Content Menu
● Understanding SMT Technology
>> Key Components of SMT Lines
● The SMT Manufacturing Process
● Advantages of Using SMT Lines
● Types of SMT Lines
● Challenges in SMT Production
● Recent Innovations in SMT Technology
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What types of components can be used with SMT lines?
>> 2. How does solder paste affect the quality of PCB assembly?
>> 3. What is the difference between automatic and semi-automatic SMT lines?
>> 4. How do inspection systems contribute to quality control in SMT?
>> 5. What are some common challenges faced during SMT production?
● Citations:
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry by allowing for the efficient assembly of electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). An SMT line is an automated production system designed to facilitate this process, significantly improving speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional assembly methods. This article will delve into the workings of an SMT line, its components, advantages, challenges, and the overall manufacturing process.
Understanding SMT Technology
SMT refers to the method of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB. Unlike through-hole technology (THT), where components are inserted into holes and soldered from the back, SMT allows for a more compact design by placing components on both sides of the board. This technique supports smaller and lighter electronic devices, which is crucial in today's tech-driven world.
Key Components of SMT Lines
An SMT line comprises several essential machines that work in tandem to ensure efficient production:
- Solder Paste Printer: This machine applies solder paste to designated areas on the PCB, preparing it for component placement.
- Pick and Place Machine: This automated device accurately picks up surface mount devices (SMDs) from reels or trays and places them onto the solder-pasted areas of the PCB.
- Reflow Oven: After component placement, PCBs pass through a reflow oven where heat is applied to melt the solder paste, creating permanent connections between the components and the board.
- Inspection Systems: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems check for defects in component placement and solder joints to ensure quality control.
- Cleaning Machine: This machine removes excess flux and debris from the PCB and ensures that the PCB is clean and ready for final assembly.
- PCB Transport Systems: These devices ensure safe transport of PCBs between individual machines. The PCBs are automatically placed on a conveyor belt by a destacker and moved to subsequent modules.
- Software MES - Traceability: State-of-the-art SMT manufacturing companies use software to control and monitor the SMT production line. This includes real-time monitoring and control of machines, as well as advanced data analysis tools that can help optimize production processes.
The SMT Manufacturing Process
The SMT manufacturing process can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Solder Paste Printing: The process begins with a stencil printer that applies a precise layer of solder paste onto the PCB pads. This paste acts as both an adhesive and a conductor when heated.
2. Solder Paste Inspection (SPI): After printing, an SPI system inspects the solder paste application for accuracy in volume and placement.
3. Component Placement: The pick-and-place machine then picks up SMDs from their packaging and places them onto the PCB at specified locations.
4. Reflow Soldering: The assembled PCB enters the reflow oven where it undergoes controlled heating. This process melts the solder paste, bonding the components to the PCB.
5. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): After reflow, AOI systems inspect the board for any placement errors or solder defects.
6. Functional Testing: Some lines include functional testing to ensure that all components operate correctly after assembly.
7. Conformal Coating (Optional): If required, a conformal coating is applied for protection against environmental factors.
8. Packaging and Shipping: Finally, completed boards are packaged and prepared for delivery to customers or further assembly processes.
Advantages of Using SMT Lines
SMT lines offer numerous benefits over traditional assembly methods:
- Increased Production Speed: Automated systems can assemble thousands of components per hour, significantly reducing production time.
- Enhanced Precision: The use of robotics ensures accurate placement of components, leading to higher quality products with fewer defects.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation reduces labor costs and minimizes material wastage, resulting in lower overall production costs.
- Flexibility: SMT lines can easily adapt to different product designs and component types without extensive reconfiguration.
- Higher Quality Control: Integrated inspection systems help identify defects early in the process, ensuring reliable end products.

Types of SMT Lines
SMT lines can be categorized based on their level of automation:
- Fully Automatic Lines: These lines operate without manual intervention throughout the entire process. They are ideal for high-volume production environments where efficiency is paramount.
- Semi-Automatic Lines: These require some manual handling during certain stages, such as loading or unloading PCBs. They are often used in lower-volume production settings or for prototypes.
Challenges in SMT Production
While SMT lines provide many advantages, they also come with challenges:
- Initial Setup Costs: The investment required for high-quality SMT equipment can be substantial, which may deter smaller manufacturers.
- Complexity of Equipment: Operating an SMT line requires skilled personnel who understand both the machinery and the intricacies of PCB design.
- Material Handling: Proper handling and storage of SMDs are crucial to prevent damage from static electricity or environmental factors.
Recent Innovations in SMT Technology
Recent advancements have further enhanced SMT capabilities:
- Micro-SMT: Enabling ultra-small components like 0201 passives and microBGAs has opened new avenues for miniaturization in electronics design.
- 3D Packaging Techniques: Innovations such as System-in-Package (SiP) allow multiple functions to be integrated into a single package, enhancing performance while saving space.
- AI Integration: The incorporation of artificial intelligence into SMT processes enables predictive maintenance and real-time optimization of production workflows. AI-driven systems analyze data from machinery to identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements[1][2].
Conclusion
In conclusion, an SMT line is a vital component in modern electronics manufacturing that enhances efficiency and product quality while reducing costs. By automating various stages of PCB assembly—from solder paste application to final inspection—SMT technology has transformed how electronic devices are produced. As technology continues to advance, SMT lines will likely evolve further, incorporating even more sophisticated automation and inspection technologies to meet growing demands for miniaturization and high performance in electronics.
