Content Menu
● Common Issues Faced by Users of SMT SMD Pick and Place Machines
>> 1. Component Placement Inaccuracy
>> 2. Component Pick-Up and Release Problems
>> 3. Component Damage During Placement
>> 4. Machine Overheating and Mechanical Failures
>> 5. Sensor and Camera Issues
>> 6. Programming and Software Errors
>> 7. Maintenance Neglect and Operator Errors
● Solutions and Best Practices for SMT Pick and Place Machine Issues
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What causes inaccurate component placement in SMT pick and place machines?
>> 2. How can component pick-up failures be prevented?
>> 3. Why do SMT pick and place machines overheat, and how can this be avoided?
>> 4. How important is operator training for SMT pick and place machine performance?
>> 5. What maintenance practices are essential for SMT pick and place machines?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) pick and place machines have revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry by enabling the rapid and precise placement of surface-mount devices (SMDs) onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). These machines are integral to achieving high throughput and consistent quality in the assembly process. However, despite their advanced automation and capabilities, users frequently encounter a variety of challenges that can hinder machine performance, reduce production efficiency, and increase defect rates. This comprehensive article explores the most common issues faced by users of SMT SMD pick and place machines, their underlying causes, and practical solutions to overcome these obstacles.
Common Issues Faced by Users of SMT SMD Pick and Place Machines
1. Component Placement Inaccuracy
Accurate component placement is the cornerstone of SMT assembly. The precision with which an SMT pick and place machine places components directly affects the electrical functionality and reliability of the final product. Unfortunately, component placement inaccuracies are among the most common issues users face. These inaccuracies manifest as components being offset from their intended positions, rotated incorrectly, or completely missed.
Several factors contribute to placement inaccuracies:
- Machine Calibration Errors: Over time, the mechanical and optical systems of the pick and place machine can drift out of calibration. This affects the accuracy of the placement head and camera alignment, causing misplacement.
- Feeder Malfunctions: Feeders are responsible for delivering components to the pick-up area. Damaged, misaligned, or improperly loaded feeders can cause components to be picked incorrectly or in the wrong orientation.
- Programming Mistakes: Errors in the pick and place program, such as incorrect component coordinates or orientation data, lead to inaccurate placement.
- Fiducial Recognition Problems: Fiducials are reference marks on the PCB used by the machine's vision system to align the board correctly. Dirty lenses, damaged fiducials, or poor lighting conditions can impair fiducial detection, resulting in placement errors.
The consequences of inaccurate placement include soldering defects, electrical shorts, and functional failures, which increase rework and scrap rates.
2. Component Pick-Up and Release Problems
The pick and place process depends heavily on the machine's ability to reliably pick components from feeders and release them onto the PCB. Users often report issues such as components not being picked up, dropped prematurely, or sticking to the nozzle after placement.
Common causes include:
- Vacuum Pressure Issues: The vacuum system must generate sufficient and consistent suction to pick up components. Leaks, clogged filters, or damaged vacuum pumps reduce suction power.
- Nozzle Wear and Damage: Nozzles are delicate parts that can wear out or become damaged from repeated use or improper handling. Worn nozzles lose their ability to hold components securely.
- Feeder Vibration Problems: Vibration feeders orient and feed components into the pick-up position. If vibration intensity is too low or inconsistent, components may not be properly aligned or fed.
- Component Characteristics: Some components, especially very small or irregularly shaped SMDs, are inherently difficult to pick up due to their size, weight, or surface finish.
Failure in pick-up or release results in production stoppages, increased manual intervention, and lower throughput.
3. Component Damage During Placement
SMD components are often fragile and sensitive to mechanical stress. Damage during placement can lead to latent defects that are difficult to detect until final testing or field use.
Factors causing component damage include:
- Excessive Placement Force: If the placement head applies too much pressure, it can crack or deform components, especially ceramic capacitors or delicate ICs.
- Incorrect Z-Axis Height Settings: The vertical position of the placement head must be precisely adjusted according to component and PCB thickness. Incorrect settings can cause collisions or excessive force.
