Content Menu
● What Are SMT Stencils?
● Why Stainless Steel Is the Material of Choice for SMT Stencils
>> Durability and Longevity
>> Excellent Heat Resistance and Stability
>> Superior Print Quality and Paste Release
>> Corrosion Resistance
>> Cost-Effectiveness
● Types of Stainless Steel SMT Stencils
● Manufacturing and Material Considerations
>> Laser Cutting and Precision
>> Fine Grain Stainless Steel
>> Thickness Selection
● Advantages of Stainless Steel SMT Stencils
● Impact on Modern Electronics Manufacturing
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
>> 1. What makes stainless steel SMT stencils better than other materials?
>> 2. How does the grain size of stainless steel affect stencil performance?
>> 3. What are the common thicknesses of stainless steel SMT stencils?
>> 4. Can stainless steel SMT stencils be reused?
>> 5. What types of stainless steel SMT stencils are available?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) stencils are indispensable tools in modern electronics manufacturing, enabling the precise application of solder paste onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). Among various materials used for SMT stencils, stainless steel stands out as the preferred choice due to its exceptional properties. This article explores why stainless steel SMT stencils dominate the industry, detailing their advantages, material characteristics, manufacturing processes, and impact on print quality and production efficiency.
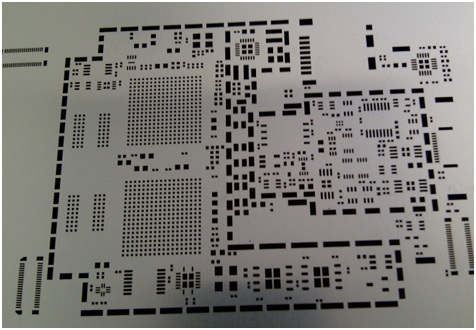
What Are SMT Stencils?
SMT stencils are thin metal sheets with laser-cut apertures that correspond exactly to the solder pads on a PCB. These apertures allow for controlled deposition of solder paste, which is critical for forming reliable solder joints between electronic components and the PCB. The stencil is aligned on the PCB, and solder paste is applied over it; when removed, paste remains only on the pads, ready for component placement.
The quality and consistency of solder paste application directly influence the yield and reliability of electronic assemblies. Therefore, the choice of stencil material and manufacturing process is crucial in SMT production.
Why Stainless Steel Is the Material of Choice for SMT Stencils
Durability and Longevity
One of the primary reasons stainless steel SMT stencils are preferred is their exceptional durability. Stainless steel is a robust metal alloy known for its strength and resistance to mechanical wear. In high-volume SMT production lines, stencils undergo repeated cycles of printing, cleaning, and handling. Materials like polyester or nickel may degrade or deform under such conditions, leading to inconsistent solder paste deposition and increased defect rates.
Stainless steel's hardness and resistance to abrasion allow it to maintain aperture integrity over thousands of print cycles. This longevity reduces the frequency of stencil replacement, lowering overall manufacturing costs and downtime.
Excellent Heat Resistance and Stability
During the stencil manufacturing process, laser cutting generates intense localized heat. Materials that are sensitive to heat can warp or distort, compromising aperture accuracy and stencil flatness. Stainless steel, especially high-grade types such as 300 series stainless steel or fine grain stainless steel, exhibits excellent heat resistance, minimizing thermal deformation.
Maintaining a perfectly flat stencil surface is critical because any warping can cause uneven contact with the PCB. This unevenness leads to solder paste smearing, bridging between pads, or insufficient paste deposits. Stainless steel's dimensional stability ensures consistent print quality and reduces the need for frequent calibration or adjustments on the production line.
Superior Print Quality and Paste Release
The internal surface quality of stencil apertures significantly affects solder paste release. Stainless steel SMT stencils, particularly those made from fine grain stainless steel, have smooth aperture walls due to the metal's uniform grain structure. This smoothness prevents solder paste from sticking inside the apertures, facilitating clean and complete paste release onto the PCB pads.
Improved paste release translates into more precise and consistent solder paste volumes, which is especially important for fine-pitch components, micro-BGAs, and other advanced packaging technologies. This precision reduces solder defects such as bridging, insufficient solder, and tombstoning, enhancing overall assembly reliability.
Corrosion Resistance
SMT stencils are exposed to various chemicals, including flux residues and cleaning solvents. Stainless steel's natural corrosion resistance protects the stencil from rust and chemical degradation. This resistance not only extends stencil life but also maintains aperture dimensions and surface smoothness, preserving print quality over time.
Cost-Effectiveness
Although stainless steel SMT stencils may have a higher upfront cost compared to some alternatives, their durability and performance yield significant cost savings in the long term. Reduced stencil replacements, fewer print defects, and less rework contribute to lower total cost of ownership. Additionally, stainless steel stencils support high-volume manufacturing with minimal downtime, improving overall production efficiency.
Types of Stainless Steel SMT Stencils
The versatility of stainless steel allows it to be used in various stencil formats tailored to different manufacturing needs:
- Framed Stencils: Stainless steel foil permanently mounted within a rigid frame. These stencils offer excellent stability and are ideal for high-volume and automated printing processes. The frame supports the stencil, maintaining tension and flatness during printing.
- Frameless Stencils (Foil Stencils): Thin stainless steel sheets without a frame, used mainly for prototyping, small batch production, or low-volume runs. They are lightweight, easy to store, and cost-effective but require careful handling to avoid deformation.
- Step Stencils: These stencils have varying thicknesses in different areas to accommodate components with different solder paste volume requirements on the same PCB. Stainless steel's mechanical strength allows precise step formation without compromising stencil integrity.
