Content Menu
● What Are the Key Advantages of SMD Electronics in Modern Manufacturing?
>> Understanding SMD Electronics
>> The SMT Manufacturing Process
>> Advantages of SMD Electronics
>> Applications of SMD Electronics
>> Future Trends in SMD Electronics
>> Challenges Facing SMD Electronics
>> Best Practices for Working with SMD Electronics
>> Conclusion
>> Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Key Advantages of SMD Electronics in Modern Manufacturing?
S electronics refer to components that are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This method contrasts with traditional through-hole technology, where components are inserted into holes in the PCB. The transition to SMD technology has been driven by several factors:
- Space Efficiency: SMD components are typically smaller than their through-hole counterparts, allowing for denser packing on PCBs.
- Automated Assembly: The SMT process facilitates automation, reducing labor costs and increasing production speed.
- Improved Performance: SMDs often exhibit better performance characteristics due to shorter lead lengths and reduced parasitic inductance.
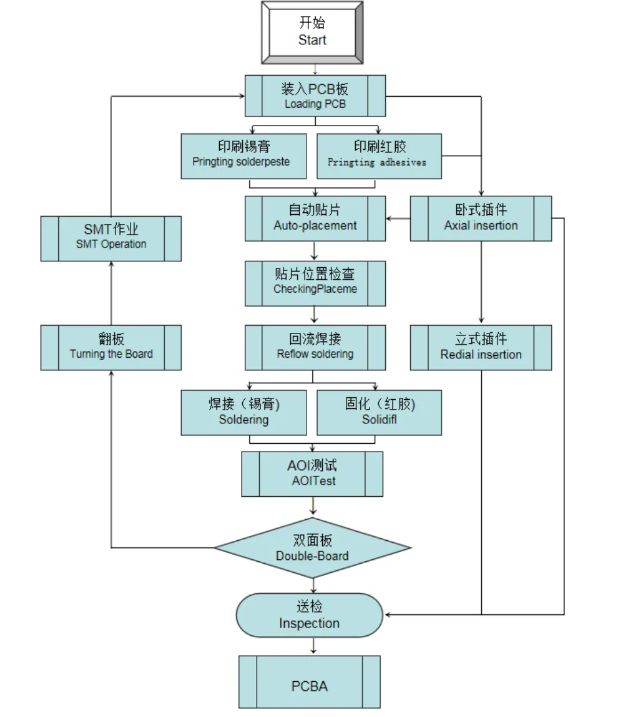
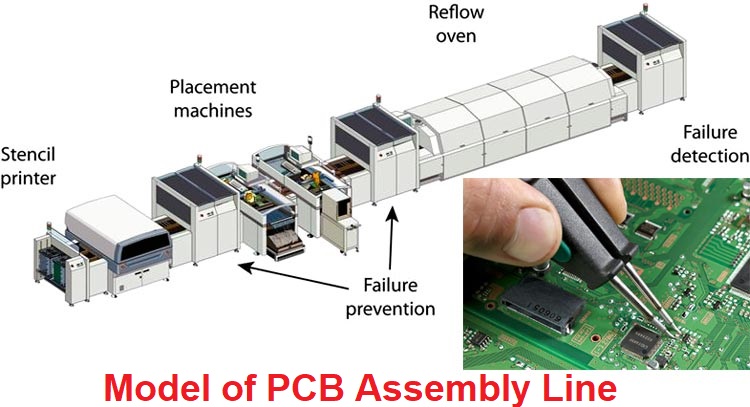
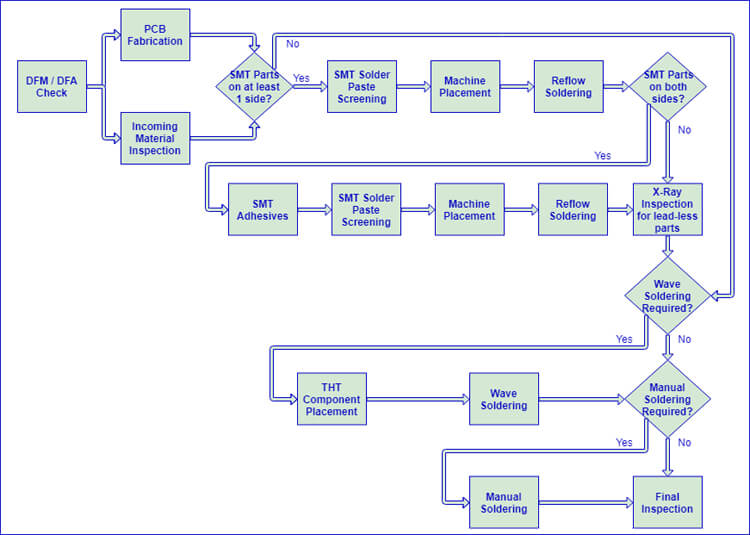
The SMT Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for SMD electronics can be broken down into several key stages:
1. Design and Fabrication of PCBs: The initial step involves designing the PCB layout to accommodate SMD components. The fabrication process includes creating solder pads that will hold the components.
