Content Menu
● Understanding Surface Mount Technology
● Advantages of SMT in Electronics Manufacturing
>> Higher Component Density
>> Improved Performance
>> Cost Efficiency
>> Design Flexibility
>> Enhanced Reliability
>> Reduced Assembly Time
>> Lower Weight and Size
>> Simplified PCB Design
>> Less Waste Generation
● Additional Benefits of Using SMT
>> Scalability
>> Compatibility with Automated Processes
>> Faster Time-to-Market
>> Support for Advanced Technologies
>> Improved Signal Integrity
● Challenges Associated with SMT
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
>> 2. What tools are essential for SMT?
>> 3. How does SMT improve product reliability?
>> 4. What are some challenges associated with implementing SMT?
>> 5. Can SMT be used for all types of electronic devices?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry, providing numerous advantages over traditional through-hole technology. As manufacturers strive for efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness, SMT has emerged as a preferred choice for assembling electronic components. This article explores the advantages of using SMT in electronics manufacturing, delving into its impact on design flexibility, production efficiency, and overall product quality.
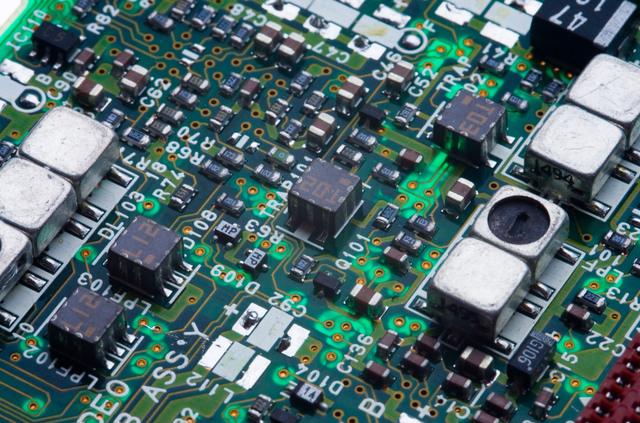
Understanding Surface Mount Technology
Before discussing the advantages of SMT, it is essential to understand what it entails. Surface Mount Technology involves mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional methods where components are inserted through holes in the PCB, SMT allows for a more compact design and a higher density of components.
The tools and equipment used in SMT include:
- Pick and Place Machines: These machines are crucial for accurately placing surface mount components on PCBs. They use advanced vision systems to ensure precise placement.
- Reflow Ovens: After placement, PCBs are passed through reflow ovens where solder paste is melted to create reliable electrical connections.
- Stencil Printers: These are used to apply solder paste onto the PCB before component placement.
- Inspection Equipment: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems are employed to verify the correct placement and soldering of components.
Understanding these tools is vital for appreciating how SMT enhances manufacturing processes.
Advantages of SMT in Electronics Manufacturing
Higher Component Density
One of the most significant advantages of SMT is its ability to accommodate a higher density of components on a PCB. This is particularly beneficial for modern electronics that require miniaturization. By eliminating the need for leads that extend through the board, components can be placed closer together. This increased density allows for smaller devices without compromising functionality.
Improved Performance
SMT can enhance the performance of electronic devices. The shorter leads used in surface-mounted components reduce inductance and resistance, leading to better electrical performance. Additionally, SMT allows for better thermal management due to the reduced size and weight of components, which can be critical in high-performance applications.
Cost Efficiency
Using SMT can significantly reduce manufacturing costs. The compact nature of surface-mounted components requires less material for PCBs, leading to lower material costs. Moreover, the automated processes associated with SMT reduce labor costs and increase production speed. With fewer manual interventions needed, manufacturers can achieve higher throughput.
Design Flexibility
SMT provides designers with greater flexibility when creating electronic devices. The ability to place components on both sides of a PCB allows for more intricate designs and functionalities. Designers can also take advantage of various component types that are only available in surface mount formats, enabling innovative product features that were not possible with traditional methods.
Enhanced Reliability
The reliability of electronic devices is crucial for customer satisfaction and brand reputation. SMT contributes to enhanced reliability through improved solder joints and reduced mechanical stress on components. The soldering process used in SMT creates strong bonds that can withstand thermal cycling and vibrations better than through-hole connections.
Reduced Assembly Time
The automated nature of SMT assembly leads to reduced assembly times compared to manual processes used in through-hole technology. Pick and place machines can rapidly position thousands of components per hour, significantly speeding up production cycles. This efficiency not only saves time but also allows manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands.

