Content Menu
● Understanding the Role of Solder Paste in the SMT PCB Process
>> Functions of Solder Paste:
● The Solder Paste Application Process in SMT
>> Key Steps in Solder Paste Application:
● Why Is Solder Paste Application Critical?
>> 1. Ensures Proper Solder Joint Formation
>> 2. Maintains Component Placement Accuracy
>> 3. Controls the Rheological Properties for Optimal Printing
>> 4. Influences Reflow Soldering Performance
>> 5. Directly Impacts Yield and Reliability
● Factors Affecting Solder Paste Application Quality
>> Solder Paste Storage and Handling
>> Stencil Design and Condition
>> Printing Parameters
>> Paste Composition
● Best Practices for Effective Solder Paste Application in SMT PCB Process
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the role of solder paste in the SMT PCB process?
>> 2. Why is the viscosity of solder paste important during application?
>> 3. How does improper solder paste application affect PCB assembly?
>> 4. What are the best storage practices for solder paste?
>> 5. How can solder paste application be inspected in the SMT process?
● Citations:
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has become the cornerstone of modern electronic manufacturing, enabling the production of smaller, faster, and more reliable devices. At the heart of the SMT PCB process lies the solder paste application, a step that is both delicate and decisive for the success of the entire assembly. This article explores why solder paste application is critical in the SMT process, detailing its role, the factors influencing its effectiveness, and best practices to ensure high-quality PCB assemblies.
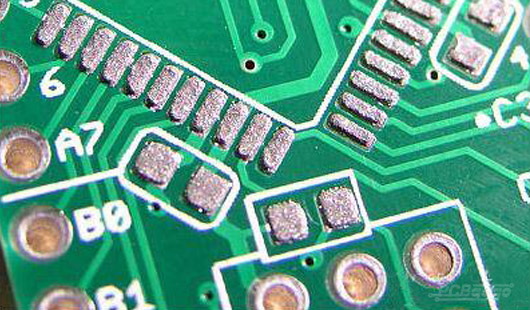
Understanding the Role of Solder Paste in the SMT PCB Process
Solder paste is a specialized material used in the SMT process to attach surface mount devices (SMDs) onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). It is a mixture of fine solder alloy particles suspended in a flux medium, which serves multiple functions during assembly[2][10].
Functions of Solder Paste:
- Electrical and Mechanical Connection: Solder paste forms the electrical pathways and mechanical bonds between the PCB pads and SMD leads after reflow soldering[3][5].
- Temporary Adhesive: Before reflow, solder paste holds the components in place on the PCB, ensuring accurate placement during handling[5].
- Oxidation Removal and Protection: The flux within the paste cleans oxidation from metal surfaces and protects components during heating[5].
Without proper solder paste application, these functions cannot be reliably achieved, leading to defects such as poor electrical connectivity, component misalignment, and soldering failures.
The Solder Paste Application Process in SMT
The application of solder paste is a precise process that involves depositing the correct amount of paste onto each pad of the PCB where components will be placed. The most common method is stencil printing, which uses a metal stencil aligned with the PCB pads to transfer solder paste accurately[1][8].
Key Steps in Solder Paste Application:
1. Stencil Preparation and Alignment: A stencil with apertures matching the PCB pads is aligned precisely over the board.
2. Paste Printing: A squeegee forces solder paste through the stencil openings, depositing a controlled volume of paste onto the pads[1][9].
3. Component Placement: Surface mount components are placed onto the paste deposits, which act as a temporary adhesive[5].
4. Reflow Soldering: The PCB assembly is heated in a reflow oven, melting the solder particles to form permanent joints[8].
The accuracy of paste application directly affects the quality of solder joints and component placement.
Why Is Solder Paste Application Critical?
1. Ensures Proper Solder Joint Formation
The volume and placement of solder paste determine the size and shape of the solder joint after reflow. Too little paste can cause weak or open joints, while too much can lead to bridging and short circuits[1][7]. Proper paste application ensures:
- Adequate solder volume for reliable electrical and mechanical connections.
- Prevention of defects like solder bridging, tombstoning, and insufficient wetting.
2. Maintains Component Placement Accuracy
Solder paste acts as a tacky adhesive that holds components in place during handling and reflow. Inaccurate paste printing can result in components shifting or misaligning, causing assembly defects and rework[5].
3. Controls the Rheological Properties for Optimal Printing
The viscosity and rheology of solder paste are crucial for smooth printing and transfer through the stencil. Paste must have the right flow characteristics to fill stencil apertures without smearing or collapsing[9]. Incorrect paste viscosity can cause printing defects such as:
- Insufficient paste deposition.