2. Solder Paste Printing: A stencil is used to apply solder paste to the PCB pads. This paste serves as both an adhesive and a conductive medium during soldering.
3. Component Placement: Using pick-and-place machines, SMD components are accurately positioned on the solder paste-covered pads.
4. Reflow Soldering: The assembled PCB is heated in a reflow oven, where the solder paste melts and solidifies, creating strong electrical connections.
5. Inspection and Testing: After soldering, PCBs undergo rigorous inspection to ensure quality and functionality.
Advantages of SMD Electronics
The adoption of SMD technology offers numerous benefits:
- Compact Design: The smaller size of SMD components allows for more compact designs, which is crucial for modern electronic devices that demand portability.
- Higher Reliability: With fewer mechanical connections, SMDs tend to be more robust against vibrations and shocks.
- Cost Efficiency: Although initial setup costs for SMT equipment can be high, the reduction in labor costs and increased production speed lead to lower overall manufacturing costs.
- Enhanced Performance: Due to their design, SMD components often have superior electrical performance compared to traditional components. They exhibit lower resistance and inductance, which is vital for high-speed applications.
- Thermal Management: Many SMD components are designed with better thermal characteristics, allowing them to dissipate heat more effectively than through-hole components.
Applications of SMD Electronics
SMD technology is prevalent across various industries including:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearables utilize SMDs for their compactness and efficiency.
- Automotive Industry: Modern vehicles incorporate numerous electronic systems that rely on SMD technology for functionalities like navigation systems, engine management systems, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
- Medical Devices: Precision instruments often use SMDs for their reliability and small form factor. Devices such as pacemakers and diagnostic equipment benefit from the compact nature of these components.
- Telecommunications: High-frequency applications in telecommunications equipment rely heavily on SMD technology due to its performance advantages at high frequencies.
Future Trends in SMD Electronics
As technology advances, several trends are shaping the future of SMD electronics:
- Miniaturization: Continued efforts towards smaller component sizes will further enhance device performance. Innovations such as 3D packaging techniques allow manufacturers to create even more compact designs without sacrificing functionality.
Miniaturization in Electronics
- Integration with IoT: The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) necessitates efficient and compact electronic solutions. As devices become smarter and more interconnected, the demand for advanced SMD technologies will increase significantly.
IoT Devices
- Sustainability Initiatives: Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on environmentally friendly practices throughout the SMT process. This includes using lead-free solder materials and optimizing production processes to reduce waste.
Challenges Facing SMD Electronics
While there are many advantages to using SMD technology, there are also challenges that manufacturers must navigate:
- Complexity in Design: Designing PCBs with SMD components can be more complex than traditional methods. Engineers must consider factors such as thermal management and signal integrity during the design phase.
PCB Design Complexity
- Repairability Issues: Repairing or replacing faulty SMD components can be more challenging compared to through-hole components due to their small size and placement on the PCB.
Repairing SMD Components
- Equipment Costs: While automation can reduce long-term costs, the initial investment in SMT equipment can be significant. Smaller manufacturers may struggle with these upfront costs.
Best Practices for Working with SMD Electronics
To maximize the benefits of SMD technology while mitigating potential challenges, manufacturers should consider implementing best practices:
1. Invest in Quality Equipment: High-quality pick-and-place machines and reflow ovens can significantly improve production efficiency and product quality.
2. Focus on Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Engaging in DFM practices during the design phase can help identify potential issues early on, reducing costly modifications later.
3. Implement Rigorous Testing Protocols: Regular testing throughout the manufacturing process ensures that any defects are identified early, maintaining high-quality standards.
4. Train Staff on New Technologies: Continuous training programs for staff on new technologies and processes will help keep production lines running smoothly.
5. Stay Updated on Industry Trends: Keeping abreast of advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques can provide a competitive edge.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SMD electronics represent a significant advancement in manufacturing technology, offering numerous advantages over traditional methods. As a leading player in this field, Global Soul Limited continues to innovate and provide high-quality solutions that meet the demands of a rapidly changing market. The future looks promising as we embrace miniaturization, IoT integration, and sustainable practices within the realm of electronics manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between SMT and through-hole technology?
- SMT involves mounting components directly on the surface of PCBs, while through-hole technology requires inserting leads into holes on the board.
2. Why are SMD components preferred in modern electronics?
- They are smaller, facilitate automated assembly, provide improved performance characteristics such as lower resistance and inductance.
3. What industries benefit from SMD electronics?
- Industries such as consumer electronics, automotive applications, medical devices, telecommunications equipment benefit significantly from SMD technology.
4. How does reflow soldering work?
- Reflow soldering involves heating solder paste until it melts and then cooling it to create strong electrical connections between components and PCBs.
5. What future trends should we expect in SMD manufacturing?
- Expect trends like miniaturization of components, integration with IoT technologies, increased focus on sustainability practices within manufacturing processes.




















