Content Menu
● Introduction to SMT Stencils
>> Key Functions of SMT Stencils
● Challenges in SMT Stencil Design
>> Dual Thickness Stencils
>> Benefits of Dual Thickness Stencils
● Design Considerations for Dual Thickness Stencils
>> Manufacturing Techniques
● Applications of Dual Thickness Stencils
>> Mixed Technology Assemblies
>> High-Density PCBs
● Optimization Techniques for SMT Stencils
>> Nano-Coating
>> Custom Aperture Designs
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the primary advantage of using dual thickness stencils in SMT assembly?
>> 2. How do dual thickness stencils improve production efficiency?
>> 3. What materials are commonly used for dual thickness stencils?
>> 4. What design considerations are crucial for dual thickness stencils?
>> 5. Can nano-coatings enhance the performance of dual thickness stencils?
● Citations:
The Surface Mount Technology (SMT) process is a cornerstone of modern electronics manufacturing, enabling the production of smaller, faster, and more efficient electronic devices. A crucial component in this process is the SMT stencil, which plays a vital role in applying solder paste onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). One of the innovative solutions to optimize the SMT process is the use of dual thickness stencils. These stencils allow for the simultaneous printing of different solder paste volumes, catering to the diverse needs of various components on a single PCB.
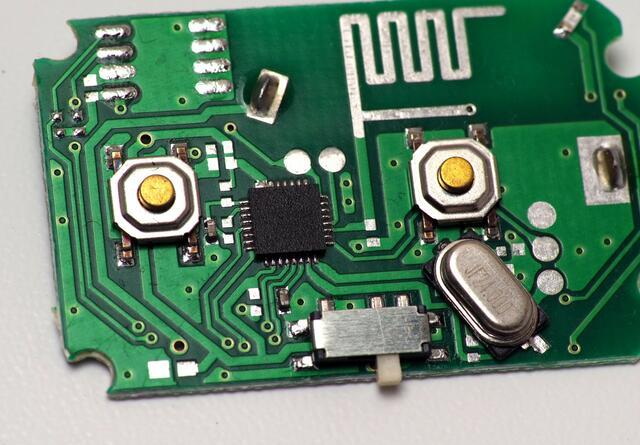

Introduction to SMT Stencils
SMT stencils are thin metal sheets, typically made of stainless steel or nickel alloys, with laser-cut apertures that correspond to the solder pad locations on a PCB. The choice of stencil material and design is critical for ensuring optimal solder paste deposition and minimizing defects. Stainless steel is the most common material due to its durability and cost-effectiveness, while nickel stencils offer smoother aperture walls for improved paste release[4][7].
Key Functions of SMT Stencils
1. Solder Paste Deposition: SMT stencils enable precise application of solder paste onto PCB pads, ensuring the right amount of solder for each component.
2. Consistency: Stencils maintain consistency in solder paste volume and shape across multiple PCBs, reducing defects and improving product quality.
3. Efficiency: Automated solder paste application saves time and increases production efficiency compared to manual methods[4].
Challenges in SMT Stencil Design
One of the primary challenges in SMT stencil design is accommodating components with varying solder paste volume requirements. Conventional stencils may struggle to provide sufficient paste for larger components while maintaining precision for smaller ones. This is where dual thickness stencils come into play, offering a solution by allowing different thicknesses within a single stencil.
Dual Thickness Stencils
Dual thickness stencils are designed to address the issue of varying solder paste volume requirements. These stencils have different thicknesses in different areas, allowing for more precise control over solder paste deposition. For example, thicker areas can be used for larger components or through-hole components that require more solder paste, while thinner areas cater to smaller surface mount components like 0201s or microBGAs[1][9].
Benefits of Dual Thickness Stencils
1. Flexibility: Dual thickness stencils can accommodate a wide range of components on a single PCB, reducing the need for multiple stencils.
2. Efficiency: They streamline the production process by minimizing the number of stencil changes required during manufacturing.
3. Cost-Effectiveness: By reducing the need for multiple stencils and minimizing waste, dual thickness stencils can lower production costs.
Design Considerations for Dual Thickness Stencils
When designing dual thickness stencils, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance:
1. Component Variety: The stencil must accommodate the diverse solder paste volume requirements of different components.
2. Stencil Material: The choice of material affects durability and paste release. Fine Grain Stainless Steel is often preferred for its smooth aperture walls[2].
3. Aperture Design: Aperture size and shape must be optimized for each component type to ensure proper solder paste deposition[4].
4. Aspect Ratio: The width of the aperture divided by the stencil thickness should meet minimum requirements to prevent clogging[6].
5. Area Ratio: A higher area ratio generally results in better paste release, with a minimum recommended ratio of 0.66[7].
Manufacturing Techniques
Dual thickness stencils can be manufactured using a combination of laser cutting and CNC milling. Laser cutting provides precise aperture geometries, while CNC milling ensures smooth transitions between different thicknesses[9].
Applications of Dual Thickness Stencils
Dual thickness stencils are particularly useful in assemblies that require mixed technologies, such as SMT and through-hole components, or in applications where components have significantly different solder paste requirements.
Mixed Technology Assemblies
In assemblies combining SMT and through-hole components, dual thickness stencils can efficiently provide the necessary solder paste volumes for both types of components. This is especially beneficial in processes like "Pin in Paste" or "Intrusive Reflow," where large solder paste volumes are required for through-hole components[1][5].
High-Density PCBs
For high-density PCBs with a mix of large and small components, dual thickness stencils ensure that each component receives the appropriate amount of solder paste, improving overall assembly quality and reducing defects.