- Machine Wear or Malfunction: Aging or poorly maintained machines may produce inconsistent placement force or vibrations that damage components.
- Poor Component Quality: Low-quality or counterfeit components are more prone to damage during handling.
Damaged components contribute to product failures, increased warranty claims, and damage to brand reputation.
4. Machine Overheating and Mechanical Failures
SMT pick and place machines operate continuously at high speeds, generating heat and mechanical wear. Overheating and mechanical breakdowns are common issues that disrupt production.
Key contributors to overheating and mechanical failures include:
- Continuous Operation Without Breaks: Running the machine at maximum speed for extended periods without cooling intervals can cause overheating of motors, drives, and electronic components.
- Accumulated Dirt and Lack of Lubrication: Dust and debris increase friction on moving parts, causing motors and belts to work harder and overheat.
- Electrical Supply Problems: Voltage fluctuations, poor grounding, or unstable power sources can damage electrical components and cause erratic machine behavior.
- Worn Mechanical Parts: Belts, gears, bearings, and sensors degrade over time and can fail unexpectedly if not replaced timely.
Mechanical failures often result in unplanned downtime, costly repairs, and loss of production.
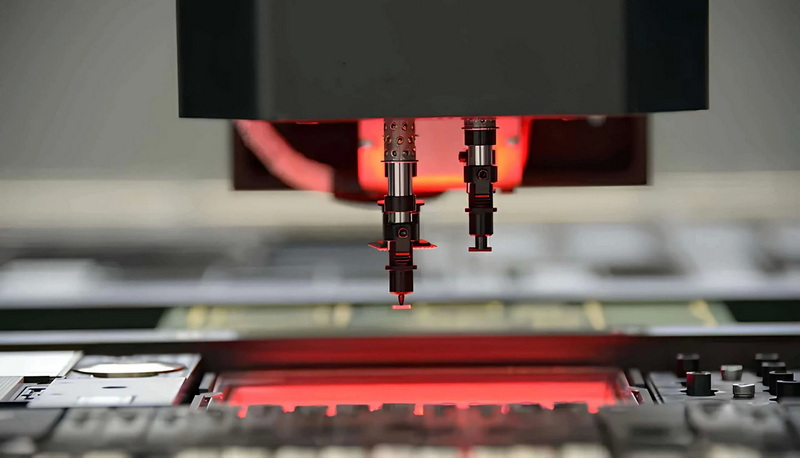

5. Sensor and Camera Issues
The vision system of an SMT pick and place machine is essential for detecting component positions, orientations, and PCB alignment. Sensor and camera problems can severely impact placement accuracy.
Common issues include:
- Dirty or Contaminated Sensors: Dust, solder paste residue, or fingerprints on sensors and camera lenses reduce image clarity and cause false readings.
- Faulty Sensors: Sensors can fail due to electrical faults, physical damage, or aging components.
- Camera Calibration Errors: Cameras require precise calibration to ensure accurate fiducial and component recognition. Miscalibration leads to placement errors.
- Lighting Problems: Insufficient or inconsistent lighting in the vision system's field of view impairs image processing.
These problems often trigger machine alarms, halt production, and require troubleshooting.
6. Programming and Software Errors
The pick and place software controls the entire placement sequence, including feeder assignments, component orientation, and placement coordinates. Programming errors are a frequent source of issues.
Typical programming mistakes include:
- Incorrect Feeder Assignments: Assigning the wrong feeder to a component leads to picking incorrect parts.
- Wrong Component Orientation Settings: Polarized components like diodes and capacitors must be oriented correctly. Incorrect polarity settings cause functional failures.
- Coordinate Mismatches: Errors in component X-Y coordinates cause misplacement.
- Outdated Software Versions: Using outdated or buggy software can introduce errors or reduce machine compatibility.
Careful program verification and updates are necessary to avoid these problems.
