Content Menu
● Understanding SMT Stencil Aspect Ratio and Area Ratio
● Impact of Different Materials on SMT Stencil Aspect Ratio
>> 1. Mechanical Properties and Thickness Control
>> 2. Aperture Wall Smoothness and Surface Finish
>> 3. Manufacturing Process Compatibility
● How Material Choice Influences SMT Stencil Design Parameters
>> Aspect Ratio Optimization
>> Area Ratio and Paste Transfer Efficiency
● Practical Considerations for Selecting SMT Stencil Materials
>> Durability and Longevity
>> Cost vs. Performance Trade-offs
>> Cleaning and Maintenance
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the ideal SMT stencil aspect ratio for good solder paste release?
>> 2. How does stencil material affect aperture wall smoothness?
>> 3. Can thinner stencil materials improve aspect ratio?
>> 4. Why is area ratio important alongside aspect ratio?
>> 5. How do manufacturing processes interact with stencil materials?
● Citations:
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) stencils are critical components in the electronics manufacturing process, specifically in solder paste printing. The SMT stencil aspect ratio—defined as the ratio of the aperture width to the stencil thickness—is a fundamental parameter influencing solder paste transfer efficiency and print quality. Different stencil materials affect this aspect ratio and related printing performance in significant ways. This article explores how various materials impact the SMT stencil aspect ratio, the underlying physics, and practical considerations for stencil design and manufacturing.
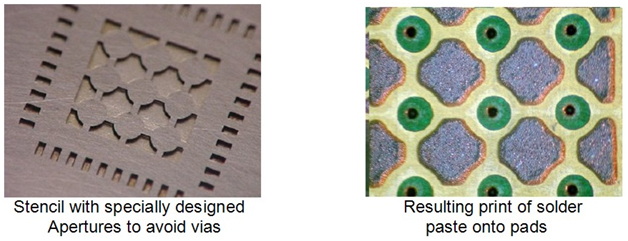
Understanding SMT Stencil Aspect Ratio and Area Ratio
Before delving into material impacts, it is essential to clarify the concepts of aspect ratio and area ratio in SMT stencil design.
- Aspect Ratio (AR) is the ratio of the aperture width (W) to the stencil thickness (T):
Aspect Ratio=TW
A higher aspect ratio generally facilitates better solder paste release from the stencil aperture onto the PCB pad. Industry guidelines typically recommend an aspect ratio greater than 1.5 for acceptable paste release[1][5].
- Area Ratio is a more comprehensive measure that considers the aperture opening area relative to the surface area of the aperture walls:
Area Ratio=2(L+W)×TL×W
where L and W are the aperture length and width, and T is the stencil thickness. An area ratio above 0.66 is generally considered optimal for paste release[1][4].
While aspect ratio is a simplified one-dimensional metric, area ratio provides a better prediction of print performance, especially for complex aperture shapes.
Impact of Different Materials on SMT Stencil Aspect Ratio
The choice of stencil material directly influences the achievable aspect ratio and printing quality. Common SMT stencil materials include stainless steel, electro-polished stainless steel, and specialty alloys. Their mechanical and surface properties affect aperture precision, wall smoothness, and ultimately solder paste transfer.
1. Mechanical Properties and Thickness Control
- Stainless Steel Foils are the industry standard due to their strength and durability. However, thickness uniformity and mechanical stability can vary by grade and manufacturing process. Thicker foils reduce the aspect ratio for a given aperture size, potentially lowering print quality[3].
- Electro-Polished Stainless Steel undergoes a surface treatment that smooths aperture walls and slightly alters thickness. This process can improve paste release by reducing surface roughness and minimizing solder paste adhesion to aperture walls[2].
- Specialty Alloys or coated foils may offer enhanced mechanical properties, allowing thinner stencils without compromising durability. Thinner stencils increase the aspect ratio for the same aperture width, improving paste release[2][3].
2. Aperture Wall Smoothness and Surface Finish
The smoothness of aperture walls is critical for solder paste release. Rough or uneven walls increase the likelihood of paste sticking inside the aperture, reducing transfer efficiency.
- Electro-polished materials exhibit smoother aperture walls, which correlates with better paste release and more predictable printing performance across a range of aspect ratios and area ratios[2].
- Materials with rougher surfaces or burrs from laser cutting or chemical etching tend to have lower transfer efficiency, especially at lower aspect ratios[1][2].
3. Manufacturing Process Compatibility
Different stencil materials respond differently to manufacturing methods such as laser cutting, chemical etching, or electroforming.
- Laser cutting is compatible with stainless steel foils and can produce apertures with aspect ratios approaching 1:1 (aperture width to stencil thickness), which is beneficial for fine-pitch applications[1].
- Chemical etching struggles to achieve aspect ratios below 1.5 due to undercutting and tapered aperture walls, limiting paste release performance[1].
- Electro-polishing after laser cutting can further refine aperture walls and improve aspect ratio effectiveness by reducing roughness[2].

How Material Choice Influences SMT Stencil Design Parameters
Aspect Ratio Optimization
Material selection affects the minimum achievable stencil thickness and aperture precision, which in turn influences the SMT stencil aspect ratio.
