Content Menu
● Advancements in SMD Soldering Machines and Processes
>> Enhanced Precision and Miniaturization
>> Intelligent Automation and AI Integration
>> Vacuum and Energy-Efficient Soldering Techniques
● Revolutionary Materials and Substrate Innovations
● Diverse Soldering Machines for Varied Production Needs
● Emerging Trends and Best Practices in SMD Soldering
>> Process Optimization and Real-Time Monitoring
>> Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
>> Integration with Industry 4.0
>> Training and Skill Development
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What types of soldering machines are commonly used for SMD components?
>> 2. How does AI improve soldering machines for SMD?
>> 3. What are the benefits of vacuum reflow soldering in SMD assembly?
>> 4. How do new materials impact SMD soldering technology?
>> 5. What sustainability trends are influencing SMD soldering?
Surface-Mount Device (SMD) soldering technology has undergone significant advancements in recent years, driven by the demand for smaller, more efficient, and higher-performing electronic devices. As electronics continue to miniaturize and diversify, the soldering machine for SMD components has evolved to meet new challenges in precision, speed, and sustainability. This article explores the latest innovations in SMD soldering technology, highlighting breakthroughs in materials, automation, artificial intelligence integration, and energy-efficient processes that are shaping the future of electronic manufacturing.
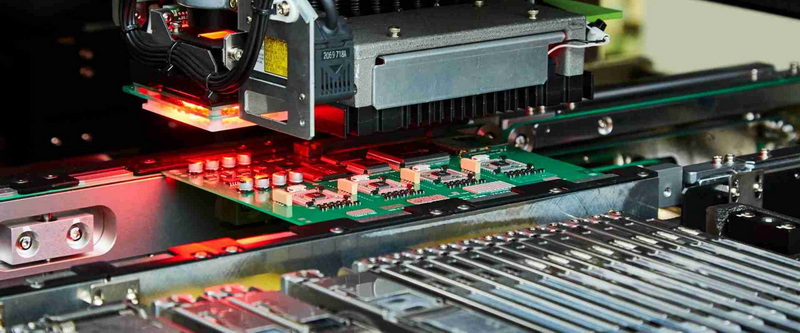
Advancements in SMD Soldering Machines and Processes
Enhanced Precision and Miniaturization
One of the most notable trends in SMD soldering technology is the push toward miniaturization. Modern soldering machines for SMD components now accommodate ultra-small parts such as 0201 and 01005 resistors, which require extremely precise solder paste application and component placement. Advances in solder paste printers and pick-and-place machines have enabled this precision by improving the control of solder paste volume and alignment accuracy. These machines use high-resolution cameras and robotic arms capable of placing thousands of components per hour with micron-level accuracy, reducing defects and improving yield.
The integration of nanotechnology and hybrid materials in soldering processes further enhances the reliability of solder joints in compact designs. These materials improve thermal management and electrical conductivity, ensuring that even the smallest SMD components perform reliably in demanding environments such as wearable devices and IoT sensors.
Additionally, the development of ultra-fine pitch soldering machines addresses challenges posed by increasingly dense PCB layouts. These machines feature advanced nozzle designs and micro-dispensing systems that precisely deposit solder paste onto tiny pads, minimizing solder bridging and improving joint integrity. This precision is critical for high-frequency and high-speed electronic applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Intelligent Automation and AI Integration
Automation in SMD soldering has reached new heights with the introduction of collaborative robots (cobots) and AI-driven control systems. Modern soldering machines for SMD utilize AI algorithms to optimize soldering parameters dynamically, predict potential failures, and adjust processes in real-time. This results in higher throughput, consistent quality, and reduced waste.
For example, intelligent DC reflow soldering ovens leverage deep learning neural networks to predict and optimize temperature profiles for different PCB designs, improving solder joint quality and reducing thermal stress on components. AI-powered vision systems inspect solder joints during and after the soldering process, enabling immediate correction and quality assurance without slowing down production lines.
Moreover, AI integration enables predictive maintenance of soldering machines for SMD, minimizing downtime. Sensors embedded in machines collect data on temperature fluctuations, mechanical wear, and solder paste viscosity, feeding this information into AI models that forecast maintenance needs before failures occur. This proactive approach enhances production efficiency and reduces costly interruptions.
Vacuum and Energy-Efficient Soldering Techniques
Vacuum reflow soldering technology is another innovation enhancing soldering quality by minimizing voids in solder joints. Vacuum systems remove trapped air and flux gases during solder melting, resulting in stronger and more reliable connections. New-generation vacuum reflow ovens also incorporate energy-saving features such as fluid simulation and AI-driven energy management, reducing power consumption while maintaining high production efficiency.
Selective soldering machines have also evolved with electromagnetic pumps and precise spray nozzles, combining top hot air and bottom infrared preheating for uniform thermal distribution. These machines allow for soldering of specific components on complex boards without affecting nearby parts, crucial for high-value or heat-sensitive SMDs.
In addition to vacuum and selective soldering, laser soldering has emerged as a promising technique for SMD applications. Laser soldering machines offer pinpoint heat application, drastically reducing thermal impact on adjacent components and substrates. This method is especially useful for soldering heat-sensitive or miniaturized components on multi-layer PCBs, enhancing joint quality and reliability.
Energy efficiency in soldering machines for SMD is also being addressed through innovations such as rapid heating elements, improved insulation materials, and optimized conveyor systems. These improvements reduce thermal losses and shorten cycle times, contributing to lower operational costs and environmental impact.

Revolutionary Materials and Substrate Innovations
The materials used in SMD soldering and PCB substrates have seen remarkable innovation. Graphene-infused composites and ceramic-polymer hybrids offer superior thermal resistance and electrical conductivity, enabling better heat dissipation and durability in compact assemblies. Flexible polyimide substrates have become popular for wearable and bendable electronics, providing mechanical resilience without compromising solder joint integrity.
