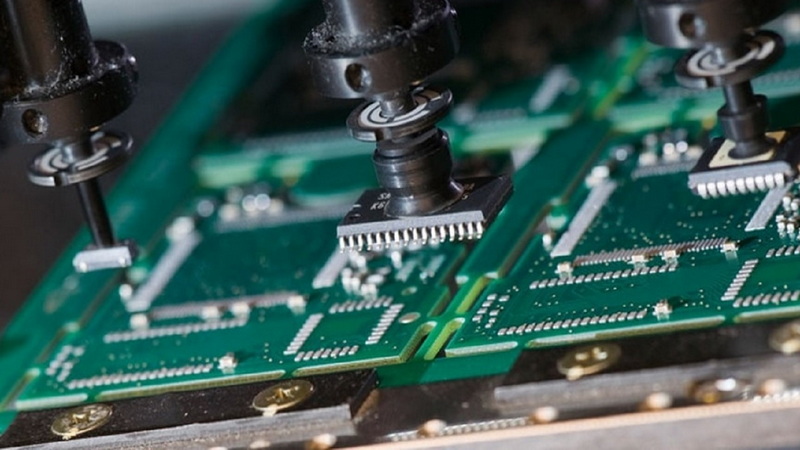
Key Features of Pick and Place SMD Machines
Robotic Arms and Nozzles
Robotic arms equipped with vacuum nozzles pick components from feeders and place them on the PCB. The nozzles are designed to handle delicate components without damage, and multiple nozzle sizes accommodate different component footprints. Some advanced machines feature multi-head systems that can place several components simultaneously, further increasing throughput.
Vision Systems
Cameras and sensors verify component orientation and placement accuracy. Fiducial recognition systems identify PCB alignment marks to ensure precise positioning. These vision systems enable real-time error detection and correction, which is crucial for maintaining high quality in high-speed production environments.
Component Feeders
Components are supplied to the machine via feeders, which can hold reels, trays, or tubes. Efficient feeder design and management are critical for continuous operation and minimizing downtime. Automated feeder loading systems and intelligent feeder tracking software help maintain smooth production flow.
Software and Programming
Pick and place machines are programmed with the PCB layout and component data. Software optimizes the placement sequence to reduce head travel time and maximize throughput. Some machines offer user-friendly interfaces requiring minimal training, while others provide advanced features like automatic feeder calibration and real-time production monitoring.
Common Challenges and Maintenance
Despite their advantages, pick and place SMD machines require regular maintenance to sustain performance. Common issues include nozzle wear, vacuum pressure inconsistencies, and calibration drift, which can lead to placement errors or component damage. Routine cleaning, calibration, and timely replacement of parts are essential to prevent downtime and maintain assembly quality.
Additionally, operators must ensure that feeders are correctly loaded and components are free from contamination or damage. Environmental factors such as dust and humidity can also affect machine performance, so maintaining a clean and controlled production environment is important.
Future Trends in Pick and Place SMD Machines
As electronics continue to miniaturize and become more complex, pick and place machines are evolving to meet new challenges. Emerging trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI-powered vision systems can improve defect detection and adapt placement strategies dynamically.
- Higher Speed and Precision: Newer machines are pushing the limits of speed without compromising accuracy, using multi-head and multi-robot configurations.
- Integration with Industry 4.0: Smart factories use IoT connectivity to monitor machine health, optimize production schedules, and enable predictive maintenance.
- Handling of 3D Components: Advanced pick and place machines are being developed to handle 3D components and flexible PCBs, expanding their application scope.
Conclusion
Pick and place SMD machines have revolutionized PCB assembly by dramatically improving speed, accuracy, and cost efficiency. Their ability to handle complex SMT components with precision and flexibility makes them indispensable in modern electronics manufacturing. By integrating advanced robotics, vision systems, and software, these machines enable manufacturers to meet the growing demand for high-quality PCBs while reducing production time and costs. As technology advances, pick and place machines will continue to evolve, further enhancing PCB assembly efficiency and supporting innovation in the electronics industry.
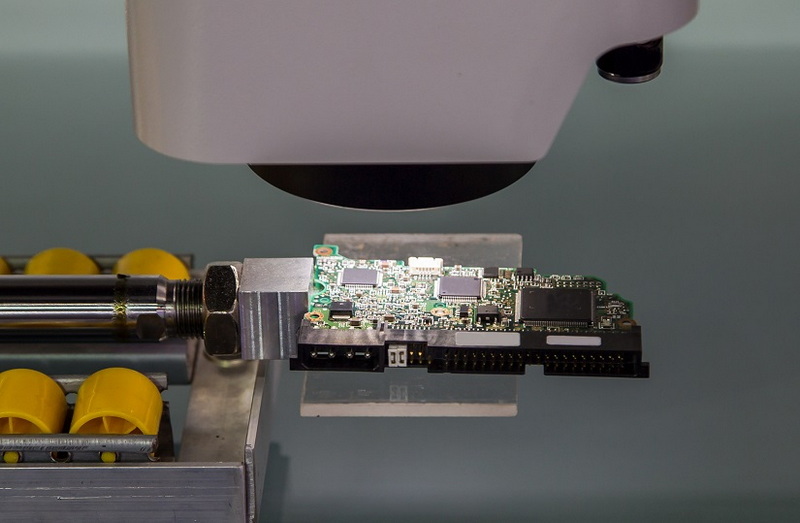
FAQ
1. What is the primary function of a pick and place SMD machine?
A pick and place SMD machine automates the process of picking electronic components and placing them accurately onto PCBs during assembly, improving speed and precision compared to manual methods.
2. How does a pick and place machine improve PCB assembly quality?
By using vision systems and precise robotic placement, pick and place machines reduce human errors, ensure correct component orientation, and minimize defects, leading to higher quality PCBs.
3. Can pick and place machines handle different component sizes and types?
Yes, these machines are versatile and can handle a wide range of components, including small resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and complex packages like BGAs.
4. What maintenance is required for pick and place SMD machines?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning nozzles and cameras, calibrating placement accuracy, checking vacuum pressure, and replacing worn parts to prevent errors and downtime.
5. How does PCB design affect pick and place machine efficiency?
Optimized PCB design, including logical component placement and proper fiducial marks, reduces machine travel time and placement errors, improving overall assembly efficiency and yield.




















