Content Menu
>> I. What is SMT and Why is it Important?
>> II. The SMT Assembly Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
>>> 1. PCB Preparation
>>> 2. Solder Paste Application
>>> 3. Component Placement
>>> 4. Reflow Soldering
>>> 5. Inspection
>>> 6. Testing
>>> 7. Cleaning
>>> 8. Final Inspection
>> III. Key Equipment in an SMT Line
>> IV. Types of PCB SMT Machines
>> V. Popular PCB SMT Machine Manufacturers
>> VI. Factors to Consider Before Investing in a PCB SMT Machine
>> VII. Advantages of Using a PCB SMT Machine
>> VIII. Finding the Right PCB SMT Machine Manufacturer
>> IX. Cost Analysis: Is it Worth the Investment?
>> X. Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
● FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About PCB SMT Machines
>>> Q1: What is the main purpose of a PCB SMT machine?
>>> Q2: What are the main components of an SMT line?
>>> Q3: What are the benefits of SMT over through-hole technology?
>>> Q4: What factors should I consider before investing in a PCB SMT machine?
>>> Q5: How do I choose the right PCB SMT machine manufacturer?
I. What is SMT and Why is it Important?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) involves mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB[1][5]. This automated process contrasts with older through-hole technology, offering higher component density, improved reliability, and reduced manufacturing costs[3]. SMT is crucial for producing smaller, more efficient electronic devices[3].
II. The SMT Assembly Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The SMT assembly process comprises several key stages[1]:
1. PCB Preparation
The PCB is cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect soldering[1].
2. Solder Paste Application
A stencil printing machine applies solder paste to the PCB where components will be placed[1][3]. The solder paste mixer can efficiently mix the solder powder and the solder paste evenly[3].
3. Component Placement
A pick and place machine accurately places surface mount components onto the PCB[1][3]. Component placement is determined by design data to ensure proper positioning[1].
4. Reflow Soldering
The board is heated in a reflow oven, melting the solder paste and creating solder joints[1][3]. There are many types of reflow, such as hot air reflow, Infrared reflow, hot gas reflow, etc, in which, hot air reflow is generally used[3].
5. Inspection
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) is used to check for defects like missing components, misalignment, or solder bridges[1][3]. In some cases, X-ray inspection can be used to check the quality of a solder joint if there are components with hidden or fine-pitch leads[1]. Also, a SPI Machine (Solder Paste Inspection) might be used after solder paste printing for checking the thickness, area, and volume distribution of solder paste printed on the PCBs[3].
6. Testing
The board undergoes tests to ensure it functions correctly[1].
7. Cleaning
The PCB may be cleaned to remove leftover flux[1].
8. Final Inspection
A final check ensures everything looks good before packing[1].
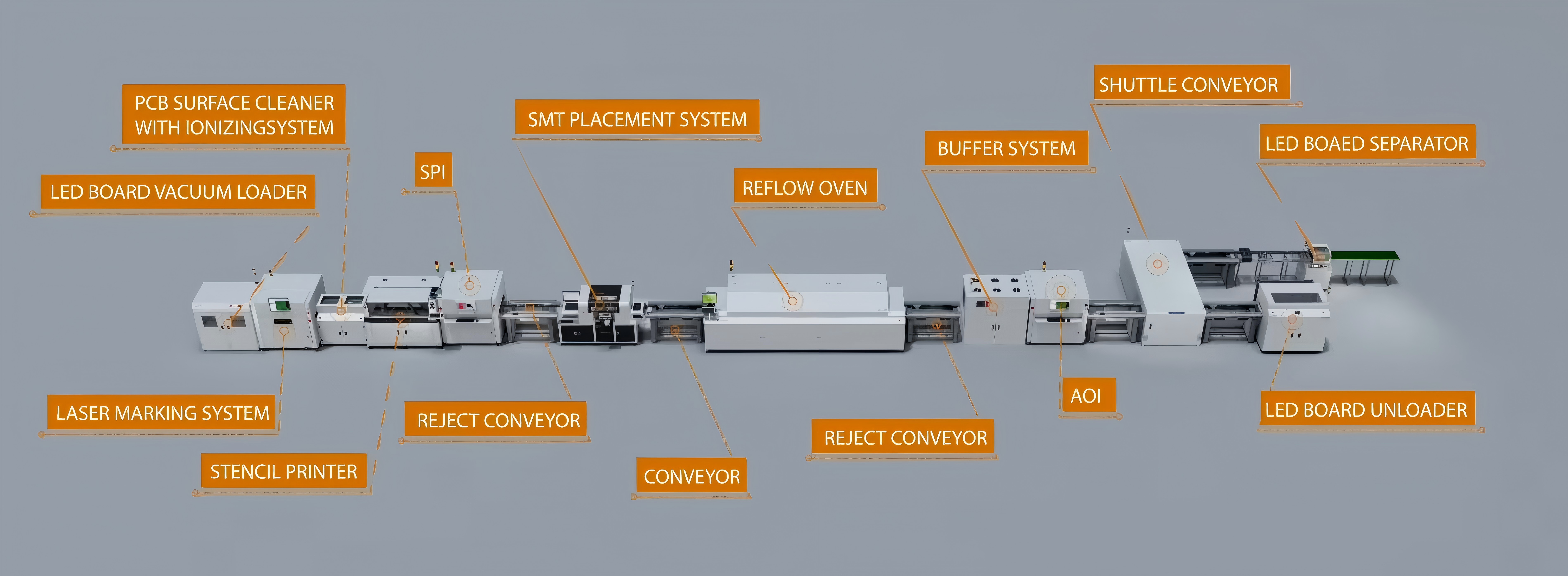
III. Key Equipment in an SMT Line
An SMT line consists of several interconnected machines[1][3]:
1. SMT Loader: Automatically loads PCBs onto the conveyor[1][3].
2. Stencil Printing Machine: Applies solder paste to the PCBs[1][3].
3. Pick and Place Machine: Places components onto the PCB[1][3].
4. Reflow Oven: Melts the solder[1][3].
5. AOI Machine: Inspects for defects[1][3].
6. SMT Unloader: Receives completed PCBs[1][3].
7. Docking Station: Used as a connection station between different equipment in an SMT line[3].
IV. Types of PCB SMT Machines
PCB SMT machines vary in automation level[7]:
* Manual Pick and Place Machines: The SMT operator performs the picking and placement procedure manually on this machine[7].
* Semi-automatic Pick and Place Machines: Features advanced computer interface technology and vision assistance, making the operator's job easier[7].
* Automated Pick and Place Machines: Incorporate picking and placement centering methods to enhance SMT productivity[7].
V. Popular PCB SMT Machine Manufacturers
Several manufacturers offer PCB SMT machines[2][4][6]:
* Mycronic: Known for strong software and precise material handling[2].
* JUKI: Offers a large portfolio of placement machines[2].
* DDM Novastar: Designs pick-and-place equipment for low-to-medium applications[2][4].
* Neoden SMT: Specializes in full automatic SMT lines[2].
* Panasonic: Advocates for Smart Factory Solutions and versatile SMT machines[2].
* Hanwha Precision Machinery: Has manufactured SMT mounters since 1989[2].
* Europlacer: A top SMT machine manufacturer[6].
* Assemblon: A top SMT machine manufacturer[6].
* PCB Unlimited: Offers a convenient way for engineers and businesses to order high-quality SMT assembly machines. They have partnered with excellent SMT manufacturers like DDM Novastar, LPKF, Dektec, etc[4].
VI. Factors to Consider Before Investing in a PCB SMT Machine
Before investing in a PCB SMT machine, consider these factors:
* Production Volume: Determine your current and projected production needs.
* Component Complexity: Ensure the machine can handle the range of components you use.
* Budget: Establish a budget for initial investment, operation, and maintenance.
* Automation Level: Choose the appropriate automation level for your needs[7].
* Space Requirements: Consider the space needed for the SMT line.
* Training and Support: Evaluate the training and support offered by the manufacturer.
VII. Advantages of Using a PCB SMT Machine
* Increased Efficiency: Automates the assembly process, increasing speed and throughput.
* Improved Accuracy: Reduces human error in component placement.
* Reduced Costs: Lowers labor costs and material waste.
* Higher Reliability: Produces more consistent and reliable solder joints.
* Smaller Size: Enables the production of smaller and more compact electronic devices.
VIII. Finding the Right PCB SMT Machine Manufacturer
Choosing the right PCB SMT machine manufacturer is crucial for a successful investment. Look for manufacturers with:
* Experience and Expertise: A proven track record in the industry.
* Comprehensive Product Range: Machines to meet diverse needs.
* Customization Options: Ability to tailor machines to specific requirements.
* Excellent Service and Support: Installation, training, and ongoing support.
* Positive Customer Reviews: A good reputation among existing customers.
PCB Unlimited has partnered with the industry's top manufacturers, such as DDM Novastar, LPKF, Spide, Torch, and Dektec[4].
IX. Cost Analysis: Is it Worth the Investment?
Determining whether a PCB SMT machine is a worthwhile investment requires a thorough cost analysis:
1. Initial Investment: The cost of the machine itself.
2. Installation Costs: Expenses related to setting up the machine.
3. Training Costs: The cost of training personnel to operate the machine.
4. Operating Costs: Ongoing expenses like labor, materials, and energy.
5. Maintenance Costs: The cost of regular maintenance and repairs.
Compare these costs with the potential benefits, such as increased production, reduced labor, and improved quality, to determine the Return on Investment (ROI).
X. Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Investing in a PCB SMT machine is a significant decision. By understanding the SMT process, the types of machines available, and the factors influencing cost and performance, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your manufacturing needs and budget. Careful evaluation and selection of a reliable PCB SMT machine manufacturer will further ensure a successful investment.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About PCB SMT Machines
Q1: What is the main purpose of a PCB SMT machine?
A: To automate the process of placing electronic components onto the surface of a PCB[1].
Q2: What are the main components of an SMT line?
A: SMT loader, stencil printing machine, pick and place machine, reflow oven, AOI machine, and SMT unloader[1][3].
Q3: What are the benefits of SMT over through-hole technology?
A: Higher component density, improved reliability, and reduced manufacturing costs[3].
Q4: What factors should I consider before investing in a PCB SMT machine?
A: Production volume, component complexity, budget, and automation level.
Q5: How do I choose the right PCB SMT machine manufacturer?
A: Look for experience, a comprehensive product range, customization options, and excellent service and support.



