7. Maintenance Neglect and Operator Errors
Proper maintenance and skilled operation are fundamental to the smooth running of SMT pick and place machines. Neglecting these aspects leads to many avoidable problems.
Common maintenance and operator-related issues include:
- Infrequent Cleaning: Dirt buildup on nozzles, feeders, and sensors degrades machine performance.
- Lack of Lubrication: Moving parts require regular lubrication to prevent excessive wear.
- Improper Machine Settings: Incorrect speed, force, or vacuum settings reduce placement quality.
- Irregular Maintenance Schedules: Skipping routine inspections allows minor issues to escalate.
- Insufficient Operator Training: Untrained operators may mishandle equipment, misinterpret alarms, or fail to perform necessary maintenance.
Investing in regular maintenance and comprehensive operator training greatly reduces downtime and defects.
Solutions and Best Practices for SMT Pick and Place Machine Issues
To overcome the common challenges associated with SMT SMD pick and place machines, manufacturers should implement a combination of technical and operational best practices:
- Regular Calibration: Periodically calibrate placement heads, cameras, and feeders to maintain accuracy.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Establish and adhere to maintenance schedules that include cleaning, lubrication, part replacement, and system checks.
- Vacuum System Checks: Monitor vacuum pressure levels and replace filters and pumps as needed to ensure reliable component pick-up.
- Feeder Management: Inspect feeders regularly for damage or misalignment and reload components carefully.
- Software Verification: Thoroughly review and test pick and place programs before production runs. Keep software updated.
- Operator Training: Provide comprehensive training on machine operation, troubleshooting, and maintenance procedures.
- Environmental Controls: Maintain a clean, temperature-controlled production environment to reduce dust and thermal stress.
- Use High-Quality Components: Source components from reputable suppliers to minimize damage and placement difficulties.
- Monitor Machine Health: Use built-in diagnostics and monitoring tools to detect early signs of mechanical or electrical issues.
By adopting these strategies, manufacturers can enhance the reliability, efficiency, and output quality of their SMT pick and place operations.
Conclusion
SMT SMD pick and place machines are indispensable tools in modern electronics manufacturing, enabling fast and precise assembly of complex PCBs. However, users commonly face a variety of challenges that can compromise machine performance and product quality. These issues include component placement inaccuracies, pick-up and release failures, component damage, overheating, sensor and camera malfunctions, programming errors, and maintenance neglect.
Understanding the root causes of these problems and implementing proactive solutions such as regular calibration, maintenance, operator training, and software verification are essential to achieving optimal machine performance. By addressing these common issues, manufacturers can reduce downtime, lower defect rates, improve yield, and extend the lifespan of their SMT pick and place machines.
Investing in proper machine care and skilled operation not only enhances production efficiency but also ensures the delivery of reliable, high-quality electronic products in today's competitive market.

FAQ
1. What causes inaccurate component placement in SMT pick and place machines?
Inaccurate placement is often caused by incorrect machine calibration, damaged or misaligned feeders, programming errors, and poor fiducial recognition due to dirty cameras or sensors.
2. How can component pick-up failures be prevented?
Ensuring optimal vacuum pressure, replacing worn or damaged nozzles, maintaining effective vibration feeders, and using components suitable for the machine's capabilities help prevent pick-up failures.
3. Why do SMT pick and place machines overheat, and how can this be avoided?
Overheating can result from continuous high-speed operation without breaks, accumulated dirt increasing friction, and electrical supply issues. Regular maintenance, cleaning, proper lubrication, and stable power supply management help avoid overheating.
4. How important is operator training for SMT pick and place machine performance?
Operator training is critical because skilled operators can correctly handle the machine, perform necessary maintenance, identify issues early, and ensure accurate programming, all of which contribute to efficient and reliable operation.
5. What maintenance practices are essential for SMT pick and place machines?
Essential maintenance practices include regular cleaning of nozzles and sensors, lubrication of moving parts, calibration of placement heads and cameras, inspection and replacement of worn parts, and adherence to scheduled maintenance routines.




