- Nano-Coated Stencils: Stainless steel stencils treated with a nano-coating to enhance solder paste release and reduce cleaning frequency. The coating creates a non-stick surface, improving print consistency and extending stencil life.

Manufacturing and Material Considerations
Laser Cutting and Precision
The manufacturing of stainless steel SMT stencils relies heavily on laser cutting technology. Laser cutting produces sharp, precise aperture edges essential for accurate solder paste deposition. The quality of the laser cut depends on the stainless steel's thickness, grain structure, and surface finish.
Premium stainless steel used for SMT stencils is precision-rolled and stress-relieved to minimize thickness variation and internal stresses. This treatment reduces distortion during laser cutting and ensures aperture dimensions remain within tight tolerances.
Fine Grain Stainless Steel
Fine grain stainless steel is a specialized form of stainless steel with significantly smaller grain size compared to standard stainless steel. The reduction in grain size leads to smoother aperture walls and crisper stencil steps. This improvement enhances solder paste release and print quality, particularly for ultra-fine pitch components.
Independent studies and industry reports have demonstrated that fine grain stainless steel stencils outperform standard stainless steel, nickel, and nickel-plated stencils in terms of print consistency and stencil longevity.
Thickness Selection
Stainless steel SMT stencil thickness typically ranges from 0.1 mm to 0.2 mm. The choice of thickness depends on the solder paste volume required for the PCB design. Thicker stencils deposit more paste, suitable for larger components or boards with high stand-off requirements, while thinner stencils are used for fine-pitch components to avoid solder bridging.
Stainless steel's mechanical strength allows for thinner stencils without sacrificing durability, enabling manufacturers to optimize solder paste volume precisely.
Advantages of Stainless Steel SMT Stencils
- Precision Deposition: Stainless steel stencils ensure uniform solder paste application, reducing defects like bridging or insufficient solder joints.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Stainless steel stencils allow simultaneous paste application across multiple PCBs, speeding up production lines.
- Consistency and Quality Control: Stainless steel maintains print quality over many cycles, improving product reliability and yield.
- Cost Savings: The durability and reusability of stainless steel stencils minimize material waste and rework costs due to precise paste volume control.
- Flexibility: Stainless steel stencils are suitable for a wide range of PCB designs, including fine-pitch and complex layouts.
- Environmental Benefits: By improving first-pass yield and stencil longevity, stainless steel stencils reduce waste and energy consumption in electronics manufacturing.
Impact on Modern Electronics Manufacturing
The electronics industry is continuously pushing for smaller, more complex, and higher-density PCB assemblies. This trend demands extremely precise solder paste application to ensure reliable connections in fine-pitch components, micro-BGAs, and other advanced packaging technologies.
Stainless steel SMT stencils meet these challenges by providing:
- High Precision: The ability to produce apertures with tight tolerances and smooth walls.
- Repeatability: Consistent print results over thousands of cycles.
- Adaptability: Compatibility with various stencil designs, including step and nano-coated stencils.
- Reliability: Resistance to wear, corrosion, and thermal distortion.
As a result, stainless steel SMT stencils contribute significantly to reducing defects, improving yields, and enabling the production of cutting-edge electronic devices.
Conclusion
Stainless steel SMT stencils have become the industry standard due to their unmatched combination of durability, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and print quality. Their ability to maintain flatness and precise aperture dimensions under demanding manufacturing conditions ensures consistent solder paste deposition, which is critical for reliable PCB assembly.
While alternatives exist, stainless steel offers the best balance of performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness, making it the preferred material for SMT stencils in both high-volume and specialized electronics manufacturing. Investing in high-quality stainless steel SMT stencils ultimately translates into improved product quality, reduced manufacturing costs, and enhanced production efficiency.
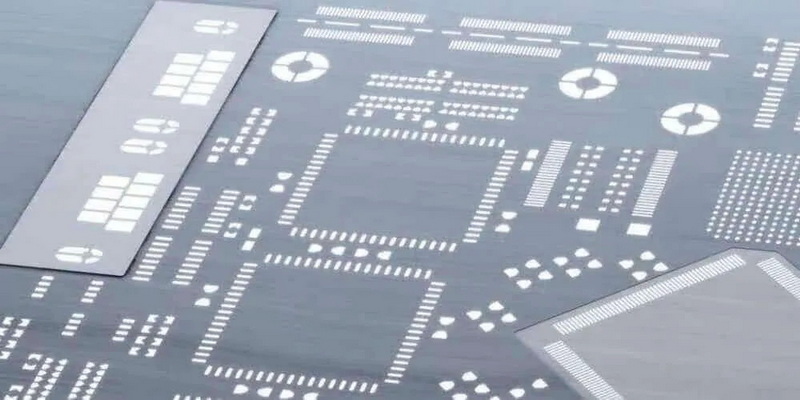
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What makes stainless steel SMT stencils better than other materials?
Stainless steel offers superior durability, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and precision compared to other materials like nickel or polyester, resulting in longer stencil life and better print quality.
2. How does the grain size of stainless steel affect stencil performance?
A smaller grain size in stainless steel (fine grain stainless steel) produces smoother aperture walls, which improves solder paste release and print quality, reducing defects in solder joints.
3. What are the common thicknesses of stainless steel SMT stencils?
Typical stencil thicknesses range from 0.1 mm to 0.2 mm, with 0.15 mm being a common choice that balances paste volume and print precision.
4. Can stainless steel SMT stencils be reused?
Yes, stainless steel stencils are highly durable and can be cleaned and reused multiple times without significant loss of print quality, making them cost-effective for production.
5. What types of stainless steel SMT stencils are available?
Common types include framed, frameless (foil), step, and nano-coated stainless steel stencils, each suited for different production volumes and PCB complexity.




