- Using thinner, high-strength materials allows designers to maintain or increase aperture widths while reducing stencil thickness, thereby increasing the aspect ratio and improving solder paste release[3].
- Materials that allow for smoother aperture walls reduce the need to oversize apertures to compensate for poor paste release, enabling tighter pitch designs and smaller apertures without sacrificing print quality[2][4].
Area Ratio and Paste Transfer Efficiency
The interplay between material and aperture geometry affects the area ratio, which is crucial for paste release.
- Materials that enable precise aperture shapes with minimal burrs or roughness help maintain the recommended area ratio of 0.66 or higher, ensuring consistent paste volume and transfer efficiency[1][4].
- For round or irregular apertures, material smoothness and manufacturing precision become even more critical, as the area ratio calculation is more sensitive to aperture wall conditions[1].
Practical Considerations for Selecting SMT Stencil Materials
Durability and Longevity
- Stainless steel stencils are durable and resist wear over many print cycles, but thicker foils reduce aspect ratio.
- Electro-polished stencils may have slightly reduced mechanical strength but offer better print consistency and longer usable life due to reduced paste sticking[2].
Cost vs. Performance Trade-offs
- Specialty materials and surface treatments increase stencil cost but can reduce defects and rework, improving overall manufacturing efficiency.
- For high-volume or fine-pitch SMT production, investing in high-quality materials that optimize aspect ratio and area ratio is justified[3].
Cleaning and Maintenance
- Material surface finish affects how easily solder paste residues can be cleaned from apertures.
- Smoother, electro-polished surfaces facilitate easier cleaning, maintaining consistent aspect ratios and print quality over time[4].
Conclusion
The SMT stencil aspect ratio is a key determinant of solder paste printing quality, directly influenced by stencil material properties. Materials that allow thinner, stronger foils with smooth aperture walls enable higher aspect ratios and better paste release. Electro-polished stainless steel, for example, improves aperture wall smoothness, enhancing transfer efficiency even at challenging area ratios. Selecting appropriate stencil materials and manufacturing processes is essential to optimize stencil aspect ratio, area ratio, and ultimately, SMT assembly yield and reliability.
FAQ
1. What is the ideal SMT stencil aspect ratio for good solder paste release?
The industry standard recommends an aspect ratio greater than 1.5 to ensure efficient solder paste transfer from the stencil aperture to the PCB pad[1][5].
2. How does stencil material affect aperture wall smoothness?
Materials like electro-polished stainless steel have smoother aperture walls compared to standard stainless steel, reducing solder paste adhesion and improving print consistency[2].
3. Can thinner stencil materials improve aspect ratio?
Yes, thinner but mechanically strong materials increase the aspect ratio for a given aperture width, enhancing solder paste release and print quality[3].
4. Why is area ratio important alongside aspect ratio?
Area ratio accounts for both aperture opening and wall surface area, providing a more accurate prediction of paste release efficiency, especially for non-rectangular apertures[1][4].
5. How do manufacturing processes interact with stencil materials?
Laser cutting combined with electro-polishing yields precise apertures with smooth walls, enabling lower aspect ratios and better print performance than chemical etching, which struggles below 1.5 aspect ratio[1][2].
Citations:
[1] https://www.qualiecocircuits.co.nz/stencil-technology-other-aspects.htm
[2] https://www.ipc.org/system/files/technical_resource/E6&S35_03.pdf
[3] https://fctsolder.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/123387-20515.solder-paste-stencil-printing.pdf
[4] https://pcbpit.com/smt-stencil-a-comprehensive-guide/
[5] https://smtnet.com/library/files/upload/SMT%20STENCIL%20DESIGN.pdf
[6] https://www.circuitinsight.com/pdf/Effect_Area_Shape_Area_Ratio_Solder_Paste_Printing_Performance_smta.pdf
[7] https://www.ipc.org/system/files/technical_resource/E38&S12-02%20-%20Chrys%20Shea.pdf
[8] https://blueringstencils.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/What-Is-Area-Ratio-8-24-23.pdf
[9] https://www.surfacemountprocess.com/a-guide-to-effective-stencil-design.html
[10] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bja7dXezDyo
[11] https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/baztech/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-article-BAT5-0036-0017/c/httpwww_bg_utp_edu_plartme20nr12009me12009steplewski.pdf
[12] https://smartsmttools.com/thicknessofsmtstencils/
[13] https://www.indium.com/blog/formula-for-area-ratio-of-elongated-d.php
[14] https://www.multi-circuit-boards.eu/en/pcb-design-aid/smd-stencils.html
[15] https://app.lpkfusa.com/articles/stencil/Conquering%20SMT%20Stencil%20Challenges%202009-03.pdf
[16] https://smtnet.com/Forums/index.cfm?fuseaction=view_thread&CFApp=1&Thread_ID=5792
[17] https://www.ipc.org/system/files/technical_resource/E10&S33_01.pdf
[18] https://www.eevblog.com/forum/manufacture/stencil-apertures/
[19] https://www.7pcb.com/blog/design-principles-stencil-aperatures
[20] https://www.circuitinsight.com/pdf/impact_stencil_quality_technology_solder_paste_printing_performance_smta.pdf




















