Content Menu
● Understanding SMD SMT Machines and Their Role in Electronics Manufacturing
● Key Automation Technologies in SMD SMT Machines Enhancing Quality Control
>> 1. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
>> 2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics
>> 3. Precision Component Placement and Solder Paste Printing
>> 4. Automated Testing and Functional Verification
>> 5. Error-Proofing Mechanisms (Poka-Yoke)
● How Automation Improves Quality Control in SMD SMT Machines
>> Consistency and Repeatability
>> Early Defect Detection and Reduced Rework
>> Enhanced Process Monitoring and Control
>> Increased Throughput Without Compromising Quality
>> Data-Driven Continuous Improvement
● Benefits of Automation in SMD SMT Machines for Quality Control
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the role of Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) in SMT quality control?
>> 2. How does AI improve the SMT manufacturing process?
>> 3. Why is precision important in SMD SMT machine component placement?
>> 4. What quality control measures are integrated into automated SMT lines?
>> 5. How does automation reduce labor costs in SMT assembly?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Surface Mount Devices (SMD) have revolutionized modern electronics manufacturing by enabling compact, high-density circuit assemblies. Central to this process are SMD SMT machines, which automate component placement on printed circuit boards (PCBs). Automation in these machines not only accelerates production but profoundly enhances quality control, ensuring reliability and consistency in electronic products. This article explores in depth how automation in SMD SMT machines improves quality control, the technologies involved, and the resulting benefits for manufacturers.
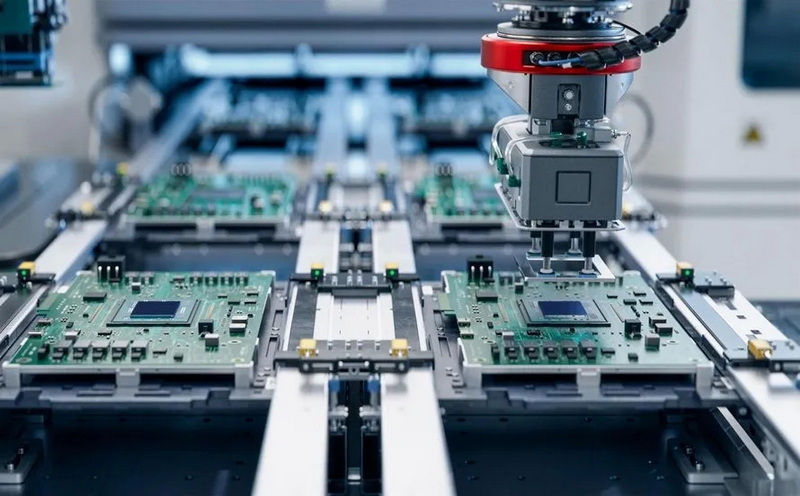
Understanding SMD SMT Machines and Their Role in Electronics Manufacturing
SMD SMT machines are specialized automated equipment used to place surface mount devices onto PCBs with high precision. These machines integrate multiple technologies such as pick-and-place heads, vision systems, solder paste printers, and reflow ovens to complete the assembly process efficiently.
- SMD (Surface Mount Devices): Components designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of PCBs.
- SMT (Surface Mount Technology): The technology and process of mounting SMDs onto PCBs.
The automation of these machines has transformed traditional manual assembly into a highly efficient, repeatable process that reduces human error and variability.
The importance of SMD SMT machines cannot be overstated in today's electronics industry, where miniaturization and high reliability are critical. Manual assembly methods are no longer sufficient to meet the demands of modern electronic devices, which often contain thousands of components per board. Automated SMD SMT machines provide the speed, accuracy, and repeatability necessary to produce complex PCBs at scale.
Key Automation Technologies in SMD SMT Machines Enhancing Quality Control
1. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI systems use high-resolution cameras and advanced image processing algorithms to inspect PCBs at various assembly stages. These systems detect defects such as:
- Component misplacement
- Solder bridges
- Tombstoning (components standing on end)
- Missing components
By automating inspection, AOI provides consistent, objective, and rapid defect detection, minimizing the risk of faulty assemblies reaching later stages or customers.
AOI is typically integrated at multiple points in the SMT line: after solder paste printing, after component placement, and after reflow soldering. This multi-stage inspection ensures that defects are caught early and at the most relevant point in the process, reducing costly rework and scrap.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics
AI integration in SMT lines enables real-time correlation of data from multiple sources such as pick-and-place machines, AOI, solder paste inspection (SPI), and in-circuit testing (ICT). AI algorithms analyze this data to:
- Predict failures before they occur
- Optimize process parameters dynamically
- Reduce waste by early defect detection
- Enhance decision-making for quality improvement
This holistic AI-driven approach creates a digital twin of the SMT process, allowing manufacturers to maximize yield and assembly quality.
For example, AI can detect subtle patterns in solder paste volume variations or component placement deviations that may not be obvious to human operators. By learning from historical data, AI systems can recommend adjustments to machine settings that improve quality without slowing production.
3. Precision Component Placement and Solder Paste Printing
Automated pick-and-place machines ensure components are positioned with micron-level accuracy, reducing misalignment and placement errors. Similarly, automated solder paste printers apply consistent, uniform solder paste deposits critical for reliable solder joints.
Automation reduces variability caused by manual handling and ensures repeatability across production runs, directly impacting final product quality.
Modern SMD SMT machines use advanced motion control systems, including linear motors and vision-guided placement heads, to achieve placement speeds exceeding 100,000 components per hour while maintaining accuracy within ±0.02 mm. This precision is essential for fine-pitch components and high-density PCB designs.
