Content Menu
● Understanding SMD Manufacturing Machines in PCB Assembly
● The SMT PCB Assembly Process and the Role of SMD Manufacturing Machines
>> 1. Solder Paste Printing
>> 2. Solder Paste Inspection (SPI)
>> 3. Pick-and-Place Component Mounting
>> 4. Reflow Soldering
>> 5. Post-Reflow Inspection
>> 6. Final Testing and Quality Control
● Key Components of an SMD Manufacturing Machine
● Advantages of Using SMD Manufacturing Machines in PCB Assembly
● Challenges and Considerations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the primary function of an SMD manufacturing machine in PCB assembly?
>> 2. How does the pick-and-place machine ensure accurate component placement?
>> 3. Why is solder paste printing important in the SMT process?
>> 4. What types of components can SMD manufacturing machines handle?
>> 5. How do inspection machines contribute to the SMT assembly process?
Surface Mount Device (SMD) manufacturing machines play a crucial role in the modern printed circuit board (PCB) assembly process. These machines are designed to automate the placement and soldering of electronic components directly onto the surface of PCBs, enabling high-speed, precise, and efficient production of electronic devices. This article explores in detail how an SMD manufacturing machine works within the PCB assembly process, covering each stage from solder paste application to final inspection.
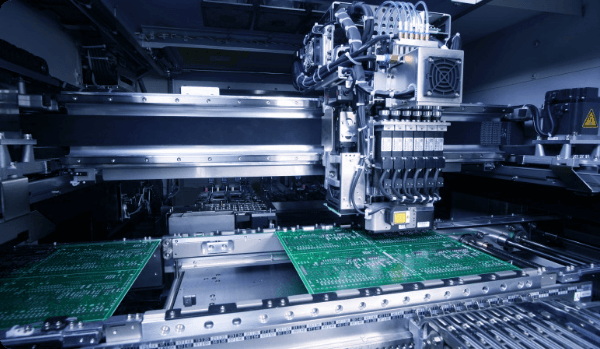
Understanding SMD Manufacturing Machines in PCB Assembly
An SMD manufacturing machine is part of a broader Surface Mount Technology (SMT) assembly line. SMT is a method where components known as surface mount devices (SMDs) are mounted directly onto the surface of PCBs without the need for drilling holes, unlike traditional through-hole technology. This method allows for smaller, lighter, and more compact electronic products.
The SMD manufacturing machine typically refers to the automated equipment involved in placing and soldering these components, including solder paste printers, pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and inspection systems.
The SMT PCB Assembly Process and the Role of SMD Manufacturing Machines
The SMT assembly process involves several key stages, each supported by specialized SMD manufacturing machines. These stages include:
1. Solder Paste Printing
The first step in the SMT process is applying solder paste to the PCB pads where components will be placed. This is done using a solder paste printing machine, which uses a metal stencil precisely aligned over the PCB. The solder paste, a mixture of tiny solder balls and flux, is spread across the stencil openings, depositing paste only on the designated pads.
The solder paste printer is highly precise, often featuring automated vision systems to align the stencil with micron-level accuracy and mechanisms to ensure consistent paste thickness and coverage. This step is critical because the quality of solder paste application directly affects the reliability of solder joints formed later.
2. Solder Paste Inspection (SPI)
After printing, the PCB passes through a solder paste inspection machine. This machine uses infrared or optical cameras to capture detailed images of the paste deposits, checking for correct placement, volume, and shape. If defects are detected, the process can be paused for troubleshooting to prevent defective assemblies downstream.
3. Pick-and-Place Component Mounting
Once the solder paste is verified, the PCB moves to the pick-and-place machine, the heart of the SMD manufacturing process. This robotic system automatically picks SMD components from feeders loaded with reels, trays, or tubes and places them onto the solder-pasted pads on the PCB.
The pick-and-place machine uses vacuum nozzles to pick components and high-resolution cameras to orient and align each part precisely before placement. The machine is programmed with the PCB's design data, allowing it to place thousands of components per hour with placement accuracy often within ±0.05 mm.
There are typically two types of pick-and-place machines used in a line: high-speed machines for small passive components like resistors and capacitors, and functional placement machines for larger or more complex parts like integrated circuits and connectors.
4. Reflow Soldering
After all components are placed, the PCB enters a reflow oven. This oven heats the board through a controlled temperature profile, melting the solder paste and creating permanent solder joints between the components and the PCB pads.
