Content Menu
● Introduction
● Understanding Surface Mount Devices
>> Definition of Surface Mount Devices
>> Types of Surface Mount Devices
● How Surface Mount Devices Work
>> The Soldering Process
>> Advantages of Surface Mount Devices
● Applications of Surface Mount Devices
>> Consumer Electronics
>> Automotive Industry
>> Medical Devices
>> Industrial Applications
● Challenges and Considerations
>> Handling and Placement
>> Repair and Rework
>> Thermal Management
● Future Trends in Surface Mount Technology
>> Miniaturization
>> Advanced Materials
>> Automation and AI
● Conclusion
● Related Questions
>> 1. What is the difference between surface mount devices and through-hole components?
>> 2. How are surface mount devices soldered to a PCB?
>> 3. What are the common types of surface mount devices?
>> 4. What industries commonly use surface mount devices?
>> 5. What challenges are associated with using surface mount devices?
Introduction
In the realm of modern electronics, the term surface mount device (SMD) has become increasingly prevalent. These devices are integral to the design and manufacturing of compact, efficient electronic circuits. This article delves into what surface mount devices are, how they function, their advantages, applications, and the technology behind them. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of SMDs and their significance in the electronics industry.
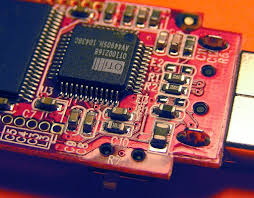
Understanding Surface Mount Devices
Definition of Surface Mount Devices
A surface mount device is a type of electronic component that is mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). Unlike traditional components that require holes drilled into the PCB for insertion, SMDs are soldered onto pads on the board's surface. This method of mounting allows for a more compact design and is essential for modern electronic devices that demand miniaturization.
Types of Surface Mount Devices
Surface mount devices come in various forms, including:
- Resistors: Used to limit current flow in circuits.
- Capacitors: Store and release electrical energy.
- Inductors: Store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Complex components that can perform various functions, from simple logic operations to complex processing tasks.
- Diodes: Allow current to flow in one direction only, used for rectification and signal modulation.
Each type of SMD has specific characteristics and applications, making them versatile components in electronic design.
How Surface Mount Devices Work
The Soldering Process
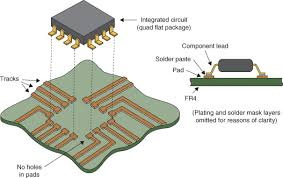
The process of attaching surface mount devices to a PCB involves several steps:
1. Solder Paste Application: A solder paste, which is a mixture of tiny solder balls and flux, is applied to the pads on the PCB where the SMDs will be placed.
2. Component Placement: SMDs are placed on the solder paste using automated pick-and-place machines. This precision placement is crucial for ensuring that the components are correctly aligned with the pads.
3. Reflow Soldering: The PCB is then heated in a reflow oven, causing the solder paste to melt and form a solid connection between the SMDs and the PCB. This process is critical for creating reliable electrical connections.
4. Inspection and Testing: After soldering, the assembled PCB undergoes inspection and testing to ensure that all components are correctly placed and functioning as intended.
Advantages of Surface Mount Devices
The use of surface mount devices offers several advantages over traditional through-hole components:
- Space Efficiency: SMDs are typically smaller than their through-hole counterparts, allowing for more components to be placed on a single PCB. This is particularly important in compact devices like smartphones and tablets.
- Improved Performance: The shorter leads of SMDs reduce inductance and resistance, which can enhance the performance of high-frequency circuits.
- Automated Assembly: The ability to use automated machines for placement and soldering reduces labor costs and increases production speed.
- Design Flexibility: SMDs allow for more complex circuit designs, enabling engineers to create innovative products with advanced functionalities.
Applications of Surface Mount Devices
Surface mount devices are used in a wide range of applications across various industries:
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, SMDs are ubiquitous. They are found in devices such as smartphones, laptops, televisions, and gaming consoles. The compact nature of SMDs allows manufacturers to create sleek, lightweight products without sacrificing performance.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has increasingly adopted surface mount technology for electronic control units (ECUs), sensors, and infotainment systems. SMDs contribute to the miniaturization of components, which is essential for modern vehicles that incorporate advanced technologies like autonomous driving and connectivity.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, SMDs are used in diagnostic equipment, monitoring devices, and therapeutic instruments. The reliability and compactness of SMDs are critical in ensuring that medical devices function correctly and fit within the constraints of portable and wearable technologies.
Industrial Applications
Surface mount devices are also prevalent in industrial applications, including automation systems, robotics, and control systems. Their robustness and efficiency make them suitable for environments where reliability is paramount.

Challenges and Considerations
While surface mount devices offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges associated with their use:
Handling and Placement
SMDs are smaller and more delicate than traditional components, making them more challenging to handle during assembly. Proper training and equipment are necessary to ensure that components are not damaged during placement.
Repair and Rework
Repairing or replacing SMDs can be more complicated than through-hole components. Specialized tools and techniques are often required to desolder and replace SMDs without damaging the PCB.
Thermal Management
SMDs can generate heat during operation, and managing this heat is crucial for maintaining performance and reliability. Engineers must consider thermal dissipation in their designs to prevent overheating.
Future Trends in Surface Mount Technology
As technology continues to evolve, so does the field of surface mount devices. Some trends to watch include:
Miniaturization
The demand for smaller, more powerful devices will drive further miniaturization of SMDs. Innovations in materials and manufacturing processes will enable the development of even smaller components.
Advanced Materials
The use of advanced materials, such as flexible substrates and high-performance ceramics, will enhance the capabilities of SMDs, allowing for new applications in emerging fields like wearable technology and IoT devices.
Automation and AI
The integration of automation and artificial intelligence in the manufacturing process will improve efficiency and precision in the assembly of SMDs, reducing costs and increasing production rates.
Conclusion
Surface mount devices are a cornerstone of modern electronics, enabling the creation of compact, efficient, and high-performance products. Their unique characteristics and advantages make them indispensable in various industries, from consumer electronics to automotive and medical applications. As technology continues to advance, the role of SMDs will only grow, paving the way for innovative solutions and products that meet the demands of an increasingly connected world.
Related Questions
1. What is the difference between surface mount devices and through-hole components?
Surface mount devices are mounted directly on the surface of a PCB, while through-hole components require holes to be drilled into the board for insertion. SMDs are generally smaller and allow for more compact designs.
2. How are surface mount devices soldered to a PCB?
SMDs are soldered using a process that involves applying solder paste to the PCB, placing the components, and then heating the assembly in a reflow oven to melt the solder and create electrical connections.
3. What are the common types of surface mount devices?
Common types of SMDs include resistors, capacitors, inductors, integrated circuits, and diodes, each serving different functions in electronic circuits.
4. What industries commonly use surface mount devices?
SMDs are widely used in consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, and industrial applications due to their compact size and efficiency.
5. What challenges are associated with using surface mount devices?
Challenges include handling and placement difficulties, repair and rework complexities, and thermal management issues that must be addressed in design and manufacturing.




