- Smearing or bridging.
- Poor release from the stencil.
4. Influences Reflow Soldering Performance
The composition and uniformity of solder paste affect how it melts and wets the PCB pads and component leads during reflow. Properly mixed and applied paste ensures consistent melting behavior, reducing solder balls, voids, and cold joints[4][8].
5. Directly Impacts Yield and Reliability
Since solder paste application is one of the earliest steps in the SMT PCB process, errors here propagate through the assembly line, increasing scrap rates, rework, and production costs. Consistent paste application improves yield and long-term reliability of electronic products[3][6].

Factors Affecting Solder Paste Application Quality
Solder Paste Storage and Handling
Solder paste must be stored refrigerated (2-8°C) to preserve its chemical integrity. Before use, it must be thawed slowly to room temperature and thoroughly mixed to ensure homogeneity[4]. Improper handling leads to:
- Changes in viscosity.
- Flux degradation.
- Solder balling during reflow.
Stencil Design and Condition
Stencil aperture size, shape, and thickness influence paste volume. Worn or dirty stencils cause inconsistent paste deposits[1][9].
Printing Parameters
Squeegee speed, pressure, and angle must be optimized for each paste and stencil combination to ensure consistent printing[1].
Paste Composition
Different solder alloys (lead-based or lead-free), flux types, and particle sizes affect paste behavior and reflow characteristics[6][8].
Best Practices for Effective Solder Paste Application in SMT PCB Process
- Use High-Quality Solder Paste: Select paste with appropriate alloy composition and flux type for the application[6].
- Maintain Proper Storage: Refrigerate paste and follow recommended thawing and mixing procedures[4].
- Optimize Stencil Design: Use stencils with correct aperture dimensions and maintain cleanliness[1].
- Control Printing Parameters: Adjust squeegee speed, pressure, and stencil separation carefully[9].
- Regular Inspection: Use inspection tools like solder paste inspection (SPI) systems to verify paste volume and placement before component placement[8].
Conclusion
Solder paste application is a critical step in the SMT PCB process that significantly influences the quality, reliability, and yield of electronic assemblies. It serves as the foundation for creating strong electrical and mechanical connections between components and the PCB. Precise control over solder paste volume, placement, and properties ensures proper solder joint formation and component stability during reflow soldering. Neglecting this step can lead to a cascade of defects, increased production costs, and compromised product performance. Therefore, mastering solder paste application through proper handling, equipment setup, and process control is essential for successful SMT manufacturing.
FAQ
1. What is the role of solder paste in the SMT PCB process?
Solder paste acts as both an adhesive and soldering medium, enabling the attachment of surface mount components to PCB pads and forming electrical and mechanical connections after reflow soldering[2][5].
2. Why is the viscosity of solder paste important during application?
Viscosity affects how well solder paste flows through the stencil apertures and adheres to the PCB pads. Proper viscosity ensures accurate paste volume deposition without smearing or bridging[9].
3. How does improper solder paste application affect PCB assembly?
Incorrect paste volume or placement can cause defects such as solder bridging, open joints, tombstoning, and component misalignment, leading to increased rework and lower yield[1][7].
4. What are the best storage practices for solder paste?
Solder paste should be refrigerated at 2-8°C and thawed slowly to room temperature before use. It must be mixed thoroughly to maintain homogeneity and performance[4].
5. How can solder paste application be inspected in the SMT process?
Solder Paste Inspection (SPI) systems use optical or laser scanning to measure paste volume and placement accuracy after printing, helping identify defects early in the assembly process[8].
Citations:
[1] https://www.surfacemountprocess.com/solder-paste-printing-process.html
[2] https://www.acceleratedassemblies.com/blog/solder-paste-and-its-application-in-surface-mount-technology
[3] https://www.gmsww.com/news/your-solder-paste-process-really-important
[4] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/importance-solder-paste-handling-smt-assembly-sthlpcba-t3g9c
[5] https://www.technotronix.us/pcbblog/how-does-the-solder-paste-play-a-significant-role-in-pcb-smt-assembly/
[6] https://www.mainpcba.com/smt-solder-paste/
[7] https://www.superengineer.net/blog/soldering-smt-paste
[8] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-does-solder-paste-play-significant-role-pcb-smt-assembly-rayming-kwexc
[9] https://www.nexpcb.com/blog/basics-of-smt-solder-paste-printing
[10] https://www.electronicsandyou.com/blog/solder-paste-and-its-application-in-smt.html
[11] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3h9lytz0ftk




















