Content Menu
● Introduction
● Understanding ESD and Its Impact
● Role of SMT PCB Holders in ESD Safety
>> Key Features of ESD-Safe SMT PCB Holders
● Benefits of Using SMT PCB Holders for ESD Safety
● SMT PCB Assembly Process and ESD Considerations
● Advanced ESD Protection Measures
● Impact of ESD Safety on Product Quality and Reliability
● Future Trends in ESD Safety
● Training and Awareness in ESD Safety
● Integration with Industry 4.0 Technologies
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What is the primary purpose of using SMT PCB holders in electronics manufacturing?
>> 2. How do SMT PCB holders contribute to reducing ESD risks?
>> 3. What materials are typically used for ESD-safe SMT PCB holders?
>> 4. Can SMT PCB holders be used in conjunction with other ESD protection measures?
>> 5. How do SMT PCB holders impact the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process?
Introduction
In the realm of electronics manufacturing, particularly in the context of Surface Mount Technology (SMT), ensuring Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) safety is paramount. SMT PCB holders play a crucial role in this process by providing a secure and controlled environment for handling sensitive electronic components. This article delves into the importance of SMT PCB holders in maintaining ESD safety during the assembly and manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs).
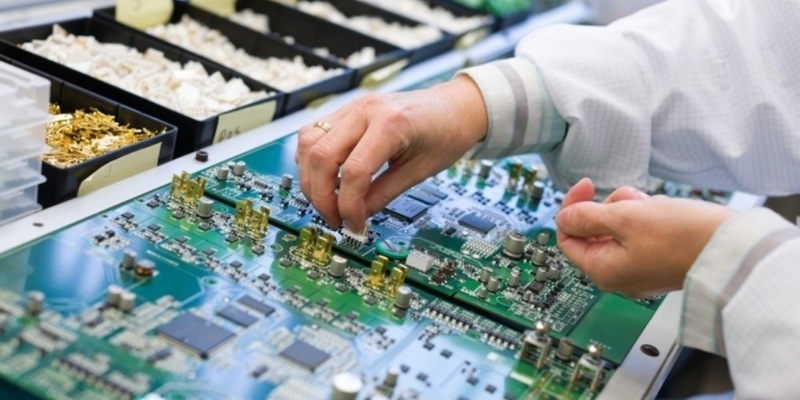

Understanding ESD and Its Impact
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects. It poses significant risks to sensitive electronic components, potentially causing damage that may not be immediately apparent but can lead to latent defects or reduced reliability over time. Even low voltages, as minimal as 30V, can be destructive to microelectronics. Therefore, preventing ESD during manufacturing is critical.
Role of SMT PCB Holders in ESD Safety
SMT PCB holders are designed to support and secure PCBs during various stages of assembly and testing. These holders are typically made from materials that are either conductive or static dissipative, ensuring that any electrostatic charges are safely discharged to ground. This feature is essential for preventing ESD events that could damage components.
Key Features of ESD-Safe SMT PCB Holders
1. Material Selection: ESD-safe holders are constructed from materials with specific electrical resistance properties, usually in the range of $$10^8$$ to $$10^{11}$$ ohm-cm. This allows them to dissipate static charges effectively without causing damage to components.
2. Grounding Mechanisms: These holders often include grounding points or clips that ensure the PCB is connected to a common ground, further reducing the risk of static buildup.
3. Design for Component Protection: The design of SMT PCB holders ensures that components are not directly touched or handled, minimizing the risk of transferring static charges from personnel to sensitive parts.
4. Compatibility with ESD Workstations: SMT PCB holders are designed to be used within ESD Protected Areas (EPAs), which are controlled environments equipped with antistatic materials and grounding systems to prevent ESD.
Benefits of Using SMT PCB Holders for ESD Safety
The use of SMT PCB holders contributes significantly to maintaining ESD safety in several ways:
- Reduced Risk of Component Damage: By providing a grounded and controlled environment, these holders minimize the risk of ESD damage to components during handling and assembly.
- Improved Manufacturing Efficiency: ESD-safe holders streamline the assembly process by ensuring that components are securely positioned and protected, reducing downtime due to ESD-related failures.
- Enhanced Reliability: Components assembled using ESD-safe holders are less likely to suffer from latent defects, leading to more reliable end products.