Optimization Techniques for SMT Stencils
To further enhance the performance of dual thickness stencils, several optimization techniques can be employed:
Nano-Coating
Applying a nano-coating to the stencil surface improves paste release and reduces the need for frequent cleaning. This treatment enhances the stencil's hydrophobic properties, making it easier for solder paste to separate from the aperture walls[2][7].
Custom Aperture Designs
For challenging components or unique PCB layouts, custom aperture designs can be implemented to optimize paste deposition. This may include modified shapes or specialized patterns to address specific printing requirements[7].
Conclusion
Dual thickness stencils offer a versatile solution for optimizing the SMT process by accommodating diverse solder paste volume requirements on a single PCB. By understanding the design considerations and benefits of these stencils, manufacturers can improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the quality of their electronic assemblies.
FAQ
1. What is the primary advantage of using dual thickness stencils in SMT assembly?
The primary advantage of dual thickness stencils is their ability to accommodate a wide range of components on a single PCB, providing the necessary solder paste volumes for both large and small components without the need for multiple stencils.
2. How do dual thickness stencils improve production efficiency?
Dual thickness stencils improve production efficiency by reducing the number of stencil changes required during manufacturing, thus streamlining the production process and minimizing downtime.
3. What materials are commonly used for dual thickness stencils?
Dual thickness stencils are typically made from stainless steel or nickel alloys. Fine Grain Stainless Steel is often preferred for its durability and smooth aperture walls.
4. What design considerations are crucial for dual thickness stencils?
Crucial design considerations include component variety, stencil material, aperture design, aspect ratio, and area ratio. Each of these factors must be optimized to ensure proper solder paste deposition and prevent defects.
5. Can nano-coatings enhance the performance of dual thickness stencils?
Yes, nano-coatings can enhance the performance of dual thickness stencils by improving paste release and reducing the need for frequent cleaning. This results in better print quality and longer stencil lifespan.
Citations:
[1] https://www.ipc.org/system/files/technical_resource/E10&S33_01.pdf
[2] https://www.ipc.org/system/files/technical_resource/E38&S12-02%20-%20Chrys%20Shea.pdf
[3] https://www.stencils.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Tecan-stencils-handbook_WEB_compressed.pdf
[4] https://rigidflexpcb.org/comprehensive-guide-to-smt-stencils/
[5] https://www.circuitinsight.com/pdf/two_print_stencil_systems_ipc.pdf
[6] https://smartsmttools.com/thicknessofsmtstencils/
[7] https://pcbpit.com/smt-stencil-a-comprehensive-guide/
[8] https://electronics.stackexchange.com/questions/214248/solder-paste-stencil-application
[9] https://beamon.com/multi-level-stencils.php
[10] https://www.macdermidalpha.com/sites/default/files/2021-09/ALPHA%20SMT%20Troubleshooting%20Guide%20EN%2001Jun20%20BR_0.pdf
[11] http://www.qualiecocircuits.co.nz/stencil-technology-other-aspects.htm
[12] https://www.surfacemountprocess.com/a-guide-to-effective-stencil-design.html
[13] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/smt-stencil-preparation-tips-tricks-design-software-alex-akulin-z2aif
[14] https://jlcpcb.com/blog/why-pcb-stencils-are-key-to-high-quality-smt-assembly
[15] https://www.ipc.org/system/files/technical_resource/E10&S28_01.pdf
[16] https://www.globalwellpcba.com/how-to-choose-a-smt-stencil/
[17] https://www.reddit.com/r/AskElectronics/comments/1230pfu/pcb_stencil_thickness/
[18] https://electronics.stackexchange.com/questions/301689/stencil-at-home-with-extremely-small-parts
[19] https://www.reddit.com/r/AskElectronics/comments/pk71xl/how_to_design_pcb_stencil_to_optimize_solder/
[20] https://www.multi-circuit-boards.eu/en/pcb-design-aid/smd-stencils.html
[21] https://www.pcbcart.com/article/content/measures-to-improve-smt-assembly-quality.html
[22] https://www.eevblog.com/forum/manufacture/solder-paste-mask-sizing/
[23] https://forum.kicad.info/t/pcb-land-pattern-layout-vs-solder-paste-stencil/411
[24] https://www.pentalogix.com/products/framed-smt-stencils
[25] https://groups.io/g/UKMicrowaves/topic/3d_printing_smt_stencils_from/105285656
[26] https://www.7pcb.com/blog/design-principles-stencil-aperatures
[27] https://www.nextpcb.com/blog/smt-stencil
[28] https://www.venture-pcba.com/smt-stencil/
[29] https://www.7pcb.com/blog/stencil-thickness-calculations
[30] https://mpe.researchmfg.com/smt-qa/
[31] https://www.circuitinsight.com/programs/49428.html
[32] https://resources.pcb.cadence.com/blog/jbj-solder-paste-and-stencil-considerations-for-double-sided-printed-circuit-boards
[33] https://e2e.ti.com/support/power-management-group/power-management/f/power-management-forum/1036581/lm2586-solder-paste-stencil-design-for-to-263-7-ddpak
[34] https://tecan.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/1-an-introduction-to-SMT-and-Stencils-compressed.pdf
[35] https://preserve.lehigh.edu/system/files/derivatives/coverpage/390477.pdf
[36] https://www.circuitinsight.com/pdf/improve_smt_assembly_yields_root_cause_analysis_ipc.pdf
[37] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/creating-optimal-smt-stencils-joshua-lawson




















