Content Menu
● Understanding Surface Mount Devices
● Common SMD Codes and Their Meanings
>> Resistor Codes
>> Capacitor Codes
>> Diode and Transistor Codes
● Why Knowing SMD Codes Matters
● Sources for SMD Code Reference
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. How are SMD codes applied on components?
>> 2. Can SMD codes be reverse-engineered?
>> 3. What tools are needed to read SMD codes?
>> 4. Are there universal SMD codes?
>> 5. Why are SMD codes important for PCB layout?
In the ever-evolving world of electronics, Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) have become essential components in modern circuit design and manufacturing. Understanding SMD codes is crucial for engineers, technicians, and hobbyists alike, as these codes provide vital information about component specifications, functionality, and compatibility. This article will delve into the key surface mount device codes you need to know, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the intricate landscape of SMDs.
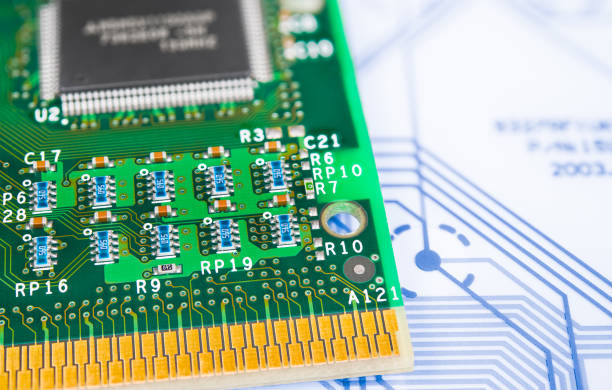
Understanding Surface Mount Devices
Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) are electronic components designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional through-hole components that require drilling holes in the PCB, SMDs are soldered onto pads on the board's surface, allowing for more compact designs and improved manufacturing efficiency.
The advantages of SMD technology include:
- Reduced Size: SMDs are typically smaller than their through-hole counterparts, enabling higher component density on PCBs.
- Automated Assembly: The manufacturing process for SMDs is highly automated, leading to faster production times and lower labor costs.
- Improved Performance: Due to their smaller size and shorter interconnections, SMDs often exhibit better electrical performance, including lower inductance and capacitance.
- Versatility: SMDs come in various types, including resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits (ICs), making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Surface Mount Devices
Common SMD Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding SMD codes is essential for identifying components quickly and accurately. These codes can vary by manufacturer but generally follow specific conventions. Below are some common SMD codes used for different types of components:
Resistor Codes
SMD resistors are typically identified by a three or four-digit code representing their resistance value. The first two or three digits indicate significant figures, while the last digit represents the multiplier. For example:
- Code 103: This indicates a resistance value of $$10 \times 10^3$$ ohms or 10 kilohms.
- Code 472: This represents $$47 \times 10^2$$ ohms or 4.7 kilohms.
Resistor sizes are denoted by a two-digit code indicating their dimensions in hundredths of an inch (e.g., 0603 represents a size of 0.06 inches by 0.03 inches).
Capacitor Codes
Capacitor codes also follow a similar format. A common three-digit code indicates capacitance values in picofarads (pF). For example:
- Code 104: This indicates a capacitance value of $$10 \times 10^4$$ pF or 100 nanofarads.
Capacitors are also labeled with voltage ratings directly on their surfaces.
Diode and Transistor Codes
Diodes and transistors have unique identification codes that often include letters indicating their type. For example:
- 1N4148: A common signal diode.
- BC547: A widely used NPN transistor.
These codes help identify the specific characteristics and functions of these devices.
Diode and Transistor Codes
Why Knowing SMD Codes Matters
Understanding SMD codes is not just beneficial; it's essential for several reasons:
- Design Accuracy: Correctly identifying components ensures that designs meet specifications and function as intended.
- Troubleshooting: When repairing or modifying circuits, knowing the correct SMD codes helps in sourcing replacements or equivalents.
- Efficiency in Production: Accurate identification speeds up assembly processes and reduces errors in component placement.
Sources for SMD Code Reference
For those looking to deepen their understanding or find specific SMD codes, several resources are available:
- Datasheets: Manufacturers often provide datasheets that include detailed specifications and code explanations.
- Online Databases: Websites like Digi-Key or Mouser offer searchable databases for identifying components based on their codes.
- SMD Codebooks: Comprehensive guides compile extensive lists of SMD codes along with their corresponding specifications.
SMD Code Reference
Conclusion
Mastering surface mount device codes is crucial for anyone involved in electronics design or repair. With the rapid advancement of technology and increasing complexity in circuit designs, having a solid grasp of these codes will not only enhance your efficiency but also improve your overall understanding of electronic components. As you continue your journey in electronics, remember that familiarity with SMD codes is an invaluable asset.
FAQ
1. How are SMD codes applied on components?
SMD codes are marked directly onto the components using printing technologies or markings.
2. Can SMD codes be reverse-engineered?
SMD codes can be difficult to reverse-engineer without manufacturer data sheets; however, online resources may assist in identification.
3. What tools are needed to read SMD codes?
Magnifying tools and accurate SMD codebooks or guides are essential for reading and interpreting SMD codes effectively.
4. Are there universal SMD codes?
No, SMD codes can vary widely between manufacturers; nevertheless, some standardized formats exist within specific categories.
5. Why are SMD codes important for PCB layout?
They ensure correct placement and functionality of components on PCBs, which is critical for high-density designs.




















