Content Menu
● Understanding SMT Production Line Components
● Key Considerations for SMT Line Layout
>> Material Flow
>> Space Utilization
>> Machine Placement
>> Ergonomics and Safety
>> Automation Integration
● Types of SMT Line Layouts
● Implementing Lean Manufacturing Principles
● Continuous Improvement Strategies
● Simulation Tools
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the key components of an SMT production line?
>> 2. How does machine placement affect productivity?
>> 3. What is lean manufacturing in relation to SMT?
>> 4. Why is ergonomics important in an SMT layout?
>> 5. How can simulation tools help in optimizing an SMT layout?
In the fast-paced world of electronics manufacturing, optimizing your Surface Mount Technology (SMT) production line layout is essential for achieving maximum efficiency and productivity. A well-structured SMT line not only improves throughput but also minimizes waste, reduces costs, and enhances product quality. This article will explore various strategies and best practices for optimizing your SMT production line layout, ensuring that your manufacturing processes run smoothly and effectively.

Understanding SMT Production Line Components
Before diving into optimization strategies, it is crucial to understand the key components of an SMT production line. Each element plays a vital role in the assembly process of electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). The primary components include:
- Stencil Printer: Applies solder paste to PCBs through a stencil.
- Pick-and-Place Machine: Accurately places electronic components onto the solder paste.
- Reflow Oven: Melts solder paste to create reliable solder joints.
- Inspection Systems: Ensures quality control through Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection.
Understanding these components helps in designing an efficient layout that facilitates smooth material flow and minimizes bottlenecks.
Key Considerations for SMT Line Layout
When optimizing your SMT production line layout, several factors must be taken into account:
Material Flow
The flow of materials through the SMT line is critical. A well-designed layout ensures a smooth, uninterrupted flow, reducing delays and bottlenecks. Machines should be arranged in a logical sequence that follows the natural workflow of the assembly process.
Space Utilization
Efficient space utilization is essential for an effective SMT line layout. Consider the available floor space and plan the arrangement of machines accordingly. Ensure there is enough room for operators to move freely and perform maintenance tasks without obstructing production flow.
Machine Placement
Strategically positioning machines is crucial for optimizing productivity. Machines should be arranged to minimize excessive movement of PCBs and reduce the risk of damage or misalignment. For example, place the stencil printer at the beginning of the line, followed by pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and inspection systems.
Ergonomics and Safety
Operator comfort should not be overlooked in SMT line design. Workstations should be designed with ergonomics in mind to reduce strain and enhance efficiency. Additionally, safety measures such as proper lighting, ventilation, and clearly marked emergency exits are essential for a safe working environment.
Automation Integration
Integrating automation into your SMT production line can significantly enhance efficiency. Automated systems like conveyors can streamline material handling, while advanced inspection technologies can improve quality control processes.
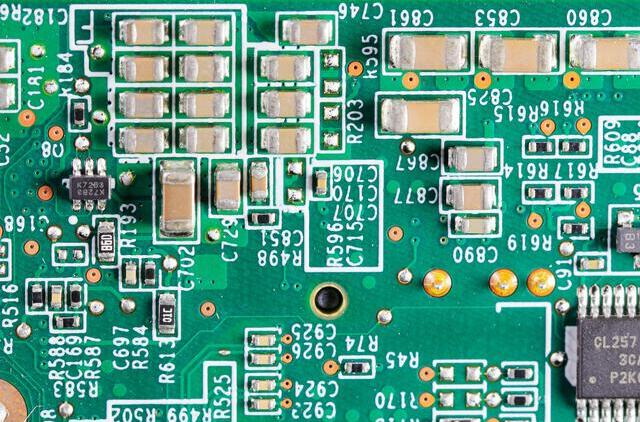
Types of SMT Line Layouts
There are several types of SMT line layouts that manufacturers can choose from based on their specific needs:
- In-line Layout: Machines are arranged in a straight line; ideal for high-volume production but less flexible.
- U-Shaped Layout: Provides flexibility and good visibility; suitable for varying board sizes.
- L-Shaped Layout: Efficient use of limited space; good for high production volumes.
- Cellular Layout: Configured into cells for specific operations; ideal for customized or low-volume productions.
- Dual Lane Layout: Two parallel lines increase throughput; effective for high-volume production.
Choosing the right layout depends on factors such as production volume, product variety, and available space.
Implementing Lean Manufacturing Principles
Applying lean manufacturing principles can further optimize your SMT production line layout by minimizing waste and improving overall efficiency. Techniques such as value stream mapping can help identify inefficiencies in the process, while methodologies like 5S (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) can streamline operations.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Optimizing an SMT production line is not a one-time task but an ongoing process of continuous improvement. Regularly reviewing performance metrics can help identify areas for enhancement. Engaging operators in feedback loops allows for practical insights into potential improvements based on their experiences on the floor.
Simulation Tools
Utilizing simulation tools can provide valuable insights when designing and optimizing SMT line layouts. These tools allow manufacturers to create virtual models of their production lines and simulate different scenarios to evaluate their impact on performance before implementation.
Conclusion
Optimizing your SMT production line layout is crucial for maximizing efficiency and productivity in electronics manufacturing. By carefully considering factors such as material flow, space utilization, machine placement, ergonomics, automation integration, and lean principles, manufacturers can create a streamlined assembly process that enhances both output quality and operational effectiveness.
As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about advancements in SMT machinery and techniques will further aid in maintaining an efficient production environment. Ultimately, a well-designed SMT production line not only meets current demands but also adapts to future challenges in the ever-changing landscape of electronics manufacturing.
FAQ
1. What are the key components of an SMT production line?
The key components include stencil printers, pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and inspection systems which work together to assemble electronic components onto PCBs.
2. How does machine placement affect productivity?
Strategic machine placement minimizes movement between processes, reduces delays caused by bottlenecks, and ensures that operators can work efficiently without obstruction.
3. What is lean manufacturing in relation to SMT?
Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity through techniques such as value stream mapping and continuous improvement practices like 5S.
4. Why is ergonomics important in an SMT layout?
Ergonomics enhances operator comfort which can lead to increased efficiency and reduced risk of injuries during repetitive tasks within the production process.
5. How can simulation tools help in optimizing an SMT layout?
Simulation tools allow manufacturers to visualize different layouts and operational scenarios before implementation, helping identify potential issues that could affect performance.




















