Content Menu
● The Evolution of PCB Assembly
>> From Through-Hole to Surface Mount
>> Understanding SMT and SMD
● The SMT Manufacturing Process
>> 1. PCB Preparation
>> 2. Solder Paste Application
>> 3. Solder Paste Inspection (SPI)
>> 4. Component Placement
>> 5. Reflow Soldering
>> 6. Inspection and Testing
● Advantages of SMD SMT Assembly in PCB Production
>> Miniaturization and Space Efficiency
>> Increased Production Efficiency
>> Improved Performance
>> Cost-Effectiveness
>> Enhanced Reliability
● Challenges and Considerations in SMD SMT Assembly
>> Component Selection
>> Thermal Management
>> Rework and Repair
>> Quality Control
● The Future of SMD SMT Assembly in PCB Production
>> Increasing Miniaturization
>> Advanced Automation
>> Integration with Other Technologies
>> Sustainability Considerations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the difference between SMT and SMD?
>> 2. How does SMD SMT assembly improve PCB production efficiency?
>> 3. What are the main challenges in SMD SMT assembly?
>> 4. Can SMD SMT assembly be used for all types of electronic components?
>> 5. How does SMD SMT assembly contribute to the miniaturization of electronic devices?
● Citations:
In the ever-evolving world of electronics manufacturing, efficiency and precision are paramount. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Surface Mount Devices (SMD) have revolutionized the way Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are produced, offering numerous advantages over traditional through-hole technology. This article delves into the crucial role of SMD SMT assembly in efficient PCB board production, exploring its benefits, processes, and impact on the electronics industry.
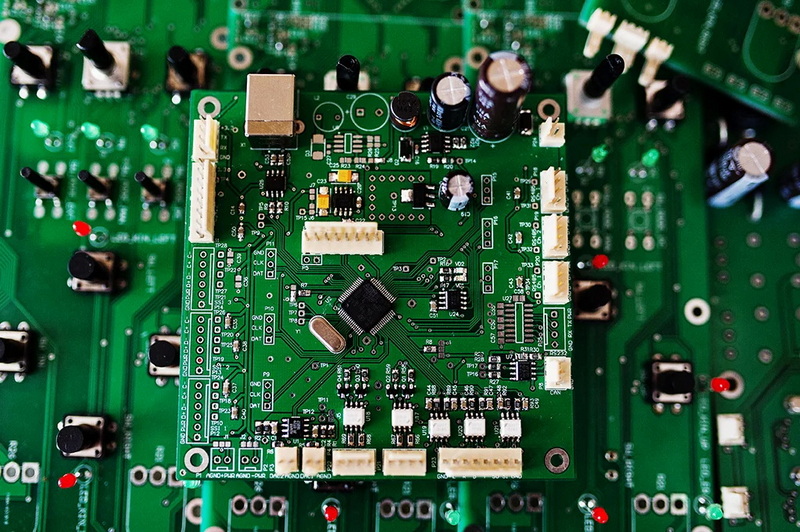
The Evolution of PCB Assembly
From Through-Hole to Surface Mount
The electronics industry has come a long way since the days of through-hole technology. While through-hole components were the standard for decades, the demand for smaller, more complex electronic devices necessitated a shift towards more efficient assembly methods. This is where SMT and SMD came into play, revolutionizing PCB board production.
Understanding SMT and SMD
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) refers to the method of producing electronic circuits where components are mounted directly onto the surface of PCBs. Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) are the components specifically designed for this technology. Together, they form the backbone of modern PCB assembly processes[1][5].
The SMT Manufacturing Process
1. PCB Preparation
The SMT manufacturing process begins with the preparation of the PCB. This involves transferring the bare PCB into a solder paste printing machine, which is the first step in the SMT assembly line[1].
2. Solder Paste Application
A crucial step in SMD SMT assembly is the application of solder paste. This is done using a stencil for silkscreen printing the solder paste onto specific areas of the PCB. The solder paste acts as both an adhesive for holding components in place and as the conductive material for forming electrical connections[1][3].
