Content Menu
● The Evolution of Surface Mount Technology
● Benefits of Automation in SMT
● Key Automation Technologies in SMT
● Challenges in Implementing Automation
● Future Trends in Automation and SMT
● Conclusion
● Related Questions
>> 1. What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
>> 2. How does automation improve quality control in SMT?
>> 3. What are pick-and-place machines?
>> 4. What challenges do manufacturers face when implementing automation?
>> 5. What future trends are expected in automation within SMT?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has transformed the landscape of electronics manufacturing, enabling the efficient assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). One of the most significant advancements in this field is the integration of automation, which plays a crucial role in enhancing productivity, accuracy, and overall efficiency in SMT processes. This article delves into the various aspects of automation in SMT, exploring its benefits, challenges, and future trends.

The Evolution of Surface Mount Technology
SMT emerged in the 1960s as a method for mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of PCBs without the need for drilling holes. This innovation marked a significant departure from traditional through-hole technology, which required components to be inserted into holes drilled into the board. The rise of SMT allowed for greater component density, reduced manufacturing costs, and improved performance characteristics of electronic devices.
As SMT gained popularity throughout the 1980s and 1990s, manufacturers began to recognize its potential for automation. The introduction of automated pick-and-place machines revolutionized the assembly process by allowing for rapid and precise placement of components on PCBs. These machines can handle thousands of components per hour, significantly increasing production rates while minimizing human error.
Benefits of Automation in SMT
The integration of automation into SMT processes offers several key benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Automated systems streamline various stages of PCB assembly, from solder paste application to component placement and inspection. This efficiency translates to shorter production cycles and faster turnaround times.
- Enhanced Precision: Automation reduces the likelihood of human error during assembly. Automated machines equipped with advanced vision systems can accurately identify component positions and ensure precise placement on the PCB.
- Improved Quality Control: Automated inspection systems can detect defects such as misaligned components or soldering issues in real-time. This capability enhances quality control measures and ensures that only high-quality products reach the market.
- Cost Reduction: By minimizing labor costs and maximizing production efficiency, automation can significantly reduce overall manufacturing expenses. This cost-effectiveness is particularly beneficial in high-volume production environments.
- Scalability: Automated SMT lines can easily scale to accommodate varying production volumes. Manufacturers can adjust their operations based on demand without compromising quality or efficiency.
Key Automation Technologies in SMT
Several automation technologies are integral to modern SMT processes:
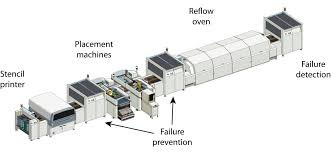
1. Pick-and-Place Machines: These machines are essential for placing surface-mounted components onto PCBs with high speed and accuracy. They utilize robotic arms and advanced vision systems to ensure precise component placement.
2. Solder Paste Printers: Automated solder paste printers apply solder paste to PCBs with precision, ensuring optimal amounts are deposited on each pad. This process is critical for creating reliable solder joints during reflow soldering.
3. Reflow Ovens: Automated reflow ovens heat PCBs with solder paste and components to create strong electrical connections. These ovens provide controlled heating profiles that ensure consistent results across batches.
4. Automated Inspection Systems: These systems use cameras and software algorithms to inspect PCBs for defects during various stages of assembly. They can identify issues such as solder bridges or misaligned components early in the process.
5. Data Analytics and AI: Advanced data analytics tools and artificial intelligence (AI) are increasingly being integrated into SMT processes. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and optimization of production workflows.
Challenges in Implementing Automation
While automation offers numerous advantages, there are challenges associated with its implementation:
- High Initial Investment: The cost of acquiring automated equipment can be significant, making it a barrier for smaller manufacturers. However, this investment often pays off through increased efficiency and reduced labor costs over time.
- Complexity of Integration: Integrating automated systems into existing workflows can be complex, requiring careful planning and execution to ensure compatibility with current processes.
- Need for Skilled Workforce: Operating automated systems requires a skilled workforce capable of managing sophisticated machinery and troubleshooting potential issues.
- Maintenance Requirements: Automated equipment requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Manufacturers must allocate resources for ongoing maintenance and support.
Future Trends in Automation and SMT
The future of automation in SMT is poised for exciting developments:
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI technologies will enhance automation capabilities by enabling real-time fault detection, optimizing component placement, and facilitating predictive maintenance.
- Increased Use of Robotics: As robotics technology advances, more sophisticated robotic systems will be integrated into SMT lines, further improving efficiency and precision.
- Smart Manufacturing: The concept of smart manufacturing involves using interconnected devices and data analytics to optimize production processes continuously. This trend is likely to reshape how SMT operations are managed.
- Sustainability Initiatives: As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers will increasingly focus on sustainable practices within their automated processes. This may include reducing waste through more efficient material usage or implementing energy-efficient machinery.
Conclusion
Automation plays a pivotal role in enhancing Surface Mount Technology by improving efficiency, accuracy, and quality control in PCB assembly processes. As manufacturers continue to embrace automation technologies such as pick-and-place machines, solder paste printers, and AI-driven inspection systems, they position themselves to meet the demands of an ever-evolving electronics market. While challenges exist in terms of initial investment and integration complexity, the long-term benefits make automation an essential component of modern SMT practices.
By staying abreast of emerging trends such as AI integration and smart manufacturing initiatives, manufacturers can leverage automation to drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge in the industry.

Related Questions
1. What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a method used for mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs) without drilling holes.
2. How does automation improve quality control in SMT?
Automation enhances quality control by incorporating advanced inspection systems that detect defects such as misalignment or soldering issues in real-time during the assembly process.
3. What are pick-and-place machines?
Pick-and-place machines are automated devices used in SMT that rapidly place surface-mounted components onto PCBs with high precision using robotic arms equipped with vision systems.
4. What challenges do manufacturers face when implementing automation?
Manufacturers may encounter challenges such as high initial investment costs, complexity in integrating automated systems into existing workflows, a need for skilled personnel, and ongoing maintenance requirements.
5. What future trends are expected in automation within SMT?
Future trends include increased integration of artificial intelligence for real-time monitoring and fault detection, greater use of robotics for enhanced efficiency, smart manufacturing practices leveraging data analytics, and sustainability initiatives aimed at reducing waste.




