These next-generation materials support the trend toward eco-friendly manufacturing by being recyclable and compliant with environmental regulations. The use of solder-free interconnections and recycled metals in solder pastes also contributes to greener production processes.
Furthermore, the development of lead-free solder alloys has progressed significantly, addressing both environmental concerns and performance requirements. New lead-free solders exhibit improved wetting properties, lower melting points, and enhanced mechanical strength, making them suitable for high-reliability applications such as automotive and aerospace electronics.
Innovations in flux formulations have also improved soldering outcomes. Modern fluxes are designed to be more active at lower temperatures, reduce residue, and minimize corrosion risks. This advancement complements the capabilities of soldering machines for SMD by ensuring cleaner joints and easier post-soldering cleaning processes.
Diverse Soldering Machines for Varied Production Needs
The market now offers a wide range of soldering machines for SMD applications tailored to different production volumes and complexity levels:
- Reflow Ovens: Ideal for small to medium batch production, these ovens transport PCBs through controlled heating zones to melt solder paste and solidify joints reliably.
- Wave Soldering Machines: Suitable for high-volume production, wave soldering creates a continuous wave of molten solder to solder exposed leads and pads, though less precise for fine-pitch SMDs.
- Selective Soldering Systems: Designed for complex assemblies, these systems solder specific components with high precision, using advanced heating and solder delivery methods.
- Soldering Robots: Fully automated soldering robots combine precise motion control and heat delivery for large-scale production, commonly used in aerospace and advanced electronics manufacturing.
- Hand Soldering Stations: While not automated, these stations provide flexibility for prototyping, repairs, and detailed soldering tasks, often complementing automated lines.
Choosing the right soldering machine for SMD depends on component size, production scale, and specific assembly requirements. For instance, reflow ovens remain the backbone of most SMD assembly lines due to their versatility and throughput, while selective soldering machines are indispensable when mixed technology boards require precise soldering of through-hole and surface-mount components.
Emerging Trends and Best Practices in SMD Soldering
Process Optimization and Real-Time Monitoring
The latest soldering machines for SMD incorporate real-time monitoring systems that track solder joint quality and process parameters throughout production. This data-driven approach enables immediate adjustments, reducing defects and rework.
Advanced sensor arrays measure temperature, solder paste viscosity, and humidity, feeding data into centralized control units. This integration allows manufacturers to maintain optimal soldering conditions continuously, ensuring consistent quality across batches.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
Sustainability is increasingly influencing SMD soldering technology. Manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly solder pastes, reducing solvent use, and implementing energy-saving equipment. The push for solder-free interconnections and recyclable materials aligns with global environmental goals.
Moreover, soldering machines for SMD are being designed with modular components that facilitate repair and upgrades, extending equipment life and reducing electronic waste. The adoption of lead-free solders and halogen-free fluxes further aligns with environmental standards and worker safety.
Integration with Industry 4.0
SMD soldering technology is becoming an integral part of Industry 4.0 smart factories. Connected soldering machines communicate with other production equipment, enabling seamless workflow automation, predictive maintenance, and enhanced traceability.
By integrating soldering machines into the factory's digital ecosystem, manufacturers can leverage big data analytics to optimize production schedules, identify bottlenecks, and improve supply chain coordination. This connectivity also supports remote monitoring and control, empowering operators to manage soldering processes from anywhere.
Training and Skill Development
As soldering machines for SMD become more sophisticated, operator training and skill development are critical. Manufacturers invest in simulation tools and virtual reality environments to train technicians on machine operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting without risking production downtime.
This emphasis on human-machine collaboration ensures that the workforce can effectively harness the capabilities of advanced soldering technology, maximizing productivity and quality.
Conclusion
The latest innovations in SMD soldering technology reflect a dynamic convergence of miniaturization, intelligent automation, advanced materials, and sustainable manufacturing practices. Soldering machines for SMD components have evolved from simple heating devices to sophisticated systems equipped with AI, vacuum technology, and real-time monitoring, delivering unprecedented precision and efficiency. As electronics continue to shrink and become more complex, these advancements ensure that soldering processes keep pace with industry demands, enabling the production of reliable, high-performance devices across consumer, medical, automotive, and aerospace sectors. The future of SMD soldering is not only smarter and faster but also greener and more adaptable, driving the next generation of electronic innovation.

FAQ
1. What types of soldering machines are commonly used for SMD components?
Common soldering machines for SMD include reflow ovens for melting solder paste, wave soldering machines for high-volume production, selective soldering systems for precision work, soldering robots for automation, and hand soldering stations for prototyping and repairs.
2. How does AI improve soldering machines for SMD?
AI enhances soldering machines by optimizing temperature profiles, predicting failures, adjusting parameters in real-time, and enabling automated inspection of solder joints, which improves quality and reduces waste.
3. What are the benefits of vacuum reflow soldering in SMD assembly?
Vacuum reflow soldering reduces voids in solder joints by eliminating trapped gases during solder melting, resulting in stronger, more reliable connections and improved overall solder quality.
4. How do new materials impact SMD soldering technology?
Innovative materials like graphene composites and ceramic-polymer hybrids improve thermal management, electrical conductivity, and mechanical durability of SMD assemblies, enabling smaller, more robust electronic devices.
5. What sustainability trends are influencing SMD soldering?
Sustainability trends include the use of eco-friendly solder pastes, energy-efficient soldering machines, recyclable substrates, and solder-free interconnections, all contributing to greener electronic manufacturing processes.




















