Content Menu
● Understanding SMT Production Lines
● Key Equipment in an SMT Yellow Line
>> 1. Solder Paste Printing Machine
>> 2. Pick and Place Machine
>> 3. Reflow Oven
>> 4. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) System
>> 5. Conveyor Systems
● Additional Tools and Equipment
● The Importance of Quality Control
● Future Trends in SMT Technology
● Challenges in SMT Production
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
>> 2. Why is a pick-and-place machine important?
>> 3. How does a reflow oven work?
>> 4. What role does AOI play in an SMT line?
>> 5. Why is ESD control important in SMT production?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has transformed the electronics manufacturing landscape, enabling companies to produce smaller, more efficient electronic devices. An SMT yellow line is a designated area within a manufacturing facility where surface mount components are assembled onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). The efficiency and quality of this process depend significantly on the tools and equipment utilized. This article delves into the essential tools and equipment that constitute an SMT yellow line, detailing their functions and importance in the production process.
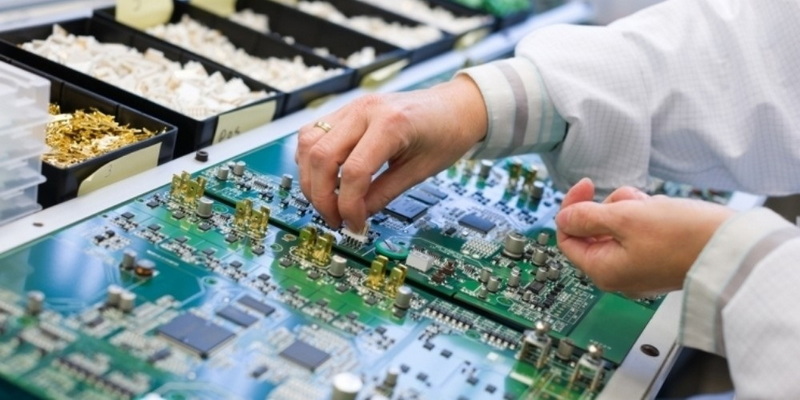

Understanding SMT Production Lines
An SMT production line is a highly automated setup designed for the assembly of electronic components onto PCBs. The term "yellow line" typically denotes a specific area where these processes occur, characterized by advanced machinery and technology to ensure high precision and speed.
The primary components of an SMT yellow line include:
- Solder Paste Printing Machines
- Pick and Place Machines
- Reflow Ovens
- Inspection Systems
- Conveyor Systems
Each piece of equipment plays a critical role in ensuring that the assembly process is efficient, reliable, and capable of producing high-quality electronic products.
Key Equipment in an SMT Yellow Line
1. Solder Paste Printing Machine
The solder paste printing machine is one of the first machines in an SMT yellow line. Its primary function is to apply solder paste onto the PCB pads where components will be placed. This process is crucial as it ensures that there is adequate solder to create reliable electrical connections once the components are soldered.
- Functionality: The machine uses a stencil to control the amount of solder paste applied, ensuring uniform coverage across all pads.
- Importance: Proper application of solder paste is vital for preventing defects such as solder bridging or insufficient solder joints.
Solder paste printing machines can be further categorized into manual and automatic types. Automatic printers are preferred for high-volume production due to their speed and accuracy. Some advanced models feature integrated vision systems that monitor print quality in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments if necessary.
2. Pick and Place Machine
The pick and place machine is arguably the most critical piece of equipment in an SMT yellow line. It is responsible for accurately placing surface mount devices (SMDs) onto the PCB.
- Functionality: Using advanced robotics, these machines can pick up components from feeders and place them precisely on designated pads on the PCB.
- Importance: The accuracy of component placement directly affects the quality of the final product. High-speed pick and place machines can significantly increase production rates.
Pick-and-place machines vary widely based on their capabilities. High-speed models can place thousands of components per hour, while flexible models allow quick changeovers between different component sizes without extensive downtime due to modular feeder systems accommodating various component types.
Modern pick-and-place machines often incorporate sophisticated software that utilizes CAD data from PCB designs to optimize placement strategies dynamically. This helps improve yield rates by ensuring precise placements even with complex layouts.
3. Reflow Oven
After components are placed on the PCB, they must be soldered into position using a reflow oven. This machine heats the PCB to melt the solder paste, creating permanent connections between the components and the board.
- Functionality: Reflow ovens utilize controlled heating profiles to ensure that all components are soldered without overheating or damaging sensitive parts.
- Importance: Proper temperature control during reflow is essential for achieving reliable solder joints and preventing defects such as cold solder joints or component warping.
Reflow ovens come in various configurations:
- Convection Ovens: Utilize hot air circulation for even heating across all areas of the PCB.