4. Automated Testing and Functional Verification
Automated testing systems integrated into SMT lines perform electrical and functional tests on assembled PCBs. These systems verify:
- Component integrity
- Circuit connectivity
- Functional performance under simulated conditions
Early detection of electrical faults prevents defective boards from advancing, reducing costly rework and scrap.
In addition to in-line testing, some SMT lines incorporate X-ray inspection systems to examine hidden solder joints, such as those under Ball Grid Array (BGA) components, which are not visible to optical inspection. This comprehensive testing ensures that all solder joints meet quality standards.
5. Error-Proofing Mechanisms (Poka-Yoke)
Automation incorporates error-proofing features such as barcode scanning for component verification and sensor-based detection of missing or misaligned parts. These mechanisms prevent common assembly mistakes, ensuring only correct components are placed and soldered.
For example, barcode readers verify component reels before placement, preventing the use of wrong or counterfeit parts. Sensors detect if a component is missing from the feeder or if the pick-and-place head fails to pick a part, triggering immediate alerts for operator intervention.

How Automation Improves Quality Control in SMD SMT Machines
Consistency and Repeatability
Automated SMD SMT machines operate with precise control over placement, solder application, and inspection processes. This consistency eliminates human variability, leading to uniform product quality across batches.
Manual assembly is prone to errors caused by fatigue, skill level differences, and environmental factors. Automation standardizes the process, ensuring that every board is assembled to the same high standard regardless of shift or operator.
Early Defect Detection and Reduced Rework
With integrated AOI, SPI, and X-ray inspection, defects such as solder bridges, insufficient solder, or component misalignment are detected immediately. Early identification allows for prompt corrective action, reducing rework rates and improving overall yield.
Detecting defects early in the SMT process is critical because fixing issues after reflow or final assembly is costly and time-consuming. Automated inspection systems provide real-time feedback, enabling quick adjustments to prevent defect propagation.
Enhanced Process Monitoring and Control
Automation systems continuously monitor critical parameters like temperature, humidity, machine calibration, and solder paste volume. Statistical Process Control (SPC) tools analyze this data to detect deviations and maintain process stability, preventing quality issues before they arise.
For example, solder paste printing requires precise control of stencil thickness, squeegee pressure, and environmental conditions. Automated solder paste inspection (SPI) measures paste volume and shape on the PCB, feeding data back to the printer to adjust settings dynamically.
Increased Throughput Without Compromising Quality
Automated SMT lines can run continuously at high speeds while maintaining stringent quality standards. This capability allows manufacturers to meet tight production deadlines without sacrificing product reliability.
High-speed pick-and-place machines combined with automated inspection and testing enable manufacturers to produce thousands of PCBs per hour. This scalability is essential for industries like consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices, where both volume and quality are critical.
Data-Driven Continuous Improvement
The integration of AI and big data analytics enables manufacturers to identify trends, root causes of defects, and opportunities for process optimization. This data-driven approach fosters continuous quality improvement and innovation.
By collecting and analyzing data across multiple production lines and shifts, manufacturers can benchmark performance, implement best practices, and reduce variability. Continuous improvement cycles driven by automation data lead to higher yields and lower costs over time.
Benefits of Automation in SMD SMT Machines for Quality Control
- Higher Yield Rates: Reduced defects and rework improve the number of good boards produced per batch.
- Improved Product Reliability: Precise assembly and thorough inspection ensure long-term performance.
- Cost Savings: Less scrap, rework, and manual labor reduce overall manufacturing costs.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Automated processes accelerate production cycles and testing.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Consistent high quality strengthens brand reputation and customer trust.
- Scalability: Automation supports rapid production scaling without compromising quality.
- Traceability: Automated systems log detailed process data, enabling full traceability for quality audits and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Automation in SMD SMT machines fundamentally enhances quality control by integrating advanced inspection, precise component placement, AI-driven analytics, and automated testing into the production process. These technologies ensure consistent, reliable, and high-quality PCB assemblies while increasing throughput and reducing costs. As electronics manufacturing becomes increasingly complex and competitive, leveraging automation in SMD SMT machines is essential for maintaining superior quality standards and achieving operational excellence. Manufacturers who embrace these automated solutions will be better positioned to meet the demands of the future electronics market with confidence and efficiency.

FAQ
1. What is the role of Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) in SMT quality control?
AOI systems use high-resolution imaging and algorithms to detect defects such as misaligned components, solder bridges, and missing parts during the SMT assembly process. This automation ensures rapid, consistent, and objective inspection, reducing human error and improving defect detection rates.
2. How does AI improve the SMT manufacturing process?
AI correlates data from various SMT equipment and inspection systems to predict failures, optimize process parameters, reduce waste, and enhance decision-making. This leads to faster defect detection, higher yield, and improved assembly quality.
3. Why is precision important in SMD SMT machine component placement?
Precise placement ensures components align perfectly with solder pads, preventing defects like tombstoning or misalignment. Automated machines achieve micron-level accuracy, which is difficult to replicate manually, thus improving solder joint reliability and product quality.
4. What quality control measures are integrated into automated SMT lines?
Automated SMT lines incorporate solder paste inspection, AOI, X-ray inspection, in-circuit testing, and functional testing. These measures detect defects at various stages, ensuring only compliant boards proceed through production.
5. How does automation reduce labor costs in SMT assembly?
Automation minimizes manual tasks such as component placement, solder paste printing, and inspection. This reduces labor intensity and errors, allowing skilled workers to focus on process optimization and quality control, ultimately lowering overall labor costs.




