3. Solder Paste Inspection (SPI)
After the solder paste application, the PCB undergoes a solder paste inspection. This step ensures that the solder paste has been applied correctly in terms of position, surface, shape, and thickness. Any issues detected at this stage can be addressed before components are placed, saving time and resources[1].
4. Component Placement
The next stage in the SMD SMT assembly process is the placement of components onto the PCB. This is typically done using automated pick-and-place machines. These machines are capable of placing a wide variety of SMD components, from small resistors and capacitors to larger integrated circuits and connectors[1][2].
5. Reflow Soldering
Once all components are placed, the PCB enters a reflow oven. This oven heats the board in a controlled manner, causing the solder paste to melt and form connections between the components and the PCB. After cooling, these connections solidify, creating robust electrical and mechanical bonds[1][2].
6. Inspection and Testing
The final steps in the SMD SMT assembly process involve inspection and testing. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) machines are used to check for any defects in component placement or soldering. For boards with Ball Grid Array (BGA) components, X-ray inspection may be used to check the hidden solder connections[1].
Advantages of SMD SMT Assembly in PCB Production
Miniaturization and Space Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of SMD SMT assembly is the ability to create smaller, more compact PCBs. SMD components are significantly smaller than their through-hole counterparts, allowing for higher component density on the board. This is crucial for the production of modern electronic devices that demand ever-smaller form factors[5][7].
Increased Production Efficiency
SMT assembly processes are highly automated, leading to faster production times and increased efficiency. Advanced pick-and-place machines can place tens of thousands of components per hour, significantly outpacing manual assembly methods[7].
Improved Performance
SMD components typically offer better electrical performance than through-hole components. The shorter leads and direct surface mounting result in lower resistance and inductance at connections. This leads to better high-frequency performance and improved electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)[7].
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in SMT equipment can be substantial, the long-term cost benefits are significant. SMD components are often less expensive than their through-hole equivalents, and the automated assembly process reduces labor costs. Additionally, the ability to place components on both sides of the PCB maximizes board real estate, potentially reducing overall board size and material costs[7].
Enhanced Reliability
SMD SMT assembly often results in more reliable PCBs. The surface tension of molten solder during the reflow process helps to self-align components, reducing the likelihood of misalignment. Additionally, SMD components typically perform better under shock and vibration conditions due to their lower mass and direct surface mounting[7].
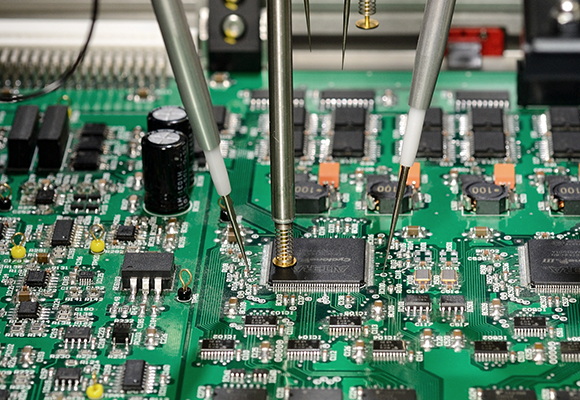
Challenges and Considerations in SMD SMT Assembly
Component Selection
Choosing the right components is crucial in SMD SMT assembly. It's important to select components that are compatible with the SMT process and can withstand the temperatures involved in reflow soldering. Using standard sizes and shapes can help streamline the manufacturing process[2].
Thermal Management
The reflow soldering process involves subjecting the entire PCB to high temperatures. This can be challenging for heat-sensitive components. Careful thermal profiling and component selection are necessary to ensure all components can withstand the reflow process without damage[2].
Rework and Repair
While SMD SMT assembly offers many advantages, rework and repair can be more challenging compared to through-hole technology. Special equipment and skills are often required to replace or repair SMD components on a populated PCB[5].