The future of SMT looks promising with trends leaning towards increased automation, integration with AI technologies, and a focus on sustainability practices within manufacturing processes[3][4][5]. As industries continue to embrace these advancements, we can expect even greater efficiency gains and innovations in electronic device design and functionality[6][7].
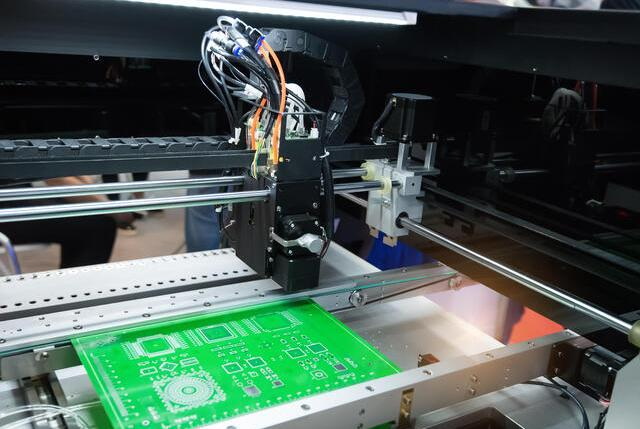
FAQ
1. What types of components can be used with SMT lines?
SMT lines accommodate various surface-mount devices including resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), diodes, and more.
2. How does solder paste affect the quality of PCB assembly?
Solder paste plays a critical role as it serves both as an adhesive during component placement and as a conductor once reflowed. Proper application ensures strong connections between components and PCBs.
3. What is the difference between automatic and semi-automatic SMT lines?
Automatic SMT lines operate without manual intervention throughout all stages of production, while semi-automatic lines require some manual handling at certain points in the process.
4. How do inspection systems contribute to quality control in SMT?
Inspection systems like Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) detect placement errors or solder defects early in the manufacturing process, ensuring that only quality products proceed to final testing or shipping.
5. What are some common challenges faced during SMT production?
Challenges include high initial setup costs for equipment, complexity in operating machinery, and careful handling requirements for sensitive electronic components to avoid damage from static electricity or environmental factors.
Citations:
[1] https://www.allsmt.com/SMT-line-concept-assembly-manufacturing-production-Assembly
[2] https://www.swfuliusmt.com/2024/07/12/understanding-smt-lines-the-backbone-of-modern-electronics-manufacturing/
[3] https://www.raypcb.com/surface-mount-technology/
[4] https://www.pcb-hero.com/blogs/lisas-column/surface-mount-technology-common-problems-and-solutions-for-efficient-smt-assembly
[5] https://www.mycronic.com/product-areas/pcb-assembly/news-and-press-releases/news/ten-key-smt-trends-you-need-to-know/
[6] https://minearc.com/what-is-an-smt-line/
[7] https://vectorbluehub.com/smt-assembly
[8] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/exciting-developments-surface-mount-technology-snehal-kale
[9] https://www.pcbasic.com/blog/smt_production_line.html
[10] https://lenalea.com/the-advantages-of-smt-assembly-in-electronics-manufacturing/
[11] https://emsginc.com/resources/the-evolution-of-surface-mount-technology/
[12] https://www.viasion.com/blog/common-challenges-in-smt-assembly-and-solutions/
[13] https://www.rhsmt.com/news/smt-industrys-future-trends-the-impact-of-ai-and-automation/
[14] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surface-mount_technology
[15] https://levisonenterprises.com/5-advantages-to-using-smt/
[16] https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2024/10/14/2962707/28124/en/Surface-Mount-Technology-Equipment-SMT-Market-to-Surge-to-8-32-Billion-by-2028-Global-Long-term-Forecast-to-2033.html
[17] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=64w1uH8FkcM
[18] https://m.smt11.com/blog/SMT-Field/SMT-Process-Status-and-Future-Development-Trends-2023.html
[19] https://www.raypcb.com/smt-lines/
[20] https://www.hayawin.com/news-5-advantages-to-using-smt-in-your-electronic-manufacturing-project.html
[21] https://smt.fuji.co.jp/en/topics/2858
[22] https://www.protoexpress.com/blog/common-errors-surface-mount-technology-smt/
[23] https://smta.org/events/RSVPlist.aspx?id=1814998
[24] https://www.wevolver.com/article/smt-process
[25] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/advantages-smt-manufacturing-practical-cost-effective-nyn3c
[26] https://www.unmannedsystemstechnology.com/feature/mpl-explains-the-evolution-of-smt-technology/
[27] https://www.vse.com/blog/2022/03/15/8-common-smt-placement-issues-and-solutions/
[28] https://www.nbk1560.com/en-US/resources/mechatronics/article/SMT/
[29] https://www.andwinpcb.com/innovations-in-surface-mount-technology-for-enhanced-electronics/
[30] https://www.andwinpcb.com/advancements-in-smt-and-pth-assembly-techniques/
[31] https://jhdpcb.com/blog/efficient-smt-assembly/
[32] https://www.pcbcart.com/article/content/smt-assembly-development-trend.html




















