Content Menu
● Introduction
● What is an SMT Production Line?
● The Importance of SMT Production Lines
>> Increased Production Speed
>> Enhanced Precision
>> Flexibility and Scalability
>> Cost Efficiency
● Key Components of an SMT Production Line
● Advantages of Using an SMT Production Line
● Challenges in SMT Production Lines
● Future Trends in SMT Technology
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What does "SMT" stand for?
>> 2. How does an SMT production line improve efficiency?
>> 3. What are some common machines found in an SMT line?
>> 4. Why is precision important in PCB assembly?
>> 5. What future trends are expected in SMT technology?
Introduction
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the manufacturing of electronic devices, particularly in the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). An SMT production line plays a pivotal role in this process, allowing for high efficiency, precision, and scalability in PCB assembly. This article explores the significance of SMT production lines, their components, advantages, and the future of PCB assembly in the electronics industry.
What is an SMT Production Line?
An SMT production line refers to a series of automated machines and processes designed for assembling surface mount devices (SMDs) onto PCBs. The process involves several stages, each crucial for ensuring that electronic components are mounted accurately and efficiently. The main components of an SMT production line include:
- SMT Loader: Automatically loads PCBs onto the conveyor system.
- Solder Paste Printer: Applies solder paste to the PCB pads where components will be placed.
- Pick and Place Machine: Accurately places SMDs onto the solder paste.
- Reflow Oven: Melts the solder to create electrical connections between components and the PCB.
- SMT Unloader: Collects finished PCBs after soldering.
The Importance of SMT Production Lines
Increased Production Speed
One of the most significant advantages of SMT production lines is their ability to assemble thousands of components per hour. This high-speed production is essential for meeting the demands of modern electronics, where time-to-market is critical.
Enhanced Precision
SMT lines utilize advanced robotics and automation to ensure precise placement of components. This level of accuracy reduces the risk of defects and enhances overall product quality. Automated inspection systems further contribute to maintaining high standards by detecting errors before they propagate through the assembly process.
Flexibility and Scalability
Modern SMT production lines are designed to handle various component sizes and types, making them adaptable to different manufacturing needs. This flexibility allows manufacturers to switch between products with minimal downtime, accommodating changing market demands.
Cost Efficiency
By automating many aspects of the assembly process, SMT lines significantly reduce labor costs. Fewer manual interventions mean lower chances for human error, which can lead to material wastage. Additionally, the streamlined processes minimize the need for extensive storage space for semi-finished goods.
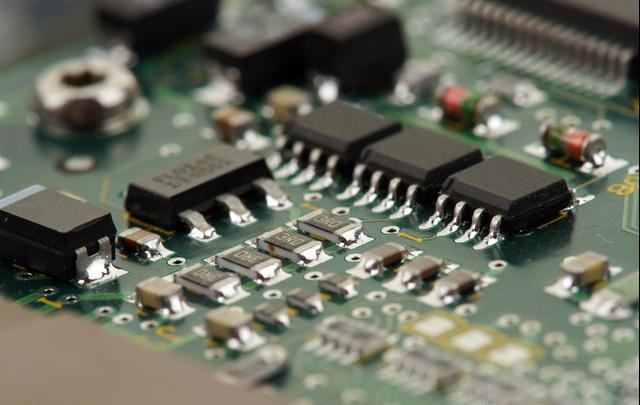
Key Components of an SMT Production Line
Understanding the various components that make up an SMT production line is crucial for appreciating its functionality:
1. Solder Paste Printer: This machine applies solder paste precisely onto designated areas of the PCB. The quality of this application is critical as it affects how well components adhere during soldering.
2. Pick and Place Machine: Often considered the heart of an SMT line, this machine uses robotic arms equipped with suction nozzles to pick components from reels and place them onto soldered pads on PCBs.
3. Reflow Oven: After placement, PCBs pass through a reflow oven where heat is applied in a controlled manner to melt solder paste and create permanent connections.
4. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Following reflow, AOI systems inspect PCBs for defects such as misaligned components or insufficient solder joints.
5. SMT Unloader: Finally, this machine collects completed PCBs from the line for packaging or further processing.
Advantages of Using an SMT Production Line
The benefits of implementing an SMT production line in PCB assembly are manifold:
- Higher Density Assembly: SMT allows for more compact designs by placing components directly on the surface of PCBs rather than through holes.
- Reduced Size and Weight: The compact nature of SMT components leads to lighter devices, which is particularly advantageous in portable electronics like smartphones and tablets.
- Improved Electrical Performance: Shorter interconnection lengths reduce parasitic effects, enhancing signal integrity and overall performance.
- Environmentally Friendly: SMT processes typically use less solder than traditional methods, resulting in lower material waste and energy consumption.
Challenges in SMT Production Lines
Despite their numerous advantages, SMT production lines also face challenges:
- Initial Setup Costs: The investment required for advanced machinery can be substantial, making it a barrier for smaller manufacturers.
- Complexity in Maintenance: Automated systems require regular maintenance and skilled technicians to ensure optimal performance.
- Component Variability: Different component types may require specific handling techniques or settings on machines, complicating production runs.
Future Trends in SMT Technology
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of SMT production lines:
- Industry 4.0 Integration: The incorporation of IoT (Internet of Things) technologies will enable smarter factories where machines communicate with each other for improved efficiency.
- AI-Powered Quality Control: Artificial intelligence will play a role in enhancing inspection processes by learning from past defects and predicting potential issues before they occur.
- Sustainability Focus: As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers will increasingly seek ways to reduce waste and energy consumption in their production processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an SMT production line is crucial for modern PCB assembly due to its ability to enhance efficiency, precision, and quality while reducing costs. As technology advances, these lines will continue to evolve, integrating new innovations that further streamline production processes. For manufacturers aiming to remain competitive in a fast-paced market, investing in an efficient SMT production line is not just beneficial; it is essential.

FAQ
1. What does "SMT" stand for?
*SMT stands for Surface Mount Technology*, which refers to a method used for mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs).
2. How does an SMT production line improve efficiency?
An SMT production line automates many steps involved in PCB assembly, allowing for faster component placement and reduced manual labor requirements.
3. What are some common machines found in an SMT line?
Common machines include solder paste printers, pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, automated optical inspection systems (AOI), and unloader systems.
4. Why is precision important in PCB assembly?
Precision ensures that components are correctly placed on PCBs without defects, which is critical for maintaining product quality and reliability.
5. What future trends are expected in SMT technology?
Future trends include greater integration with Industry 4.0 technologies, AI-powered quality control systems, and a focus on sustainability within manufacturing processes.




















