Content Menu
● Understanding Surface Mounted Technology
● Common Challenges in Implementing SMT
>> Design Complexity
>> Soldering Issues
>> Component Placement Accuracy
>> Thermal Management
>> Material Compatibility
>> Testing and Quality Assurance
>> Supply Chain Management
>> Training and Skill Development
>> Environmental Considerations
>> Cost Management
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is Surface Mounted Technology (SMT)?
>> 2. What are the main advantages of using SMT?
>> 3. How can engineers ensure accurate component placement in SMT?
>> 4. What are common soldering issues in SMT?
>> 5. How does thermal management affect SMT?
Surface Mounted Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry by allowing for more compact designs, improved performance, and increased production efficiency. However, despite its many advantages, engineers often encounter several challenges when implementing SMT in their projects. This article will explore these common challenges in detail, providing insights into how they can be addressed to ensure successful SMT integration.
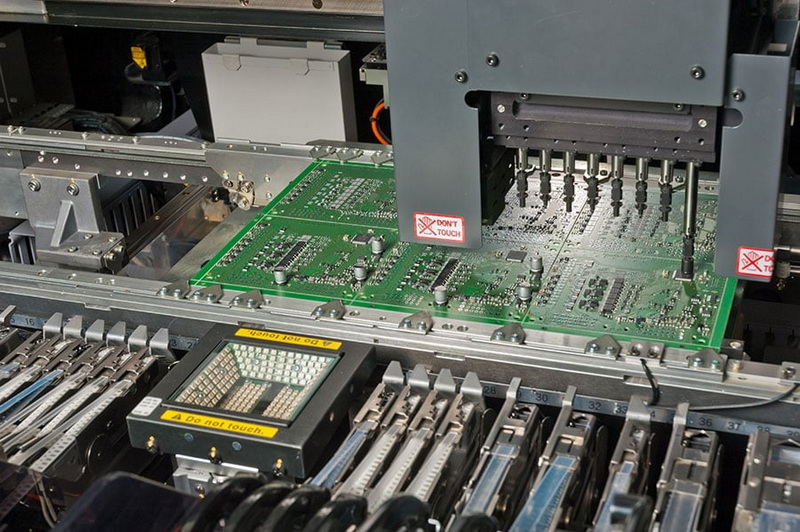
Understanding Surface Mounted Technology
Before delving into the challenges, it is essential to understand what Surface Mounted Technology entails. SMT is a method used to mount electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional through-hole technology, where components are inserted into holes drilled in the PCB, SMT allows for a more efficient use of space and materials. This technology has become the standard in modern electronics manufacturing due to its numerous benefits, including reduced size, weight, and cost of electronic devices.
Common Challenges in Implementing SMT
Design Complexity
One of the primary challenges engineers face when implementing SMT is the increased complexity of PCB design. SMT components are typically smaller and have different pin configurations compared to traditional components. This necessitates a more intricate design process, requiring engineers to be proficient in advanced design software and techniques. Additionally, the close placement of components can lead to issues such as signal interference and thermal management challenges.
Soldering Issues
Soldering is a critical aspect of SMT, and engineers often encounter various soldering challenges. The small size of SMT components makes them more susceptible to solder defects, such as bridging, insufficient solder, and cold solder joints. These defects can lead to poor electrical connections and ultimately result in device failure. Engineers must ensure that the soldering process is carefully controlled, often requiring the use of specialized equipment and techniques, such as reflow soldering and wave soldering.
Component Placement Accuracy
Accurate component placement is crucial in SMT, as misalignment can lead to significant performance issues. Engineers must ensure that components are placed precisely on the PCB to avoid problems such as short circuits or open circuits. This challenge is exacerbated by the high speed of modern SMT assembly lines, where components are placed rapidly. Engineers must implement rigorous quality control measures to ensure placement accuracy, often utilizing automated optical inspection (AOI) systems to detect misalignments.
Thermal Management
As electronic devices become more compact, managing heat dissipation has become increasingly challenging. SMT components can generate significant heat during operation, and if not properly managed, this can lead to overheating and failure. Engineers must consider thermal management strategies during the design phase, such as incorporating heat sinks, thermal vias, and proper airflow within the device. Failure to address thermal issues can result in reduced performance and shortened lifespan of electronic devices.

Material Compatibility
Another challenge engineers face is ensuring compatibility between different materials used in SMT. The choice of solder, PCB substrate, and component materials can significantly impact the reliability and performance of the final product. Engineers must carefully select materials that can withstand the thermal and mechanical stresses of the manufacturing process and the operating environment. Incompatibility can lead to issues such as delamination, solder joint failure, and reduced overall reliability.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing SMT assemblies can be more complex than traditional methods due to the density of components and the intricacies of the design. Engineers must develop comprehensive testing protocols to ensure that each assembly meets the required specifications. This often involves a combination of functional testing, in-circuit testing, and visual inspection. The challenge lies in balancing thorough testing with production speed, as extensive testing can slow down the manufacturing process.
Supply Chain Management
The global nature of the electronics industry means that engineers must navigate a complex supply chain when sourcing SMT components. Issues such as component shortages, lead times, and quality control can significantly impact project timelines and budgets. Engineers must establish strong relationships with suppliers and implement effective inventory management strategies to mitigate these risks.
Training and Skill Development
As SMT technology continues to evolve, engineers must stay updated on the latest techniques and best practices. This requires ongoing training and skill development, which can be a challenge for organizations with limited resources. Engineers must be proactive in seeking out educational opportunities, whether through formal training programs, workshops, or online resources, to ensure they remain competitive in the field.
Environmental Considerations
With increasing regulations surrounding environmental sustainability, engineers must consider the environmental impact of their SMT processes. This includes selecting lead-free solder, minimizing waste, and ensuring proper disposal of electronic waste. Engineers must stay informed about regulatory changes and implement practices that align with sustainability goals while maintaining product quality and performance.
Cost Management
Finally, managing costs is a significant challenge when implementing SMT. While SMT can reduce manufacturing costs in the long run, the initial investment in equipment, training, and materials can be substantial. Engineers must carefully analyze the cost-benefit ratio of SMT implementation and develop strategies to minimize expenses without compromising quality.
Conclusion
Implementing Surface Mounted Technology presents a range of challenges for engineers, from design complexity and soldering issues to thermal management and cost control. By understanding these challenges and developing effective strategies to address them, engineers can successfully integrate SMT into their projects, leading to improved performance and reliability of electronic devices. As technology continues to advance, staying informed and adaptable will be crucial for engineers working in this dynamic field.
FAQ
1. What is Surface Mounted Technology (SMT)?
Surface Mounted Technology (SMT) is a method of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), allowing for more compact designs and improved manufacturing efficiency.
2. What are the main advantages of using SMT?
The main advantages of SMT include reduced size and weight of electronic devices, increased production speed, lower manufacturing costs, and improved performance due to shorter electrical paths.
3. How can engineers ensure accurate component placement in SMT?
Engineers can ensure accurate component placement by utilizing automated placement machines, implementing rigorous quality control measures, and using automated optical inspection (AOI) systems to detect misalignments.
4. What are common soldering issues in SMT?
Common soldering issues in SMT include solder bridging, insufficient solder, and cold solder joints, which can lead to poor electrical connections and device failure.
5. How does thermal management affect SMT?
Thermal management is crucial in SMT as compact designs can lead to overheating. Engineers must incorporate strategies such as heat sinks and thermal vias to dissipate heat effectively and ensure device reliability.




















