Content Menu
● Introduction to SMT Stencil Printers
>> Benefits of SMT Stencil Printers
● Optimizing Stencil Design
>> Key Considerations in Stencil Design
>> Advanced Stencil Materials and Techniques
● Optimizing Printer Settings
>> Key Printer Settings
>> Advanced Printer Features
● Process Control and Quality Assurance
>> Process Control Measures
>> Implementing Quality Control Systems
>> Advanced Quality Assurance Techniques
>> Enhancing Production Efficiency
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What is the primary function of a PCB stencil in SMT manufacturing?
>> 2. How does stencil thickness affect solder paste application?
>> 3. What factors influence the choice of solder paste viscosity in stencil printing?
>> 4. Why is stencil cleaning important in the solder paste printing process?
>> 5. How does the use of nanocoatings improve stencil performance?
● Citations:
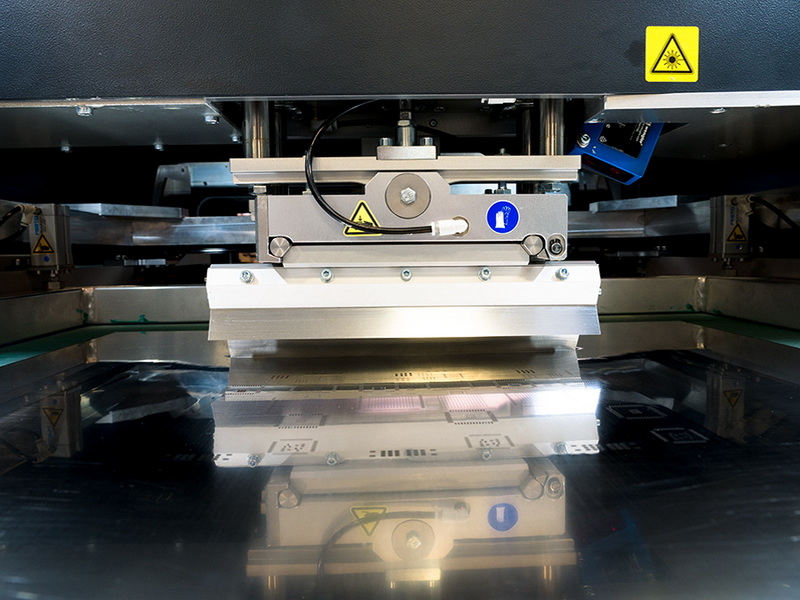
Optimizing solder paste application is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs) in surface mount technology (SMT) manufacturing. The use of stencil printers has become a standard practice in this field due to their ability to accurately and efficiently apply solder paste onto PCBs. In this article, we will explore the methods and techniques for optimizing solder paste application using a stencil printer, focusing on key factors such as stencil design, printer settings, and process control.

Introduction to SMT Stencil Printers
SMT stencil printers are automated machines designed to apply solder paste to PCBs using stencils. These printers offer high precision and consistency, making them ideal for large-scale production environments. They operate by aligning the stencil over the PCB, applying solder paste through the stencil's apertures, and then removing the stencil to leave a precise layer of paste on the board's pads.
Benefits of SMT Stencil Printers
- Efficiency and Cost Reduction: By automating the solder paste printing process, these printers significantly increase production efficiency and reduce labor costs.
- Precision and Consistency: They ensure precise placement of solder paste, minimizing the risk of short circuits or faulty connections and maintaining uniformity across multiple PCBs.
- Speed: Stencil printing is fast and suitable for high-volume production, making it a preferred method in industrial applications.
Optimizing Stencil Design
The design of the stencil is critical for achieving optimal solder paste application. Factors such as stencil thickness, aperture size, and material selection must be carefully considered based on the PCB layout and component types.
Key Considerations in Stencil Design
- Stencil Thickness: The thickness affects the volume of solder paste applied. Thicker stencils are used for components requiring more solder, while thinner stencils are suitable for smaller components.
- Aperture Size and Shape: Apertures should match the pad sizes on the PCB to ensure the correct amount of solder paste is applied. Specialized apertures may be needed for certain components like BGAs or through-hole components.
- Material Selection: Common materials include stainless steel and laser-cut stencils. The choice depends on the desired level of precision and durability.
Advanced Stencil Materials and Techniques
- Nano-Coated Stencils: These stencils reduce paste residue and improve print quality by minimizing underwipe and enhancing paste release.
- Step Stencils: Used for components with varying paste requirements, step stencils allow for different thicknesses in a single stencil.
- Framed vs. Frameless Stencils: Framed stencils provide better support and alignment, while frameless stencils offer flexibility and cost savings.
Optimizing Printer Settings
Printer settings play a crucial role in achieving high-quality solder paste application. These settings include print speed, squeegee pressure, and snap-off distance.
Key Printer Settings
- Print Speed: Faster speeds require higher viscosity solder paste and proper stencil design to maintain print quality. Typical high-speed printing ranges from 4 to 8 inches per second.
- Squeegee Pressure: Proper pressure ensures uniform paste application without excessive paste squeeze-out. The pressure should be adjusted based on the solder paste's rheology.
- Snap-off Distance: This setting affects how the stencil separates from the PCB, influencing the paste's release and preventing smearing.
Advanced Printer Features
- Dual-Squeegee Systems: These systems allow for better paste distribution and reduced smearing by using two squeegees in sequence.
