Content Menu
● Understanding SMT Placement Machines
● Key Benefits of SMT Placement Machines
>> 1. Increased Production Speed
>> 2. Enhanced Precision and Quality Control
>> 3. Cost Efficiency
>> 4. Flexibility and Scalability
>> 5. Improved Design Capabilities
>> 6. Enhanced Signal Integrity
>> 7. High Reliability
● The SMT Assembly Line Process
● Advantages Over Traditional Assembly Methods
● Challenges and Considerations
● Future Trends in SMT Technology
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is an SMT placement machine?
>> 2. How does an SMT assembly line work?
>> 3. What are the advantages of using SMT over traditional through-hole technology?
>> 4. Can SMT placement machines handle different types of components?
>> 5. What industries benefit most from SMT technology?
● Citations:
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has transformed the landscape of electronics manufacturing, particularly in the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). The introduction of SMT placement machines has facilitated a significant leap in efficiency, precision, and overall production quality. This article explores the key benefits of using SMT placement machines in assembly lines, highlighting their impact on manufacturing processes.
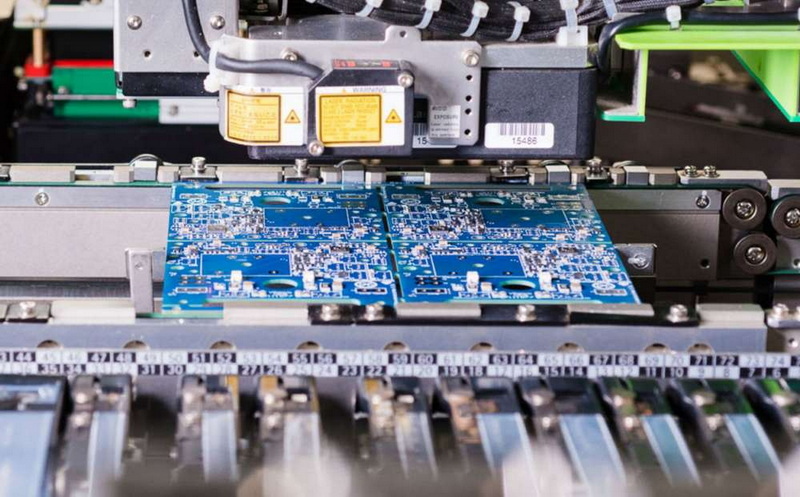
Understanding SMT Placement Machines
SMT placement machines, often referred to as pick-and-place machines, are automated devices designed to place surface mount devices (SMDs) onto PCBs with high accuracy. These machines utilize advanced robotics and vision systems to ensure that components are placed correctly and efficiently. The integration of these machines into assembly lines has revolutionized how electronic devices are produced.
Key Benefits of SMT Placement Machines
1. Increased Production Speed
One of the most significant advantages of SMT placement machines is their ability to dramatically increase production speed. These machines can place thousands of components per hour, making them ideal for high-volume production environments. This rapid assembly capability allows manufacturers to meet growing market demands without compromising quality.
2. Enhanced Precision and Quality Control
SMT placement machines are equipped with high-resolution vision systems that enable precise component placement. This precision is crucial in reducing defects and ensuring that each component is positioned correctly on the PCB. Automated inspection systems further enhance quality control by detecting errors in real-time, allowing for immediate corrections before further processing.
3. Cost Efficiency
While the initial investment in SMT placement machines may be substantial, the long-term cost savings are significant. By automating the assembly process, manufacturers can reduce labor costs and minimize material waste. Additionally, the elimination of drilling holes (as required in through-hole technology) leads to lower production costs per unit.
4. Flexibility and Scalability
SMT placement machines offer remarkable flexibility in handling various component sizes and types. This adaptability allows manufacturers to switch between different product lines with minimal downtime. As market demands fluctuate, the scalability of SMT systems enables companies to ramp up or scale down production efficiently.
5. Improved Design Capabilities
The compact nature of SMT components allows for more complex PCB designs, enabling manufacturers to create smaller and lighter electronic devices. This miniaturization is particularly advantageous in industries such as telecommunications and consumer electronics, where space is at a premium.
6. Enhanced Signal Integrity
SMT assemblies typically exhibit better electrical performance due to shorter lead lengths and reduced parasitic inductance. This improvement in signal integrity translates into faster signal transmission and higher reliability for electronic devices, which is critical for applications requiring high-frequency performance.
7. High Reliability
The automated nature of SMT placement reduces human error during assembly, leading to higher reliability in the final product. Consistent machine operation ensures that every PCB meets stringent quality standards, which is essential for industries such as aerospace and medical devices where failure is not an option.
