Content Menu
● Understanding SMT Production
● Key Steps in Setting Up an SMT Production Line
>> 1. Planning and Preparation
>> 2. Choosing the Right Equipment
>> 3. Designing the Layout
>> 4. Installation and Configuration
>> 5. Testing and Calibration
● Essential Considerations for a Successful SMT Line
>> 1. Quality Control
>> 2. Environmental Control
>> 3. Training Personnel
● Managing Inventory
● Implementing Automation
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is an SMT production line?
>> 2. How much does it cost to set up a small SMT line?
>> 3. What are the key machines needed for an SMT line?
>> 4. How do I ensure quality control in my SMT production line?
>> 5. What factors should I consider when choosing equipment for my SMT line?
Setting up a small Surface Mount Technology (SMT) production line can be a significant step for businesses involved in electronics manufacturing. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the steps, equipment, and considerations necessary to establish an efficient SMT production line tailored to your business needs.
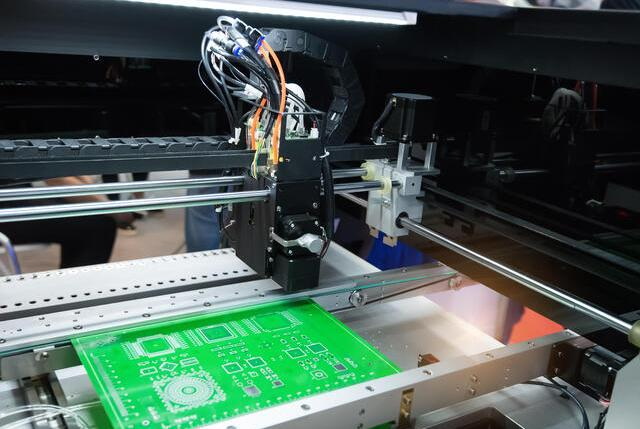
Understanding SMT Production
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a method used to mount electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This technology has become the standard in electronics manufacturing due to its efficiency, compactness, and ability to automate assembly processes.
The SMT production process involves several critical stages:
- Solder Paste Printing: Applying solder paste to the PCB pads where components will be placed.
- Component Placement: Accurately positioning electronic components onto the soldered pads using automated machines.
- Reflow Soldering: Melting the solder paste to create reliable electrical connections between the components and PCB.
- Inspection: Ensuring that all components are correctly placed and soldered through various inspection methods.
Key Steps in Setting Up an SMT Production Line
1. Planning and Preparation
Before investing in equipment or setting up your workspace, careful planning is essential. Here are the steps involved:
- Assess Production Requirements: Determine the expected volume of production, types of components, and complexity of assemblies. This information will guide your decisions regarding equipment selection and layout design.
- Budgeting: Establish a budget that covers equipment costs, facility setup, operational expenses, and raw materials. For small to medium-scale operations, initial budgets typically range from $50,000 to $130,000.
- Market Research: Conduct thorough research on market demand for your products. Understanding customer needs can help tailor your production line accordingly.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with industry regulations and standards such as IPC-A-610 for acceptability of electronic assemblies. Compliance with these standards is crucial for quality assurance and market acceptance.
2. Choosing the Right Equipment
Selecting appropriate equipment is vital for the efficiency of your SMT line. Key pieces of equipment include:
- Solder Paste Printer: This machine applies solder paste onto PCB pads where components will be placed. Options vary from semi-automatic to fully automatic printers. Consider features like stencil thickness control and alignment accuracy.
- Pick-and-Place Machine: This crucial machine accurately places components onto the PCB. Look for machines that can handle various component sizes with high speed and precision. Advanced models offer vision systems for enhanced accuracy.
- Reflow Oven: The reflow oven melts the solder paste to permanently attach components to the PCB. Consider ovens with good temperature profiling capabilities for optimal soldering results.
- Inspection Systems: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems can detect defects in component placement and solder joints, ensuring quality control. Some systems offer 3D inspection capabilities for enhanced accuracy.