- Vision Alignment Systems: These systems enhance stencil alignment accuracy, ensuring precise paste application even on complex PCBs.
Process Control and Quality Assurance
Maintaining consistent process conditions and monitoring quality are essential for optimizing solder paste application.
Process Control Measures
- Temperature and Humidity Control: These environmental factors can affect solder paste viscosity and performance. Maintaining a stable environment ensures consistent print quality.
- Stencil Cleaning and Maintenance: Regular cleaning prevents clogging and ensures precise paste application. Nanocoatings can improve stencil performance by reducing underwipe frequency.
- Quality Inspection: Regular inspection of printed PCBs helps identify issues early, reducing rework and improving overall yield.
Implementing Quality Control Systems
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): AOI systems inspect PCBs post-printing to detect defects such as insufficient or excessive solder paste.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC involves monitoring and controlling process variables to maintain consistency and prevent deviations.
Advanced Quality Assurance Techniques
- Machine Learning for Predictive Maintenance: Implementing machine learning algorithms can predict potential issues in the printing process, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Real-Time Monitoring Systems: These systems provide immediate feedback on print quality, enabling quick adjustments to printer settings and improving overall efficiency.
Enhancing Production Efficiency
- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Applying lean principles helps eliminate waste and streamline production workflows, further optimizing the solder paste application process.
- Operator Training Programs: Well-trained operators can optimize printer settings and troubleshoot issues more effectively, contributing to higher quality and efficiency.
Conclusion
Optimizing solder paste application using a stencil printer involves careful consideration of stencil design, printer settings, and process control. By focusing on these areas, manufacturers can improve the efficiency, precision, and reliability of their PCB assembly processes. The use of advanced materials and technologies, such as nanocoatings and precision stencil manufacturing, further enhances the quality and consistency of solder paste application.
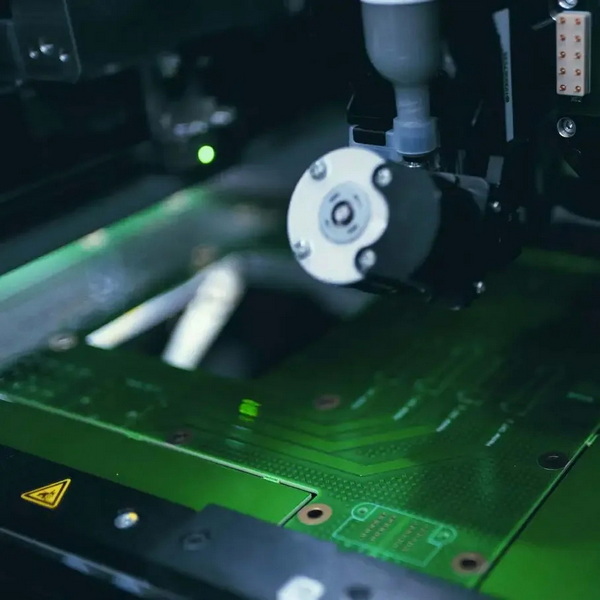

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary function of a PCB stencil in SMT manufacturing?
A PCB stencil is used to apply a precise amount of solder paste to specific locations on a PCB, ensuring accurate and consistent solder joints. This process is crucial for the reliability and performance of electronic assemblies.
2. How does stencil thickness affect solder paste application?
Stencil thickness determines the volume of solder paste applied to the PCB. Thicker stencils deposit more paste, suitable for larger components, while thinner stencils are used for smaller components requiring less solder.
3. What factors influence the choice of solder paste viscosity in stencil printing?
The choice of solder paste viscosity is influenced by print speed, squeegee pressure, and stencil design. Higher viscosity pastes are often used at faster print speeds to maintain quality.
4. Why is stencil cleaning important in the solder paste printing process?
Stencil cleaning is crucial to prevent clogging and ensure precise paste application. Regular cleaning maintains the stencil's performance and reduces defects in solder joints.
5. How does the use of nanocoatings improve stencil performance?
Nanocoatings improve stencil performance by keeping the PCB side of the stencil clean, reducing underwipe frequency, and enhancing print definition. This results in better solder paste application quality and consistency.
Citations:
[1] https://www.smtfactory.com/Optimizing-Solder-Paste-Placement-Exploring-The-Benefits-of-SMT-Stencil-Printers-id40563586.html
[2] https://www.bestpcbs.com/blog/2025/02/what-is-a-smt-stencil-printer-pcb-prototype/
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stencil_printing
[4] https://www.ipc.org/system/files/technical_resource/E38&S12-02%20-%20Chrys%20Shea.pdf
[5] https://swimbi.com/screen-printing-for-pcb/
[6] https://resources.altium.com/p/stencil-for-pcb
[7] https://www.aimsolder.com/technical-center/solder-paste-print-setting-recommendations/
[8] https://www.pcbelec.com/how-to-use-pcb-stencil.html
[9] https://www.instructables.com/SMT-Solder-Paste-Stencil-Production-Jig-using-a-/
[10] https://imapsource.scholasticahq.com/api/v1/articles/74547-innovations-in-soldering-materials-and-optimization-of-solder-paste-printing-and-inspection-parameters-for-system-in-package-assembly.pdf




















