Content Menu
● Introduction to Automatic SMD Machines
>> Key Features of Automatic SMD Machines
● Advantages of Using Automatic SMD Machines in High-Volume Production
>> Enhanced Product Quality and Consistency
>> Faster Time to Market
>> Cost Efficiency
● Operational Processes of Automatic SMD Machines
● Role of Automation in High-Volume Production
>> Case Study: Yamaha's Automated SMT Line
● Challenges and Future Developments
>> Future Trends in SMD Assembly
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What is the primary advantage of using automatic SMD machines in high-volume production?
>> 2. How do automatic SMD machines enhance product quality?
>> 3. What role does automation play in reducing production costs?
>> 4. Can automatic SMD machines handle complex components?
>> 5. How does automation impact the time-to-market for electronic products?
In the realm of modern electronics manufacturing, Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) have become the cornerstone of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assembly. The efficiency and precision required in high-volume production have led to the widespread adoption of automatic SMD machines. These machines are designed to handle the demands of mass production with speed, accuracy, and reliability. This article delves into the capabilities of automatic SMD machines in high-volume production, exploring their advantages, operational processes, and the role they play in ensuring product quality and consistency.
Introduction to Automatic SMD Machines
Automatic SMD machines are integral to the Surface Mount Technology (SMT) process, which involves the placement of components onto a PCB using automated pick-and-place machines. These machines are capable of placing thousands of components per hour, making them ideal for high-volume production. The use of SMDs in conjunction with automated assembly processes significantly reduces production time and costs compared to traditional through-hole components.
Key Features of Automatic SMD Machines
1. High-Speed Placement: Automatic SMD machines can place up to 28,000 components per hour, depending on the model and configuration. This high-speed capability is crucial for meeting the demands of high-volume production.
2. Precision and Accuracy: These machines ensure precise placement of components, reducing errors and defects. Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems are often integrated to verify component placement before the soldering process.
3. Flexibility in Component Handling: Automatic SMD machines can handle a wide range of component sizes, from small packages like .01005 to larger components such as BGAs and flip-chip devices.
4. Efficient Production Lines: By automating the assembly process, manufacturers can achieve faster production cycles and quicker time-to-market for their products. This is particularly beneficial in the rapidly evolving electronics industry.
Advantages of Using Automatic SMD Machines in High-Volume Production
Enhanced Product Quality and Consistency
The automated nature of SMD machines ensures that each PCB is assembled with uniform quality. By minimizing human intervention, these machines prevent errors and inconsistencies that can arise from manual assembly processes. This results in reliable and consistent products, which is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Faster Time to Market
High-volume PCB assembly using automatic SMD machines allows manufacturers to produce large quantities quickly. This capability enables companies to respond rapidly to market demands and launch products sooner than competitors. The fast turnaround times and short lead times provided by automated production lines are critical advantages in the competitive electronics sector.
Cost Efficiency
SMDs are generally less expensive than through-hole components due to their smaller size and simpler manufacturing process. Additionally, the automated assembly process reduces labor costs significantly, as fewer manual interventions are required. This makes SMD-based manufacturing highly cost-effective for mass-market products.
Operational Processes of Automatic SMD Machines
The operational process of automatic SMD machines involves several key steps:
1. Design and Machine Programming: The PCB design is created using software, and the machine is programmed with CAD-generated data to ensure accurate component placement.
2. Solder Paste Application: Solder paste is applied to the PCB pads using a stencil printer. This process is critical and must be done precisely to avoid defects.
3. Component Placement: The pick-and-place machine places SMD components onto the PCB. This is where the high-speed and precision capabilities of automatic SMD machines are most evident.
4. Inspection and Soldering: Automated optical inspection (AOI) verifies component placement before the PCB is passed through a reflow oven to solder the components in place.
5. Final Inspection and Packaging: After soldering, the PCBs undergo final inspections and are packaged for distribution.