- Conveyor Systems: These systems transport PCBs between different stages of the assembly process smoothly. Ensure that conveyors are adjustable to accommodate various PCB sizes.
3. Designing the Layout
The layout of your SMT line should maximize efficiency and minimize bottlenecks. Considerations include:
- Flow of Materials: Arrange equipment in a logical sequence that follows the production process: solder paste printing → component placement → reflow soldering → inspection.
- Space Management: Ensure adequate spacing between machines for maintenance and troubleshooting. Consider implementing a lean manufacturing approach to minimize waste and optimize space usage.
- Future Expansion: Design your layout with potential future expansions in mind to save costs later on as production needs grow. Modular setups allow for easy addition of new machines or processes.
4. Installation and Configuration
Once you have selected your equipment and designed your layout, it's time to set up:
- Installation: Follow manufacturer instructions carefully for each piece of equipment. Ensure all connections are secure and that machines are calibrated correctly.
- Software Configuration: Most modern SMT machines come with software for controlling operations. Configure settings according to your production requirements, including component libraries and placement coordinates.
- Integration: Ensure that communication between machines is properly established for seamless operation. This may involve setting up network connections and configuring data exchange protocols.
5. Testing and Calibration
After setup, thorough testing is essential:
- Conduct initial tests using test boards to verify that all equipment functions correctly.
- Pay attention to critical parameters such as component placement accuracy and solder joint quality.
Essential Considerations for a Successful SMT Line
1. Quality Control
Implement regular inspections using AOI systems at various stages of production and conduct functional testing on completed assemblies to verify performance. Establish a feedback loop where defects are analyzed, and corrective actions are taken promptly.
2. Environmental Control
Maintaining optimal conditions in your production environment is crucial:
- Implement Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) protection measures to safeguard sensitive components.
- Ensure proper temperature and humidity levels are maintained within the facility. Utilizing HVAC systems can help regulate these factors effectively.
3. Training Personnel
Ensure that staff members are adequately trained in operating machinery, handling components, and maintaining quality standards throughout the production process. Regular training sessions can help keep skills updated as technology evolves.
Managing Inventory
Effective inventory management is vital for maintaining smooth operations in an SMT production line:
- Implement Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory practices to reduce excess stock while ensuring that necessary components are available when needed.
- Utilize inventory management software that integrates with your production system to track component usage accurately and predict future needs based on production schedules.
Implementing Automation
As you scale up operations, consider integrating automation into various aspects of your SMT line:
- Use automated guided vehicles (AGVs) or robots for material handling between stations to reduce manual labor costs.
- Implement Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT devices for real-time monitoring of machine performance metrics, which can enhance efficiency by identifying issues before they escalate into significant problems.
Conclusion
Setting up a small SMT production line involves careful planning, selection of appropriate equipment, efficient layout design, installation, testing, quality control measures, inventory management, and automation strategies. With proper execution, businesses can enhance their manufacturing capabilities while meeting market demands effectively.
FAQ
1. What is an SMT production line?
An SMT production line is an automated assembly line used for mounting surface mount devices (SMDs) onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). It includes machines for solder paste printing, component placement, reflow soldering, and inspection processes.
2. How much does it cost to set up a small SMT line?
The cost can vary widely based on equipment choices and production scale but generally ranges from $50,000 to $130,000 for small to medium-scale operations.
3. What are the key machines needed for an SMT line?
Essential machines include a solder paste printer, pick-and-place machine, reflow oven, inspection systems (like AOI), and conveyor systems for transporting PCBs through different assembly stages.
4. How do I ensure quality control in my SMT production line?
Implement regular inspections using AOI systems at various stages of production and conduct functional testing on completed assemblies to verify performance.
5. What factors should I consider when choosing equipment for my SMT line?
Consider compatibility with future expansions, performance specifications (speed and precision), after-sales support from manufacturers, and compliance with industry standards when selecting equipment for your SMT line.




