The SMT Assembly Line Process
To fully appreciate the benefits of SMT placement machines, it is essential to understand their role within the broader context of an SMT assembly line:
1. Solder Paste Printing: The process begins with a solder paste printer that applies solder paste to specific areas on the PCB.
2. Component Placement: The SMT placement machine picks components from feeders using a vacuum nozzle and places them onto the soldered areas accurately.
3. Reflow Soldering: After component placement, PCBs are passed through a reflow oven where heat melts the solder paste, creating permanent electrical connections.
4. Inspection: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems check for defects or misalignments post-soldering.
5. Final Assembly: After inspection, PCBs are cleaned and prepared for final assembly or packaging.
Advantages Over Traditional Assembly Methods
Compared to traditional through-hole technology (THT), SMT offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice for modern electronics manufacturing:
- Higher Component Density: SMT allows for more components to be placed on both sides of the PCB, leading to smaller overall board sizes without sacrificing functionality.
- Faster Setup Times: Setting up an SMT line can be quicker than THT due to fewer manual processes involved.
- Reduced Manual Labor: Automation significantly decreases reliance on manual labor, reducing costs and minimizing human error.
- Improved Thermal Management: Directly mounted components dissipate heat more effectively than their through-hole counterparts.
- Greater Design Flexibility: The ability to use smaller components opens up opportunities for innovative designs that were previously not feasible.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their numerous advantages, there are challenges associated with SMT placement machines:
- Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing and maintaining advanced SMT machinery can be high.
- Complexity: Operating these machines requires skilled personnel who understand both the technology and the manufacturing process.
- Component Fragility: SMDs can be more fragile than traditional components, necessitating careful handling during assembly.
Future Trends in SMT Technology
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the field of surface mount technology. Several trends are emerging that could further enhance the capabilities of SMT placement machines:
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI can optimize machine learning algorithms for better defect detection and predictive maintenance.
- Increased Automation: The trend towards Industry 4.0 will see more fully automated factories where machines communicate with each other to streamline production processes.
- Miniaturization: Continued advancements in component design will lead to even smaller SMDs being used in increasingly compact electronic devices.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Manufacturers are focusing on reducing waste generated during production processes through more efficient material usage and recycling initiatives.
Conclusion
The integration of SMT placement machines into assembly lines has ushered in a new era of efficiency and precision in electronics manufacturing. With benefits such as increased production speed, enhanced quality control, cost efficiency, flexibility, improved design capabilities, enhanced signal integrity, and high reliability, these machines are essential for modern PCB assembly processes. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of SMT systems, ensuring that manufacturers can meet ever-increasing demands for compact and reliable electronic devices.
FAQ
1. What is an SMT placement machine?
An SMT placement machine is an automated device used in electronics manufacturing to accurately place surface mount devices (SMDs) onto printed circuit boards (PCBs).
2. How does an SMT assembly line work?
An SMT assembly line typically involves several steps: solder paste printing, component placement by pick-and-place machines, reflow soldering to create connections, inspection for quality control, and final assembly.
3. What are the advantages of using SMT over traditional through-hole technology?
SMT offers several advantages including higher component density on PCBs, reduced manufacturing costs due to fewer drilling requirements, improved electrical performance due to shorter lead lengths, and faster production speeds.
4. Can SMT placement machines handle different types of components?
Yes, modern SMT placement machines are highly flexible and can handle a wide range of component sizes and types without significant downtime during transitions between different product lines.
5. What industries benefit most from SMT technology?
Industries such as telecommunications, consumer electronics, automotive electronics, aerospace, and medical devices benefit significantly from SMT technology due to its efficiency and ability to produce compact designs.
Citations:
[1] https://www.smtfactory.com/what-is-an-smt-line-and-how-can-it-improve-your-pcb-assembly-process.html
[2] https://vectorbluehub.com/smt-assembly
[3] https://www.zjyingxing.com/info/how-does-the-smt-machine-improve-modern-indust-81643071.html
[4] https://www.pcbasic.com/blog/smt_production_line.html
[5] https://www.mpe-electronics.co.uk/2024/10/22/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-surface-mount-technology
[6] https://www.swfuliusmt.com/2024/10/03/the-evolution-of-smt-machines-revolutionizing-electronics-manufacturing/
[7] https://www.protoexpress.com/kb/smt-assembly/
[8] https://reprosupplies.co.za/smt-manufacturing/
[9] https://www.hayawin.com/resources/smt-line-an-efficient-and-cost-effective-production-line.html
[10] https://www.protoexpress.com/blog/good-not-so-good-sides-surface-mount-technology/




