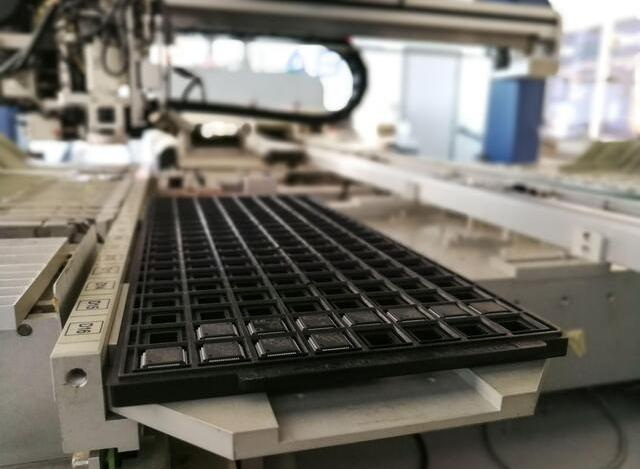

Role of Automation in High-Volume Production
Automation plays a pivotal role in achieving high-volume production efficiently. By integrating fully automated setup lines, manufacturers can minimize downtime and maximize productivity. Features like autoloading feeders and 3D inspection systems further enhance efficiency by reducing component replenishment time and defect rates.
Case Study: Yamaha's Automated SMT Line
Yamaha's approach to automation includes the use of autoloading feeders, 3D AOI, and fully automated changeovers. These features have significantly reduced setup times and defect rates, allowing for non-stop operation with minimal human intervention. The introduction of such automation has doubled production capacity without increasing space or labor requirements.
Challenges and Future Developments
Despite the advantages of automatic SMD machines, there are challenges to consider:
- Initial Investment: Implementing automated SMT lines requires a significant upfront investment in machinery and technology.
- Component Availability: Ensuring a steady supply of components is crucial for maintaining production efficiency.
- Technological Advancements: Staying updated with the latest advancements in automation and inspection technology is essential for maintaining competitiveness.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements in automation efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness. The integration of AI and IoT technologies could enhance predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, further optimizing production processes.
Future Trends in SMD Assembly
1. Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Future developments may include the integration of AI and machine learning to improve predictive maintenance, optimize production workflows, and enhance defect detection.
2. Increased Use of Robotics: Robotics will play a more significant role in handling delicate components and performing tasks that require precision beyond current capabilities.
3. Sustainability Initiatives: Manufacturers are likely to focus on sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and energy consumption, to align with environmental regulations and consumer expectations.
4. Miniaturization and Complexity: As devices become smaller and more complex, automatic SMD machines will need to adapt to handle even smaller components and more intricate designs.
5. Global Supply Chain Optimization: With the rise of global supply chains, manufacturers will need to ensure that their automated systems can integrate seamlessly with international suppliers and distributors.
Conclusion
Automatic SMD machines are well-suited for handling high-volume production due to their speed, precision, and ability to ensure consistent product quality. The advantages of using these machines include faster time-to-market, cost efficiency, and enhanced product reliability. As the electronics industry continues to evolve, the role of automation in SMT assembly will remain crucial for meeting the demands of mass production.

FAQs
1. What is the primary advantage of using automatic SMD machines in high-volume production?
The primary advantage is the ability to produce large quantities quickly and accurately, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing production costs.
2. How do automatic SMD machines enhance product quality?
Automatic SMD machines enhance product quality by minimizing human error and ensuring precise component placement, which results in reliable and consistent PCBs.
3. What role does automation play in reducing production costs?
Automation reduces production costs by minimizing labor requirements, improving efficiency, and reducing material waste through precise component placement and soldering processes.
4. Can automatic SMD machines handle complex components?
Yes, automatic SMD machines are capable of handling complex components such as BGAs and flip-chip devices, making them versatile for a wide range of PCB assembly needs.
5. How does automation impact the time-to-market for electronic products?
Automation significantly reduces the time-to-market by enabling rapid production cycles and short lead times, allowing companies to launch products sooner and respond quickly to market demands.




















