Content Menu
● Key Features That Affect the SMD Assembly Machine Price
>> 1. Machine Type and Functionality
>> 2. Placement Speed and Throughput
>> 3. Component Size and Complexity Handling
>> 4. Automation Level and Software Integration
>> 5. Machine Size and Expandability
>> 6. Precision and Quality Control Features
>> 7. Setup and Maintenance Costs
>> 8. Brand and Origin
● Pricing Models and Cost Breakdown for SMD Assembly Machines
● How to Choose the Right SMD Assembly Machine for Your Budget
>> Assess Production Volume
>> Evaluate Component Types
>> Consider Future Growth
>> Balance Automation and Labor
>> Review Total Cost of Ownership
>> Compare Brands and Support
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the typical price range for SMD assembly machines?
>> 2. How does automation affect the price of SMD assembly machines?
>> 3. Can small SMD machines handle complex components?
>> 4. Are maintenance costs included in the machine price?
>> 5. How important is machine expandability?
Surface Mount Device (SMD) assembly machines are critical in modern electronics manufacturing, enabling the precise placement and soldering of components on printed circuit boards (PCBs). The smd assembly machine price varies widely depending on several key features and factors. Understanding these features is essential for businesses and manufacturers to make informed purchasing decisions that balance cost, performance, and future scalability.
This comprehensive article explores the main features that affect the smd assembly machine price, breaking down technical specifications, operational capabilities, and other considerations that influence the cost. We also provide insights into pricing models and practical tips for selecting the right machine. Finally, a conclusion summarizes the key points, followed by a FAQ section addressing common questions.
Key Features That Affect the SMD Assembly Machine Price
1. Machine Type and Functionality
There are several types of SMD assembly machines, each serving different roles in the assembly line. The type of machine directly impacts the price:
- Pick-and-Place Machines (Mounters): These machines place components onto the PCB. Automatic and semi-automatic mounters vary in price depending on their speed, precision, and automation level. Fully automatic machines with high-speed placement capabilities cost more but improve productivity.
- Solder Paste Printers: These apply solder paste on PCB pads using stencils. Manual printers are cheaper but suitable only for prototyping, while automatic printers designed for mass production are more expensive.
- Reflow Ovens: These machines solder the components by melting the solder paste. Small reflow ovens for prototyping are less costly compared to large, high-capacity models used in mass production.
- Hot Air Rework Stations: Used for repair or rework, these are generally less expensive but essential for quality control.
The choice between manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic machines greatly influences the smd assembly machine price.
2. Placement Speed and Throughput
The speed at which an SMD machine can place components on a PCB is a crucial factor. High-speed machines capable of placing thousands of components per hour command higher prices. Speed is especially important for large-scale production environments where throughput directly impacts profitability.
For smaller production runs or prototyping, slower machines may suffice and be more cost-effective. However, buyers should consider future production volume growth to avoid under-specifying the machine.
Placement speed is often measured in components per hour (cph). Entry-level machines may place around 2,000 to 5,000 cph, mid-range machines can handle 10,000 to 20,000 cph, and high-end models exceed 40,000 cph. The jump in price between these categories can be substantial, reflecting the complexity and engineering required to maintain accuracy at high speeds.
3. Component Size and Complexity Handling
SMD machines vary in their ability to handle different component sizes and complexities:
- Machines designed for small components (e.g., 0201, 0402 packages) require higher precision and advanced vision systems, increasing costs.
- Handling of complex components such as BGAs (Ball Grid Arrays), QFPs (Quad Flat Packages), and odd-shaped parts requires sophisticated placement heads and software.
- Machines with multi-head placement capability can handle multiple components simultaneously, improving speed but increasing price.
The ability to handle fine-pitch components and ultra-small packages is particularly important in industries like mobile devices and medical electronics, where miniaturization is key. Machines that can manage these components often incorporate advanced vision systems, laser alignment, and more precise mechanical parts, all of which add to the smd assembly machine price.
4. Automation Level and Software Integration
Automation reduces labor costs but increases initial machine cost:
- Fully automated machines include features like automatic feeder loading, vision inspection, and self-calibration.
- Semi-automatic or manual machines require more operator intervention, lowering the machine price but increasing labor expenses.
- Advanced software for programming, component recognition, and process control adds to the smd assembly machine price but improves accuracy and reduces errors.
Integration with factory management systems and Industry 4.0 capabilities also increase machine cost but provide long-term efficiency benefits. For example, machines equipped with real-time data tracking and remote diagnostics can reduce downtime and improve yield, which justifies a higher upfront investment.
Software capabilities such as CAD import, component library management, and offline programming are critical for reducing setup time and improving flexibility. Machines with user-friendly interfaces and robust software ecosystems tend to have higher prices but offer better return on investment.
5. Machine Size and Expandability
The physical footprint and expandability options affect the price:
- Compact desktop or small footprint machines are less expensive and suitable for prototyping or small batch production.
- Larger machines with expandable feeder slots and conveyor systems support higher volume production and future growth but cost more.
- Machines designed for modular upgrades allow buyers to start with a basic model and add features later, balancing upfront cost and scalability.
Expandability is a key consideration for manufacturers expecting growth. Machines that can add additional feeders, vision systems, or even integrate with other assembly line equipment help protect your investment. However, these modular capabilities come at a premium.
6. Precision and Quality Control Features
High precision placement is critical for modern electronics. Machines equipped with:
- High-resolution cameras and vision systems for component alignment.
- Automated optical inspection (AOI) capabilities.
- Real-time process monitoring and error detection.
These features increase the smd assembly machine price but reduce defects and rework costs, improving overall production quality.