SMT PCB Assembly Process and ESD Considerations
The SMT PCB assembly process involves several stages, including stencil printing, component placement, reflow soldering, and testing. Each stage requires careful consideration of ESD safety:
1. Stencil Printing: This stage involves applying solder paste to the PCB. Using antistatic brushes and ensuring the printer is grounded helps prevent ESD.
2. Component Placement: Automated pick-and-place machines are used to mount components. These machines must be properly grounded to prevent static buildup.
3. Reflow Soldering: Components are soldered using a reflow oven. The PCBs are placed on shorting beds or in grounded fixtures to prevent ESD during this process.
4. Testing: Test fixtures must be grounded, and personnel should wear wrist straps to ensure ESD safety during testing.
Advanced ESD Protection Measures
In addition to using SMT PCB holders, manufacturers employ various advanced ESD protection measures:
- ESD Flooring and Workstations: Work areas are equipped with antistatic flooring and workstations that are grounded to prevent static buildup.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Personnel wear wrist straps, antistatic clothing, and shoes to prevent static transfer from their bodies to components.
- Air Ionization: Ionizers are used to neutralize static charges in the air, reducing the risk of ESD events.
Impact of ESD Safety on Product Quality and Reliability
Maintaining ESD safety is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of electronic products. Components damaged by ESD may not always show immediate signs of failure but can lead to premature wear or unexpected malfunctions in the field. This not only affects customer satisfaction but also increases warranty claims and repair costs for manufacturers.
Future Trends in ESD Safety
As electronics continue to evolve with smaller, more sensitive components, the importance of ESD safety will only increase. Future trends include the development of more advanced materials for ESD-safe equipment and the integration of ESD protection into automated assembly lines. Additionally, there will be a greater emphasis on training personnel in ESD safety practices to ensure that all stages of manufacturing are protected against ESD risks.
Training and Awareness in ESD Safety
Training personnel in ESD safety practices is essential for maintaining a safe working environment. This includes educating workers on the risks of ESD, proper use of ESD-safe equipment, and adherence to protocols for handling sensitive components. Regular audits and compliance checks also help ensure that ESD safety standards are consistently met.
Integration with Industry 4.0 Technologies
The integration of ESD safety measures with Industry 4.0 technologies offers promising opportunities for enhancing manufacturing efficiency and reliability. Automated systems can monitor ESD conditions in real-time, alerting personnel to potential risks and ensuring that all safety protocols are followed. This integration not only improves product quality but also reduces the likelihood of human error in ESD safety practices.
Conclusion
SMT PCB holders play a vital role in maintaining ESD safety during the assembly and manufacturing of printed circuit boards. By providing a secure, grounded environment for components, these holders significantly reduce the risk of ESD damage, enhance manufacturing efficiency, and improve the reliability of electronic products. As electronics continue to evolve with smaller, more sensitive components, the importance of ESD-safe SMT PCB holders will only continue to grow.
FAQs
1. What is the primary purpose of using SMT PCB holders in electronics manufacturing?
SMT PCB holders are primarily used to provide a secure and controlled environment for handling sensitive electronic components during assembly and testing, ensuring ESD safety and preventing damage to components.
2. How do SMT PCB holders contribute to reducing ESD risks?
SMT PCB holders contribute to reducing ESD risks by being made from conductive or static dissipative materials, ensuring that any electrostatic charges are safely discharged to ground. They also include grounding mechanisms to keep the PCB connected to a common ground.
3. What materials are typically used for ESD-safe SMT PCB holders?
ESD-safe SMT PCB holders are typically made from materials with specific electrical resistance properties, usually in the range of $$10^8$$ to $$10^{11}$$ ohm-cm, allowing them to dissipate static charges effectively.
4. Can SMT PCB holders be used in conjunction with other ESD protection measures?
Yes, SMT PCB holders are designed to be used within ESD Protected Areas (EPAs), which include additional ESD protection measures such as antistatic materials and grounding systems.
5. How do SMT PCB holders impact the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process?
SMT PCB holders improve manufacturing efficiency by reducing downtime due to ESD-related failures, ensuring components are securely positioned, and streamlining the assembly process.




















