Content Menu
● Introduction
● What Are Surface Mount Devices?
>> Advantages of Surface Mount Devices
● Types of Surface Mount Devices
>> 1. Resistors
>> 2. Capacitors
>> 3. Diodes
>> 4. Transistors
>> 5. Integrated Circuits (ICs)
>> 6. Inductors
>> 7. Connectors
● Applications of Surface Mount Devices
>> 1. Consumer Electronics
>> 2. Automotive Electronics
>> 3. Telecommunications
>> 4. Medical Devices
>> 5. Industrial Equipment
>> 6. Aerospace and Defense
>> 7. Internet of Things (IoT)
● The Future of Surface Mount Devices
● Conclusion
● Related Questions
>> 1. What is the difference between SMD and THT?
>> 2. What are the benefits of using SMDs in electronics?
>> 3. Can SMDs be repaired or replaced easily?
>> 4. What industries commonly use surface mount devices?
>> 5. How do I choose the right SMD for my project?
Introduction
Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) are a cornerstone of modern electronics, revolutionizing how electronic components are assembled onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional through-hole components, SMDs are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB, allowing for more compact designs and efficient manufacturing processes. This article will explore the definition, advantages, types, applications, and future trends of surface mount devices, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role in electronics.
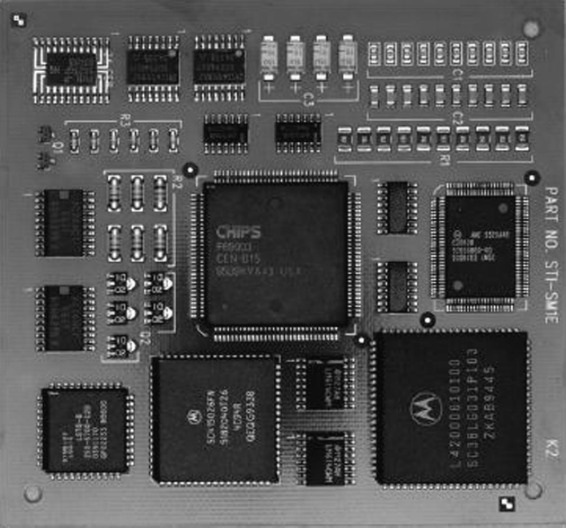
What Are Surface Mount Devices?
Surface Mount Devices are electronic components designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB. This method of assembly is known as Surface Mount Technology (SMT), which has largely replaced the older through-hole technology (THT). SMDs come in various shapes and sizes, including resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits, making them versatile for numerous applications.
Advantages of Surface Mount Devices
1. Space Efficiency: SMDs are typically smaller than their through-hole counterparts, allowing for more components to be placed on a single PCB. This compactness is crucial in the design of modern electronic devices, which often require miniaturization.
2. Improved Performance: The shorter leads of SMDs reduce the inductance and resistance in the connections, leading to better performance at high frequencies. This is particularly beneficial in applications such as RF (radio frequency) circuits.
3. Automated Assembly: SMT allows for automated assembly processes, which can significantly reduce manufacturing costs and time. Machines can place SMDs on PCBs with high precision, increasing production efficiency.
4. Dual-Sided Assembly: SMDs can be placed on both sides of a PCB, maximizing the use of available space and enabling more complex circuit designs.
5. Reduced Weight: The lighter weight of SMDs contributes to the overall reduction in the weight of electronic devices, which is essential for portable electronics.
6. Enhanced Reliability: SMDs are less prone to mechanical stress and damage compared to through-hole components, as they are firmly attached to the PCB surface. This enhances the overall reliability of the electronic device.
7. Lower Production Costs: The efficiency of SMT processes often leads to lower production costs, as fewer materials are wasted, and the speed of assembly is increased.
8. Higher Component Density: SMDs allow for a higher density of components on a PCB, which is essential for modern electronics that require complex functionalities in a compact form factor.
Types of Surface Mount Devices
Surface mount devices come in various types, each suited for specific applications. Here are some common categories:
1. Resistors
SMD resistors are available in various sizes and power ratings. They are used to limit current flow and divide voltages in circuits. SMD resistors are often preferred for their small size and ability to handle high frequencies.
2. Capacitors
SMD capacitors are used for energy storage, filtering, and coupling applications. They come in different types, including ceramic, tantalum, and electrolytic. The choice of capacitor type depends on the specific application requirements, such as voltage rating and capacitance value.
3. Diodes
SMD diodes are used for rectification, voltage regulation, and signal modulation. They are essential in power supply circuits and signal processing. Schottky diodes, Zener diodes, and standard rectifier diodes are common types of SMD diodes.
4. Transistors
SMD transistors are used for amplification and switching applications. They are critical components in digital and analog circuits. MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) and BJTs (Bipolar Junction Transistors) are popular types of SMD transistors.
5. Integrated Circuits (ICs)
SMD ICs are complex components that can contain thousands of transistors, resistors, and capacitors in a single package. They are used in microcontrollers, processors, and memory devices. The integration of multiple functions into a single IC is a significant advantage of SMD technology.
6. Inductors
SMD inductors are used in filtering applications and energy storage. They are essential in power supply circuits and RF applications. SMD inductors come in various shapes and sizes, allowing for flexibility in design.
7. Connectors
SMD connectors are used to establish electrical connections between different components or PCBs. They are available in various configurations, including headers, sockets, and terminal blocks.