Lower Weight and Size
As consumer electronics trends move toward portability and compactness, SMT plays a vital role in reducing the weight and size of electronic devices. Smaller PCBs with densely packed components lead to lighter products that are easier to transport and use.
Simplified PCB Design
SMT simplifies PCB design by allowing for fewer layers in the circuit board construction. With traditional methods requiring more space for component leads, designers often had to create multi-layer boards to accommodate all necessary connections. SMT reduces this complexity, enabling simpler designs that are easier to manufacture.
Less Waste Generation
The use of SMT contributes to less waste generation during manufacturing processes. Since surface-mounted components require less material than their through-hole counterparts, there is less scrap produced during assembly. Additionally, automated processes minimize human error, further reducing waste associated with defective products.
Additional Benefits of Using SMT
Scalability
SMT processes are highly scalable, making them suitable for both small-scale prototypes and large-scale production runs. Manufacturers can easily adjust their production volumes without significant changes to their setup or equipment.
Compatibility with Automated Processes
SMT is inherently compatible with automation technologies such as robotics and machine learning systems that enhance production efficiency further. As industries adopt Industry 4.0 practices, integrating SMT with smart manufacturing systems becomes more feasible.
Faster Time-to-Market
The combination of reduced assembly times and improved design flexibility means that products can move from concept to market more quickly than ever before. This rapid development cycle is crucial in competitive industries where being first can lead to significant market advantages.
Support for Advanced Technologies
As technology evolves, so do consumer expectations regarding device capabilities such as connectivity (e.g., IoT devices), performance (e.g., high-speed computing), and functionality (e.g., multi-functional gadgets). SMT supports these advanced technologies by enabling complex circuitry within compact spaces.
Improved Signal Integrity
In high-frequency applications such as telecommunications or RF circuits, signal integrity is paramount. The shorter leads used in SMT help maintain signal integrity by minimizing parasitic capacitance and inductance that can occur with longer leads found in through-hole designs.
Challenges Associated with SMT
While SMT offers numerous advantages, it is essential to acknowledge some challenges associated with its implementation:
- Initial Setup Costs: The initial investment in SMT equipment such as pick and place machines and reflow ovens can be high.
- Complexity in Design: Designing PCBs for surface mounting requires specialized knowledge and experience.
- Repair Difficulties: Repairing or replacing surface-mounted components can be more challenging than through-hole components due to their small size and placement on both sides of the board.
- Thermal Management: While SMT allows for better thermal management overall, it also necessitates careful consideration during design stages regarding heat dissipation from densely packed components.
- Solder Joint Reliability: Although solder joints created through reflow processes tend to be strong, they may still be susceptible to certain types of mechanical stress or thermal cycling if not designed properly.
Despite these challenges, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks for many manufacturers who prioritize efficiency and innovation in their production processes.
Conclusion
Surface Mount Technology has transformed electronics manufacturing by offering several advantages such as higher component density, improved performance, cost efficiency, design flexibility, enhanced reliability, reduced assembly time, lower weight and size, simplified PCB design, less waste generation, scalability, compatibility with automated processes, faster time-to-market, support for advanced technologies, and improved signal integrity. As technology continues to evolve, SMT will likely play an even more significant role in shaping the future of electronic devices.
Manufacturers who embrace SMT can gain a competitive edge by producing high-quality products that meet consumer demands for smaller, lighter, and more efficient electronics while also addressing the challenges associated with this technology effectively.

FAQ
1. What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a method used in electronics manufacturing where components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), allowing for higher density and improved performance compared to traditional through-hole technology.
2. What tools are essential for SMT?
Key tools for SMT include pick and place machines for component placement, reflow ovens for soldering connections, stencil printers for applying solder paste, and inspection equipment such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems.
3. How does SMT improve product reliability?
SMT improves product reliability by creating stronger solder joints with reduced mechanical stress on components due to shorter leads compared to through-hole connections.
4. What are some challenges associated with implementing SMT?
Challenges include high initial setup costs for specialized equipment, complexity in PCB design requiring specialized knowledge, difficulties in repairing or replacing small surface-mounted components, thermal management considerations due to component density, and ensuring solder joint reliability under various conditions.
5. Can SMT be used for all types of electronic devices?
While SMT is highly versatile and suitable for many applications—particularly those requiring miniaturization—it may not be ideal for all types of electronic devices; larger or more robust components typically associated with through-hole technology might still be necessary depending on specific use cases.




















