Content Menu
● Understanding SMT and Its Importance in PCB Manufacturing
● Key Components of an SMT Production Line
● Steps to Set Up Your SMT Production Line
>> Step 1: Assess Your Production Needs
>> Step 2: Select Appropriate Equipment
>> Step 3: Layout Design
>> Step 4: Implement Software Solutions
>> Step 5: Training Personnel
>> Step 6: Testing and Calibration
● Workflow Optimization Techniques
● Quality Control Measures
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the main advantages of using Universal Instruments equipment for SMT?
>> 2. How do I choose the right pick-and-place machine?
>> 3. What is the role of AOI in an SMT production line?
>> 4. How often should I calibrate my SMT equipment?
>> 5. Can I integrate my existing software with new Universal Instruments machines?
Setting up a Surface Mount Technology (SMT) production line for Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturing is a critical process that requires careful planning and execution. Universal Instruments is a leading provider of SMT equipment and solutions, making it a popular choice for manufacturers looking to optimize their PCB production. This article will guide you through the steps necessary to set up a Universal Instruments SMT production line, covering everything from equipment selection to workflow optimization.
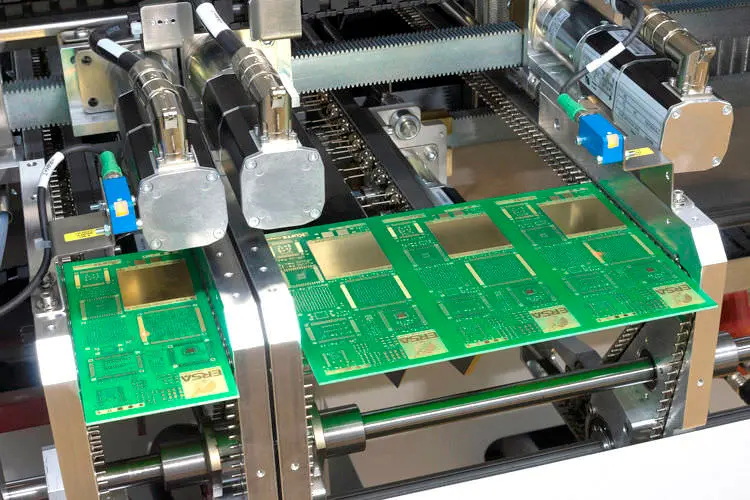
Understanding SMT and Its Importance in PCB Manufacturing
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a method used to mount electronic components directly onto the surface of PCBs. Unlike traditional through-hole technology, where components are inserted into holes in the board, SMT allows for smaller, lighter components and more efficient manufacturing processes.
The significance of SMT in PCB manufacturing cannot be overstated. It offers several advantages:
- Higher Component Density: SMT allows for more components to be placed on a PCB, maximizing space efficiency.
- Improved Performance: The shorter electrical paths in SMT designs can enhance signal integrity and reduce electromagnetic interference.
- Cost Efficiency: With fewer materials required and faster assembly times, SMT can lower overall production costs.
Key Components of an SMT Production Line
To establish an effective SMT production line, you need to understand the essential components involved:
1. Stencil Printer: This machine applies solder paste onto the PCB using a stencil, ensuring precise placement for surface-mounted components.
2. Pick-and-Place Machine: This automated device picks up components from trays or reels and places them accurately onto the PCB.
3. Reflow Oven: After placement, the PCB goes through a reflow oven where the solder paste is melted to create strong electrical connections.
4. Inspection Equipment: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems check for defects in component placement and solder joints.
5. Test Equipment: Functional testers ensure that the assembled PCBs operate as intended.
6. Conveyor Systems: These systems transport PCBs between different stages of the production line, ensuring smooth transitions and reducing manual handling.
7. Cleaning Equipment: Post-production cleaning machines remove flux residues and other contaminants from the PCBs to ensure optimal performance.
Steps to Set Up Your SMT Production Line
Setting up your SMT production line involves several critical steps:
Step 1: Assess Your Production Needs
Before acquiring any equipment, assess your production requirements:
- Volume: Determine how many PCBs you need to produce daily.
- Complexity: Consider the complexity of your designs and the types of components you will use.
- Budget: Establish a budget for your equipment and operational costs.
- Future Scalability: Evaluate potential future needs based on market trends or product evolution to ensure your setup can adapt accordingly.
Step 2: Select Appropriate Equipment
Once you have assessed your needs, select the right equipment from Universal Instruments:
- Stencil Printer Selection: Choose a printer that offers precision and speed. Look for features like automatic alignment and adjustable print speeds.