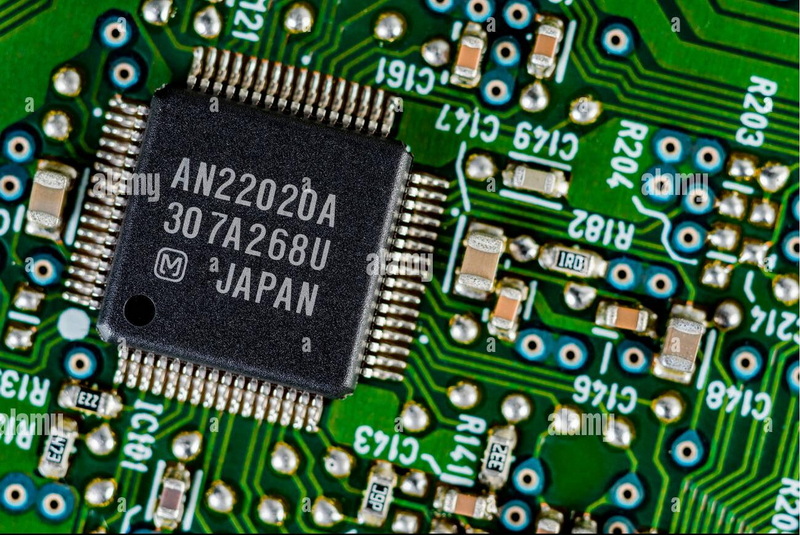
Applications of Surface Mount Devices
Surface mount devices are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Some notable applications include:
1. Consumer Electronics
SMDs are prevalent in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other consumer electronics, where space and weight are critical factors. The compact design of SMDs allows manufacturers to create sleek and lightweight devices that meet consumer demands.
2. Automotive Electronics
Modern vehicles rely heavily on electronic systems for functions such as engine control, safety features, and infotainment systems. SMDs are used extensively in these applications due to their reliability and compactness. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicle (EV) technologies also benefit from SMDs.
3. Telecommunications
SMDs are essential in telecommunications equipment, including routers, switches, and base stations, where high performance and miniaturization are required. The demand for faster and more reliable communication drives the need for advanced SMD technologies.
4. Medical Devices
In the medical field, SMDs are used in diagnostic equipment, monitoring devices, and therapeutic machines, where precision and reliability are paramount. The miniaturization of medical devices allows for less invasive procedures and improved patient outcomes.
5. Industrial Equipment
SMDs are used in various industrial applications, including automation systems, control panels, and sensors, contributing to the efficiency and reliability of industrial processes. The ability to integrate multiple functions into a single device enhances the performance of industrial equipment.
6. Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace and defense applications, SMDs are used in avionics, communication systems, and navigation equipment. The high reliability and performance of SMDs are critical in these demanding environments.
7. Internet of Things (IoT)
The rise of IoT devices has increased the demand for compact and efficient electronic components. SMDs play a crucial role in enabling smart devices that communicate and interact with each other, driving innovation in various sectors.
The Future of Surface Mount Devices
As technology continues to advance, the demand for smaller, more efficient electronic devices will only increase. The future of surface mount devices will likely involve:
1. Further Miniaturization: As the industry pushes for smaller devices, SMDs will continue to shrink in size while maintaining performance. This trend will enable the development of even more compact electronic devices.
2. Enhanced Performance: Innovations in materials and design will lead to SMDs with improved electrical characteristics, enabling higher frequencies and better efficiency. The use of advanced materials, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, may further enhance performance.
3. Integration of Functions: Future SMDs may integrate multiple functions into a single package, reducing the number of components needed and simplifying circuit design. This integration will lead to more compact and efficient designs.
4. Sustainability: The electronics industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability. Future SMDs may be designed with environmentally friendly materials and processes. The development of recyclable and biodegradable components will be essential in reducing electronic waste.
5. Smart Technology: With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), SMDs will play a crucial role in enabling smart devices that communicate and interact with each other. The integration of sensors, processors, and communication modules into SMDs will drive innovation in smart technology.
6. Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: The adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing and additive manufacturing, may revolutionize the production of SMDs. These techniques can enable the creation of complex geometries and customized components.
7. Increased Focus on Reliability: As electronic devices become more critical in various applications, the reliability of SMDs will be paramount. Manufacturers will need to invest in quality control and testing to ensure that SMDs meet stringent reliability standards.
Conclusion
Surface mount devices have transformed the landscape of electronics manufacturing, offering numerous advantages over traditional through-hole components. Their compact size, improved performance, and suitability for automated assembly make them indispensable in modern electronic devices. As technology continues to evolve, SMDs will remain at the forefront of innovation, driving advancements in various industries.
Related Questions
1. What is the difference between SMD and THT?
SMD (Surface Mount Device) components are mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB, while THT (Through-Hole Technology) components require holes to be drilled into the PCB for mounting. SMDs are generally smaller and allow for more compact designs.
2. What are the benefits of using SMDs in electronics?
The benefits of using SMDs include space efficiency, improved performance at high frequencies, the ability for automated assembly, dual-sided placement on PCBs, and reduced weight of electronic devices.
3. Can SMDs be repaired or replaced easily?
Repairing or replacing SMDs can be more challenging than THT components due to their small size and the precision required for soldering. Specialized tools and techniques are often needed for SMD repair.
4. What industries commonly use surface mount devices?
Surface mount devices are commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, telecommunications, medical devices, and industrial equipment.
5. How do I choose the right SMD for my project?
Choosing the right SMD involves considering factors such as the component's specifications (size, power rating, voltage rating), the application's requirements, and compatibility with the PCB design.




