- Infrared Ovens: Use infrared radiation for rapid heating but may require careful temperature profiling due to uneven heat distribution risks.
Advanced reflow ovens now feature multi-zone temperature controls allowing manufacturers to customize heating profiles based on specific component requirements—this capability enhances overall product reliability by minimizing thermal stress on sensitive parts during assembly.
4. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) System
Once soldering is complete, an AOI system inspects the PCBs for defects. This machine uses high-resolution cameras to detect issues such as misaligned components, insufficient solder, or other assembly errors.
- Functionality: AOI systems can quickly identify defects that might not be visible to the naked eye, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
- Importance: Early detection of defects helps reduce waste and ensures that only high-quality products proceed to further testing or packaging.
Beyond AOI systems, manufacturers often employ additional inspection technologies:
- Flying Probe Testers: These systems use movable probes that touch various points on a PCB without requiring fixtures; they are particularly useful for low-volume runs where setup costs need to be minimized.
- Functional Testing Systems: These test completed assemblies under simulated operational conditions ensuring all functionalities perform as expected before shipment—this step is critical for consumer electronics where reliability is paramount.
5. Conveyor Systems
Conveyor systems facilitate the movement of PCBs between different machines in an SMT yellow line. They play a crucial role in maintaining a smooth workflow and ensuring that each stage of production is efficiently connected.
- Functionality: These systems can be automated to transport PCBs at controlled speeds, reducing manual handling and potential damage.
- Importance: Efficient transportation minimizes bottlenecks in production and helps maintain consistent output rates.
Additional Tools and Equipment
In addition to the primary machines listed above, several other tools are essential for maintaining an effective SMT yellow line:
- Solder Paste Mixer: Ensures consistent mixing of solder paste for optimal application.
- SPI (Solder Paste Inspection) Machine: Checks the thickness and distribution of solder paste after printing.
- SMT Loader/Unloader: Automates loading PCBs into machines and unloading finished products.
- ESD Control Equipment: Protects sensitive electronic components from electrostatic discharge during handling.
- Cleaning Machines: Remove excess flux and contaminants from PCBs post-soldering.
The Importance of Quality Control
Quality control is paramount in any manufacturing process, especially in SMT production lines where precision is critical. Various inspection methods are employed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each PCB meets stringent quality standards:
- Solder Paste Inspection (SPI): Conducted immediately after solder paste application to verify thickness, area coverage, and volume distribution.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Used before and after reflow soldering to detect placement errors or solder joint defects.
These quality control measures help minimize defects, reduce rework costs, and ensure customer satisfaction with final products.
Future Trends in SMT Technology
As technology continues to evolve, so does SMT equipment. Some notable trends include:
- Increased Automation: More manufacturers are adopting fully automated lines that require minimal human intervention, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence is being integrated into SMT processes for predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and optimization of production workflows.
- Advanced Materials: The development of new materials for solder paste and components enhances performance while reducing environmental impact.
These advancements promise to further enhance productivity while maintaining high-quality standards in electronics manufacturing.
Challenges in SMT Production
While SMT technology offers numerous advantages, it also presents several challenges:
- Component Miniaturization: As electronic devices become smaller, there's a growing need for precision in placement and soldering processes. This miniaturization requires advanced equipment capable of handling tiny components without compromising quality.
- Thermal Management: With higher component densities on PCBs, managing heat during manufacturing becomes critical. Overheating can lead to component failure or reduced lifespan.
- Supply Chain Issues: The global semiconductor supply chain has faced significant disruptions recently. Manufacturers must adapt quickly to changing availability while maintaining production schedules.
Addressing these challenges requires continuous investment in technology upgrades as well as training personnel on new techniques and equipment usage.
Conclusion
The tools and equipment used in an SMT yellow line are integral to achieving high-quality electronic assemblies efficiently. From applying solder paste to inspecting completed boards, each machine plays a vital role in ensuring that products meet industry standards for performance and reliability. As technology continues to evolve, advancements in SMT equipment will further enhance production capabilities while addressing emerging challenges in electronics manufacturing.
FAQs
1. What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) refers to a method for producing electronic circuits where components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs) rather than through holes.
2. Why is a pick-and-place machine important?
A pick-and-place machine is crucial because it accurately places surface mount devices on PCBs, ensuring proper alignment for effective soldering.
3. How does a reflow oven work?
A reflow oven heats PCBs to melt solder paste applied during printing, creating permanent electrical connections between components and PCB pads.
4. What role does AOI play in an SMT line?
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems inspect completed assemblies for defects such as misalignment or insufficient solder before they move on to further processing or packaging.
5. Why is ESD control important in SMT production?
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage sensitive electronic components; therefore, ESD control measures protect these components during handling throughout the production process.




