- Pick-and-Place Machine: Opt for a machine that can handle various component sizes and shapes. Universal Instruments offers machines with advanced vision systems for accurate placement.
- Reflow Oven Specifications: Select an oven with temperature profiling capabilities to ensure optimal soldering conditions.
- Inspection Equipment Choices: Invest in AOI systems that can detect various defects such as misalignment, missing components, or insufficient solder.
Step 3: Layout Design
The layout of your production line is crucial for efficiency:
- Flow Design: Arrange your equipment in a linear flow from printing to inspection to minimize handling time.
- Space Management: Ensure there is enough space between machines for operators to work safely and efficiently.
- Ergonomics Consideration: Design workstations that minimize strain on operators while allowing easy access to tools and materials.

Step 4: Implement Software Solutions
Integrate software solutions for better management of your production line:
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES): This software helps track production processes, manage inventory, and analyze performance metrics.
- Design Software Compatibility: Ensure that your design software can seamlessly integrate with your manufacturing processes.
- Data Collection Systems: Utilize data collection systems that provide real-time feedback on production metrics such as yield rates and cycle times.
Step 5: Training Personnel
Proper training is essential for maximizing productivity:
- Operator Training: Train operators on how to use each piece of equipment effectively. This includes understanding machine settings, maintenance routines, and troubleshooting common issues.
- Quality Control Training: Educate staff on quality control measures to maintain high standards throughout the production process. This training should cover inspection techniques and defect identification.
- Cross-Training Opportunities: Encourage cross-training among staff members so they can operate multiple machines, enhancing flexibility in workforce management.
Step 6: Testing and Calibration
Before full-scale production begins, conduct thorough testing:
- Calibration of Equipment: Ensure all machines are calibrated correctly to avoid defects during assembly. Regular calibration schedules should be established based on usage frequency.
- Trial Runs: Perform trial runs with sample PCBs to identify any potential issues in the workflow. Analyze results carefully to make necessary adjustments before full-scale production begins.
Workflow Optimization Techniques
To maximize efficiency in your SMT production line, consider implementing these optimization techniques:
- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Adopt lean principles to eliminate waste and streamline processes. Focus on minimizing non-value-added activities throughout the production cycle.
- Continuous Improvement Programs: Encourage feedback from operators to identify areas for improvement regularly. Implement regular review meetings where staff can discuss challenges faced during production runs.
- Data Analysis Tools: Utilize data analytics tools to monitor performance metrics such as throughput rates, defect rates, and machine uptime. Use this data to make informed decisions about process adjustments or equipment upgrades.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is paramount in PCB manufacturing:
- In-Line Inspection Protocols: Establish protocols for in-line inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process. This ensures early detection of defects before they propagate further down the line.
- Final Testing Procedures: Implement comprehensive final testing procedures that include functional testing under various conditions to ensure reliability in real-world applications.
- Documentation Practices: Maintain detailed records of inspections, tests performed, and any corrective actions taken. This documentation will aid in traceability and continuous improvement efforts.
Conclusion
Setting up a Universal Instruments SMT production line involves careful planning, appropriate equipment selection, effective layout design, personnel training, quality control measures, and ongoing optimization efforts. By following these steps, manufacturers can create an efficient PCB manufacturing process that meets their production needs while maintaining high-quality standards. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about new developments in SMT will further enhance productivity and efficiency in PCB manufacturing.
Investing time and resources into establishing a robust SMT production line not only improves operational efficiency but also positions manufacturers competitively within the electronics market. With advancements in automation technologies continually reshaping the landscape of PCB manufacturing, embracing these changes will be crucial for sustained success in this dynamic industry.
FAQ
1. What are the main advantages of using Universal Instruments equipment for SMT?
Universal Instruments provides high-quality machines that enhance precision, speed, and flexibility in PCB manufacturing processes. Their advanced technology also supports various component types and sizes.
2. How do I choose the right pick-and-place machine?
Consider factors such as component size range, speed requirements, accuracy levels, and whether it has advanced features like vision systems for precise placement when selecting a pick-and-place machine.
3. What is the role of AOI in an SMT production line?
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) plays a crucial role in identifying defects in component placement and solder joints before final testing, ensuring higher quality standards are met during production.
4. How often should I calibrate my SMT equipment?
Calibration should be performed regularly based on manufacturer recommendations or whenever significant changes occur in production processes or equipment settings to ensure optimal performance.
5. Can I integrate my existing software with new Universal Instruments machines?
Yes, many Universal Instruments machines are designed with compatibility in mind, allowing integration with existing design software and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) for streamlined operations.




