Precision is often expressed in microns, with high-end machines capable of ±10 microns or better. This level of precision is necessary for high-density PCBs used in aerospace, automotive, and medical electronics. Investing in precision features reduces scrap rates and improves product reliability, which can offset the higher initial cost.
7. Setup and Maintenance Costs
Beyond the purchase price, setup and ongoing maintenance influence the total cost of ownership:
- Setup costs include stencil creation, machine programming, and calibration.
- Maintenance involves routine servicing, replacement parts, and software updates.
Machines with easier setup and lower maintenance requirements may have a higher initial price but reduce long-term expenses.
Some manufacturers offer service contracts or extended warranties that can help control maintenance costs. Additionally, machines with self-diagnostic tools and remote support options can reduce downtime and service expenses.
8. Brand and Origin
The manufacturer's reputation, country of origin, and after-sales support affect pricing:
- Established brands with proven reliability typically charge premium prices.
- Machines manufactured in regions with lower labor costs (e.g., China) may be cheaper but vary in quality and support.
- Warranty and availability of spare parts also influence the overall value and price.
Choosing a reputable brand often means better technical support, faster spare parts delivery, and more reliable machines, which can justify a higher smd assembly machine price. However, emerging manufacturers have improved quality and offer competitive pricing, making them attractive options for budget-conscious buyers.
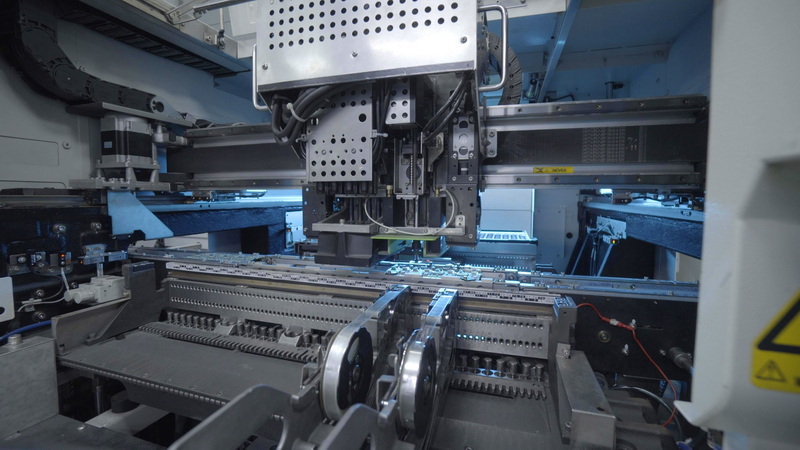

Pricing Models and Cost Breakdown for SMD Assembly Machines
Understanding pricing models helps buyers evaluate the smd assembly machine price relative to their needs.
| Cost Factor | Description | Impact on Price |
| Base Machine Cost | Cost of the core machine (pick-and-place, printer, oven) | Major portion of total price |
| Automation Features | Level of automation, software, vision systems | Increases price significantly |
| Speed and Throughput | Placement speed and capacity | Higher speed = higher price |
| Component Handling | Ability to handle small/complex components | Precision features increase price |
| Expandability | Modular upgrades, feeder slots, conveyor systems | Adds to upfront cost |
| Setup and Programming | Costs for initial setup, stencil making, programming | One-time but significant |
| Maintenance and Support | Warranty, spare parts, service contracts | Ongoing cost, affects total ownership |
| Brand and Origin | Manufacturer reputation and country of manufacture | Premium brands cost more |
How to Choose the Right SMD Assembly Machine for Your Budget
Selecting the right SMD assembly machine requires balancing cost with production requirements. Here are key steps:
Assess Production Volume
Higher volumes justify investment in faster, fully automated machines. For low-volume or prototype runs, smaller, less expensive machines may suffice.
Evaluate Component Types
Match machine precision and capabilities to your BOM. If your products use ultra-small or complex components, prioritize machines with advanced vision and placement accuracy.
Consider Future Growth
Choose machines with expandability to avoid costly replacements. Modular machines allow you to add feeders or upgrade speed as production scales.
Balance Automation and Labor
Higher automation reduces labor but increases initial price. Calculate total cost of ownership including labor savings.
Review Total Cost of Ownership
Include setup, maintenance, and support costs in budgeting. Sometimes a higher upfront price reduces long-term expenses.
Compare Brands and Support
Factor in reliability and after-sales service. A cheaper machine with poor support can cost more over time.
Conclusion
The smd assembly machine price is influenced by a complex interplay of features including machine type, speed, precision, automation level, component handling capabilities, and brand reputation. While higher-priced machines often offer advanced features and greater efficiency, selecting the right machine depends on your production needs, component complexity, and budget. Careful evaluation of these factors ensures a cost-effective investment that meets both current and future manufacturing demands.
By understanding these key features and their impact on price, manufacturers can make informed decisions that optimize their production capabilities without overspending. Whether you are a small startup or a large-scale manufacturer, aligning your machine choice with your operational goals is essential for success in today's competitive electronics market.

FAQ
1. What is the typical price range for SMD assembly machines?
The price varies widely from around $6,000 for small desktop machines to over $100,000 for high-end fully automatic systems designed for mass production.
2. How does automation affect the price of SMD assembly machines?
Higher automation levels increase the machine price due to advanced software, vision systems, and robotic features but reduce labor costs and improve throughput.
3. Can small SMD machines handle complex components?
Some small machines can handle complex components but generally with lower speed and precision compared to larger, more expensive machines designed for complex assemblies.
4. Are maintenance costs included in the machine price?
No, maintenance costs are ongoing expenses and should be considered separately when budgeting for total cost of ownership.
5. How important is machine expandability?
Expandability allows you to add feeders or upgrade capabilities as production grows, helping to protect your investment and avoid costly replacements.




