Quality Control
Given the small size of SMD components and the precision required in their placement, quality control is paramount in SMD SMT assembly. Advanced inspection techniques, including AOI and X-ray inspection, are crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of the finished PCB[1].
The Future of SMD SMT Assembly in PCB Production
As electronic devices continue to evolve, becoming smaller, more powerful, and more complex, the role of SMD SMT assembly in PCB production is set to become even more crucial. Several trends are shaping the future of this technology:
Increasing Miniaturization
The drive towards smaller and more compact electronic devices is pushing the boundaries of SMD technology. We can expect to see even smaller components and more densely packed PCBs in the future[5].
Advanced Automation
As Industry 4.0 concepts take hold in electronics manufacturing, we can expect to see even more advanced automation in SMD SMT assembly. This may include AI-driven component placement optimization and real-time quality control systems[2].
Integration with Other Technologies
SMD SMT assembly is likely to be increasingly integrated with other advanced manufacturing technologies. This could include additive manufacturing techniques for creating custom PCB structures or advanced materials science for developing new types of SMD components[7].
Sustainability Considerations
As environmental concerns become more pressing, the electronics industry is likely to focus more on sustainable manufacturing practices. This could lead to innovations in SMD SMT assembly processes that reduce waste, energy consumption, and the use of harmful materials[2].
Conclusion
SMD SMT assembly has revolutionized PCB production, offering numerous advantages in terms of efficiency, miniaturization, performance, and cost-effectiveness. As electronic devices continue to evolve, becoming smaller, more powerful, and more complex, the importance of SMD SMT assembly in PCB board production is only set to increase.
The ability to create densely packed, high-performance PCBs using automated processes has enabled the rapid advancement of electronic technology we see today. From smartphones to advanced medical devices, SMD SMT assembly plays a crucial role in bringing these innovations to life.
However, it's important to recognize that SMD SMT assembly also comes with its own set of challenges. These include the need for precise component selection, careful thermal management, and advanced quality control measures. Overcoming these challenges requires ongoing innovation and expertise in the field of electronics manufacturing.
As we look to the future, it's clear that SMD SMT assembly will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the electronics industry. With ongoing advancements in automation, miniaturization, and integration with other technologies, SMD SMT assembly will remain at the forefront of efficient PCB board production for years to come.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between SMT and SMD?
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) refers to the method of mounting components directly onto the surface of a PCB, while SMD (Surface Mount Device) refers to the components designed for this technology. SMT is the process, while SMDs are the parts used in this process[5].
2. How does SMD SMT assembly improve PCB production efficiency?
SMD SMT assembly improves efficiency through automation, allowing for faster component placement and the ability to mount components on both sides of the PCB. It also enables higher component density, reducing overall board size and material costs[7].
3. What are the main challenges in SMD SMT assembly?
The main challenges include precise component selection, thermal management during reflow soldering, more complex rework and repair processes, and the need for advanced quality control measures due to the small size of components[2][5].
4. Can SMD SMT assembly be used for all types of electronic components?
While SMD SMT assembly is suitable for a wide range of components, some specialized or large components may still require through-hole mounting. However, the majority of modern electronic components are available in SMD formats[5].
5. How does SMD SMT assembly contribute to the miniaturization of electronic devices?
SMD components are significantly smaller than their through-hole counterparts, allowing for higher component density on PCBs. This enables the creation of smaller, more compact electronic devices without sacrificing functionality[5][7].
Citations:
[1] https://www.pcbonline.com/blog/smt-manufacturing-process.html
[2] https://www.macrofab.com/blog/smt-assembly-vs-through-hole/
[3] https://www.protoexpress.com/kb/smt-assembly/
[4] https://www.nextpcb.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-smt-pcb-assembly
[5] https://www.pcbelec.com/what-is-the-difference-between-smt-and-smd.html
[6] https://www.wevolver.com/article/smt-vs-smd-vs-tht-a-comprehensive-guide-to-electronics-assembly-techniques
[7] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surface-mount_technology
[8] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surface_mount




















