Content Menu
● Understanding SMT Components
● Advantages of SMT Components
>> Compact Size and High Density
>> Improved Electrical Performance
>> Cost Efficiency
● Challenges Associated with SMT Components
>> Thermal Management
>> Mechanical Stability
>> Design Complexity
● Types of SMT Components and Their Impact on Circuit Design
>> Resistors
>> Capacitors
>> Integrated Circuits (ICs)
>> Connectors
● Best Practices for Designing with SMT Components
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the main advantages of using SMT over through-hole technology?
>> 2. How do I manage thermal issues when designing with SMT?
>> 3. What types of applications benefit most from using SMT?
>> 4. Can I mix SMT with through-hole technology on the same PCB?
>> 5. How do I select appropriate SMT components for my design?
● Citations:
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has fundamentally transformed circuit design and manufacturing processes in the electronics industry. By allowing components to be mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), SMT enables more compact designs, higher component densities, and improved performance characteristics. This article explores how different types of SMT components impact circuit design, considering their advantages, challenges, and applications.

Understanding SMT Components
SMT components are categorized into various types based on their functions and packaging styles. These include:
- Resistors: Commonly used for limiting current flow.
- Capacitors: Essential for storing electrical energy and filtering signals.
- Inductors: Used in power supplies and signal processing applications.
- Diodes: Allow current to flow in one direction, crucial for rectification.
- Transistors: Act as switches or amplifiers in circuits.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Combine multiple functions into a single package.
Each type of SMT component has unique characteristics that influence circuit design decisions.
Advantages of SMT Components
Compact Size and High Density
One of the most significant advantages of SMT components is their compact size. Compared to traditional through-hole components, SMT components are smaller and can be placed on both sides of a PCB. This allows designers to achieve higher component densities, leading to more complex and functional circuit designs within limited space. For instance, a 0402 resistor measures only 1 mm x 0.5 mm, making it ideal for space-constrained applications[3][6].
Improved Electrical Performance
SMT components also enhance electrical performance by minimizing the length of electrical paths. Shorter connections reduce resistance and inductance, resulting in lower signal interference and improved signal integrity. This is particularly beneficial in high-frequency applications where performance is critical[1][8].
Cost Efficiency
The use of SMT can lead to reduced manufacturing costs. Smaller components require less material, and their efficient placement allows for faster assembly processes. Automated assembly techniques can be employed, further lowering labor costs and increasing production speed[5][9]. Additionally, the ability to place components on both sides of a PCB maximizes space utilization, allowing for more functionality without increasing board size.
Challenges Associated with SMT Components
While SMT offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges that designers must consider.
Thermal Management
One challenge associated with SMT components is thermal management. As components become smaller and more densely packed, heat dissipation becomes critical. High-power components may require additional thermal management solutions such as heat sinks or thermal vias to prevent overheating[4][6]. Designers must carefully consider the thermal characteristics of each component during the design process.
Mechanical Stability
SMT components are generally lighter than through-hole components; however, they may be less mechanically stable in environments subject to vibration or shock. In such cases, additional support structures may be necessary to secure the components adequately[3][10].
Design Complexity
The increased variety of SMT component types can complicate the design process. Designers must be familiar with various package types and their specifications to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within the circuit[2][4].
Types of SMT Components and Their Impact on Circuit Design
Different types of SMT components have distinct impacts on circuit design based on their functionalities and characteristics.
Resistors
Resistors are fundamental in controlling current flow within circuits. The choice between standard surface mount resistors (e.g., 0603 or 0402 packages) can affect board layout due to their size and power ratings. Smaller resistors may lead to increased density but can also introduce challenges related to thermal management if not adequately spaced from heat-generating components[1][10].
Capacitors
Capacitors play a crucial role in filtering and energy storage applications. The selection between ceramic capacitors versus tantalum capacitors can significantly influence circuit performance due to differences in equivalent series resistance (ESR) and capacitance stability under varying temperatures[6][8].
Integrated Circuits (ICs)
ICs are often at the heart of modern electronic devices, integrating multiple functions into a single package. The choice between different IC packages (e.g., QFN vs. BGA) impacts not only the layout but also considerations like heat dissipation, pin accessibility for testing, and overall board complexity[2][9].
