Content Menu
● Introduction
● What is SMT Electronics Manufacturing?
>> Key Components of SMT
● The SMT Manufacturing Process
>> 1. Material Preparation
>> 2. Stencil Preparation
>> 3. Solder Paste Printing
>> 4. Component Placement
>> 5. Reflow Soldering
>> 6. Inspection and Testing
● Advantages of SMT Electronics Manufacturing
● Challenges in SMT Manufacturing
● Future Trends in SMT Electronics Manufacturing
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Introduction
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a pivotal method in the electronics manufacturing industry, allowing for the efficient assembly of electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). This technology has revolutionized how electronic devices are produced, offering numerous advantages over traditional methods. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of SMT electronics manufacturing, its processes, benefits, and challenges, while also addressing common questions related to this technology.
What is SMT Electronics Manufacturing?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) refers to a method where electronic components are mounted directly onto the surface of PCBs. Unlike traditional through-hole technology, where components are inserted into holes drilled in the PCB, SMT allows for a more compact and efficient design. This method utilizes smaller components and eliminates the need for leads to pass through the board, thus enabling higher component density and improved performance.
Key Components of SMT
1. Surface Mount Components (SMCs): These are the electronic components designed for surface mounting. They include resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), and more.
2. Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): The substrate on which SMCs are mounted. PCBs can be single-sided or double-sided.
3. Solder Paste: A mixture of solder and flux used to attach SMCs to PCBs during the soldering process.
The SMT Manufacturing Process
The SMT manufacturing process consists of several critical steps:
1. Material Preparation
Before manufacturing begins, materials such as SMCs and PCBs are prepared and inspected for quality. This step ensures that only defect-free components are used in production.
2. Stencil Preparation
A stencil is created based on the design of the PCB. This stencil is used to apply solder paste accurately to the PCB pads where components will be placed.
3. Solder Paste Printing
Using a stencil printer, solder paste is applied to the PCB. This step is crucial as it determines the amount of solder that will bond the components to the board. Proper application ensures reliable electrical connections.
Solder Paste Printing
4. Component Placement
Once solder paste is applied, the PCB moves to a pick-and-place machine. This automated equipment places SMCs onto the solder-covered pads with high precision.
Pick-and-Place Machine
5. Reflow Soldering
After placement, the assembled PCB enters a reflow oven where it undergoes a heating process:
- Preheat Zone: Gradually raises temperature to avoid thermal shock.
- Soak Zone: Maintains temperature for a specific duration to prepare for soldering.
- Reflow Zone: Melts the solder paste, creating strong connections between components and pads.
- Cooling Zone: Rapidly cools down the assembly to solidify solder joints.
Reflow Oven Process
6. Inspection and Testing
Post-soldering, PCBs undergo inspection using Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems to ensure quality and detect defects. Additional tests may include In-Circuit Testing (ICT) and functional testing.
Automated Optical Inspection
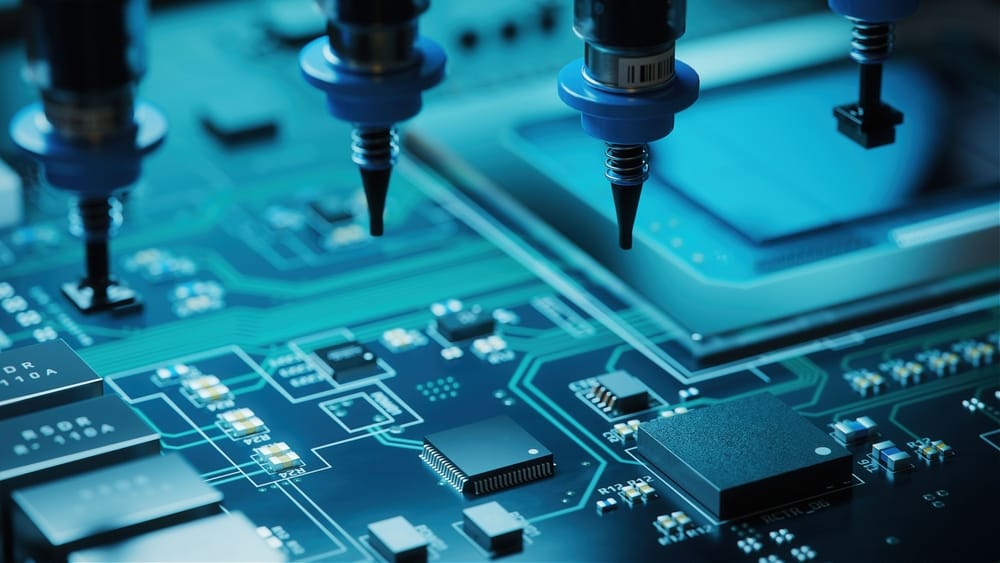
Advantages of SMT Electronics Manufacturing
1. Higher Component Density: SMT allows for more compact designs, accommodating smaller components and enabling more functionality within limited space.
2. Improved Performance: Shorter electrical paths reduce signal loss and enhance performance.
3. Cost Efficiency: Reduced material costs due to smaller components and less PCB area required.
4. Faster Production Rates: Automation in SMT processes leads to increased production speed compared to manual assembly methods.
5. Enhanced Reliability: The use of solder paste provides better mechanical strength and reliability compared to traditional methods.
Challenges in SMT Manufacturing
While SMT offers numerous advantages, it also presents challenges:
1. Complexity in Design: Designing PCBs for SMT requires specialized knowledge and tools.
2. Equipment Costs: Initial investment in automated machinery can be high.
3. Soldering Issues: Problems such as cold joints or insufficient solder can occur if not managed properly during reflow.
Future Trends in SMT Electronics Manufacturing
The future of SMT electronics manufacturing looks promising with advancements in technology:
- Miniaturization: Continued development of smaller components will push the limits of PCB design.
- Automation: Increased use of robotics and AI in manufacturing processes will enhance efficiency and accuracy.
- Sustainability: Growing emphasis on eco-friendly materials and processes will shape future practices in electronics manufacturing.
Conclusion
SMT electronics manufacturing has transformed how electronic devices are produced, offering significant advantages in efficiency, performance, and cost-effectiveness. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the methods used in SMT, paving the way for even more innovative solutions in electronics design and production.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Surface Mount Technology?
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a method for mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs).
2. What are the main steps in SMT manufacturing?
- The main steps include material preparation, stencil preparation, solder paste printing, component placement, reflow soldering, and inspection.
3. What are some advantages of using SMT?
- Advantages include higher component density, improved performance, cost efficiency, faster production rates, and enhanced reliability.
4. What challenges does SMT face?
- Challenges include design complexity, high equipment costs, and potential soldering issues.
5. How does automation impact SMT manufacturing?
- Automation increases production speed and accuracy while reducing labor costs associated with manual assembly processes.



