Reflow ovens have multiple temperature zones to gradually preheat, soak, reflow, and cool the assembly, ensuring strong solder joints without damaging components. Some ovens use nitrogen atmospheres to reduce oxidation during soldering.
5. Post-Reflow Inspection
Following soldering, the assembly undergoes automated optical inspection (AOI) to detect placement errors, solder defects, or missing components. For certain components like Ball Grid Arrays (BGAs), X-ray inspection machines check the integrity of hidden solder joints under the package.
6. Final Testing and Quality Control
The last stage involves functional testing and final quality control inspections to ensure the assembled PCBs meet all specifications and reliability standards before shipment.
Key Components of an SMD Manufacturing Machine
- Solder Paste Printer: Applies solder paste accurately on PCB pads using a stencil.
- Pick-and-Place Machine: Robotic system for rapid and precise placement of SMD components.
- Feeders: Supply components to the pick-and-place machine in an organized manner.
- Reflow Oven: Melts solder paste to form permanent solder joints.
- Inspection Systems: SPI, AOI, and X-ray machines ensure quality at different stages.
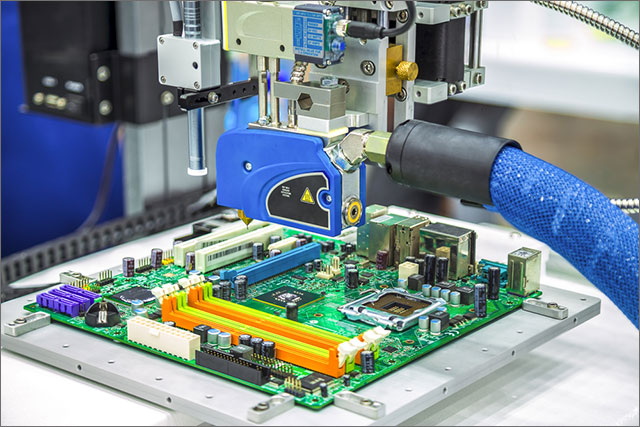
Advantages of Using SMD Manufacturing Machines in PCB Assembly
- High Precision: Machines place components with micron-level accuracy.
- Increased Speed: Automated placement can reach tens of thousands of components per hour.
- Consistency: Reduces human error and ensures uniform quality.
- Compact Designs: Enables assembly of smaller and more complex PCBs.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces labor costs and increases throughput.
Challenges and Considerations
- Setup and Programming: Requires accurate programming and setup for each PCB design.
- Maintenance: Machines need regular calibration and maintenance for optimal performance.
- Component Handling: Sensitive components require careful handling to avoid damage.
- Inspection: Continuous inspection is necessary to catch defects early.
Conclusion
An SMD manufacturing machine is a vital part of the modern PCB assembly process, enabling the efficient and precise placement and soldering of surface mount components. By automating key steps such as solder paste printing, component placement, and reflow soldering, these machines support the production of high-quality, compact, and reliable electronic devices. The integration of inspection systems ensures defects are minimized, maintaining high standards of quality. As electronics continue to evolve towards greater miniaturization and complexity, SMD manufacturing machines will remain indispensable in the electronics manufacturing industry.
FAQ
1. What is the primary function of an SMD manufacturing machine in PCB assembly?
An SMD manufacturing machine automates the application of solder paste, precise placement of surface mount components, and soldering processes, significantly increasing assembly speed and accuracy.
2. How does the pick-and-place machine ensure accurate component placement?
The pick-and-place machine uses vacuum nozzles to pick components and high-resolution vision systems to orient and align each part before placing it on the PCB with micron-level precision.
3. Why is solder paste printing important in the SMT process?
Solder paste printing deposits the solder material exactly where components will be mounted, providing the necessary bonding material for solder joints during reflow soldering.
4. What types of components can SMD manufacturing machines handle?
They can handle a wide range of components, from tiny resistors and capacitors to large integrated circuits and connectors, supplied in reels, trays, or tubes.
5. How do inspection machines contribute to the SMT assembly process?
Inspection machines like SPI, AOI, and X-ray systems detect defects in solder paste application, component placement, and solder joints, ensuring high-quality and reliable PCB assemblies.




