Connectors
While many connectors are still designed using through-hole technology due to mechanical strength requirements, there is a growing trend towards using SMT connectors for specific applications where space-saving is essential. The choice of connector type can affect assembly processes and long-term reliability under mechanical stress[7][10].
Best Practices for Designing with SMT Components
To maximize the benefits of SMT components while mitigating potential challenges, designers should follow these best practices:
- Component Selection: Choose appropriate component types based on application requirements while considering size constraints.
- Thermal Management: Implement thermal management strategies early in the design process to ensure reliable operation under varying load conditions.
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Utilize DFM principles to streamline assembly processes by optimizing component placement and minimizing soldering issues.
- Simulation Tools: Leverage simulation tools to predict circuit behavior under different conditions before finalizing designs.
- Prototyping: Create prototypes using breakout boards or custom PCBs to test configurations before full-scale production.
Conclusion
The integration of different types of SMT components has revolutionized circuit design by enabling smaller, more efficient electronic devices while enhancing performance characteristics such as speed and reliability. However, designers must navigate challenges related to thermal management, mechanical stability, and increased complexity due to the variety of available components. By adhering to best practices in selection and layout design, engineers can harness the full potential of SMT technology in their projects.
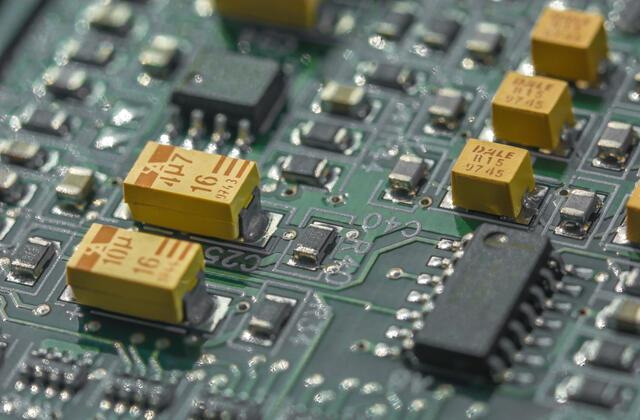
FAQ
1. What are the main advantages of using SMT over through-hole technology?
SMT offers several advantages including reduced size and weight of components, higher component density on PCBs, improved electrical performance due to shorter connections, lower manufacturing costs through automation, and the ability to place components on both sides of a PCB.
2. How do I manage thermal issues when designing with SMT?
To manage thermal issues in SMT designs, consider spacing high-power components adequately from others, using thermal vias or heat sinks as necessary, selecting capacitors with appropriate ESR ratings, and ensuring good airflow around critical areas on the PCB.
3. What types of applications benefit most from using SMT?
Applications that require compact designs with high functionality—such as smartphones, wearables, medical devices, and consumer electronics—benefit significantly from using SMT due to its space-saving capabilities.
4. Can I mix SMT with through-hole technology on the same PCB?
Yes, it is possible to mix both technologies on the same PCB. Many designs incorporate both SMT for compactness alongside through-hole technology for larger or more mechanically stressed components.
5. How do I select appropriate SMT components for my design?
Selecting appropriate SMT components involves considering factors such as size constraints, electrical specifications (like voltage ratings), thermal management needs, availability from suppliers, and compatibility with your assembly process.
Citations:
[1] https://www.protoexpress.com/blog/good-not-so-good-sides-surface-mount-technology/
[2] https://resources.pcb.cadence.com/blog/2019-surface-mount-technologies-and-devices-pesky-enclosures-and-smart-layouts
[3] https://www.ultralibrarian.com/2021/08/10/the-impact-of-smt-components-on-pcb-assembly-ulc
[4] https://jlcpcb.com/blog/design-process-of-a-surface-mount-pcb
[5] https://www.mtek.co.uk/frequently-asked-questions-smt-assembly
[6] https://www.wevolver.com/article/smd-components
[7] https://konnra.com/the-impact-of-smt-connectors-on-electronic-product-design/
[8] https://arkcircuits.com/blog/impact-of-smt-on-modern-pcb-design/
[9] https://versae.com/smt-assembly-faq/
[10] https://www.pcbonline.com/blog/pcb-smt-components.html




















