Content Menu
● Understanding Sticky SMD Parts for Pick and Place Machines
● Types of Sticky SMD Parts and Their Characteristics
● Preparing Your Pick and Place Machine for Sticky SMD Parts
>> 1. Select the Appropriate Nozzle
>> 2. Optimize Vacuum Pressure
>> 3. Calibrate Placement Parameters
>> 4. Use Adhesive Application When Needed
>> 5. Advanced Machine Settings
● Handling Sticky SMD Parts During Placement
>> 1. Component Feeding and Storage
>> 2. Pickup and Transport
>> 3. Placement Accuracy
>> 4. Post-Placement Verification
● Troubleshooting Common Issues with Sticky SMD Parts
>> Problem: Components Sticking to Nozzle After Pickup
>> Problem: Misplacement Due to Adhesive Smearing
>> Problem: Feeder Jamming with Sticky Parts
>> Problem: Difficulty Releasing Components on PCB
>> Problem: Adhesive Contamination on PCB Pads
● Best Practices for Using Sticky SMD Parts in Pick and Place Machines
● Tips for Maintaining Pick and Place Machines When Using Sticky SMD Parts
● Case Studies and Examples
>> Case Study 1: Automotive Electronics Assembly
>> Case Study 2: Consumer Electronics with Glue-dotted Components
>> Example: Using Vision Systems for Sticky Part Placement
● Environmental and Safety Considerations
● Common Mistakes When Using Sticky SMD Parts and How to Avoid Them
● Future Trends in Handling Sticky SMD Parts
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. How do I prevent sticky SMD parts from adhering to the pick and place nozzle?
>> 2. Can I use the same pick and place machine settings for sticky and non-sticky SMD parts?
>> 3. What types of adhesives are compatible with pick and place machines?
>> 4. How can I improve placement accuracy for sticky SMD parts?
>> 5. What maintenance is necessary for pick and place machines handling sticky SMD parts?
In the fast-paced world of electronics manufacturing, efficiency and precision are paramount. Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) play a critical role in modern electronic assemblies, and the pick and place machine is the backbone of automated PCB assembly lines. However, when dealing with sticky SMD parts, manufacturers face unique challenges that require specialized knowledge and techniques. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to properly using sticky SMD parts in pick and place machines, ensuring optimal performance and product quality.
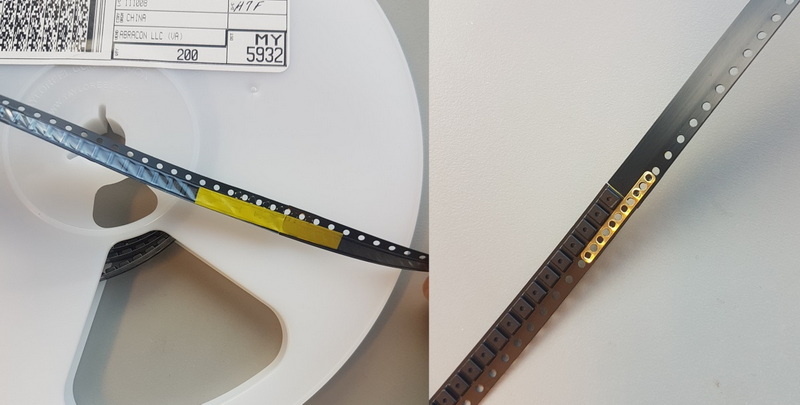

Understanding Sticky SMD Parts for Pick and Place Machines
Sticky SMD parts refer to surface mount components that have an adhesive or tacky surface, or that require adhesive application before placement to ensure they stay in position on the PCB during assembly. These parts may include components with pre-applied adhesive tapes, sticky pads, or those that need glue dots or solder paste to hold them temporarily before soldering.
Using sticky SMD parts effectively in a pick and place machine involves understanding their characteristics and how they interact with the machine's vacuum nozzles, feeders, and placement heads. Improper handling can cause components to stick to the nozzle, misalign, or be damaged during placement.
Types of Sticky SMD Parts and Their Characteristics
Sticky SMD parts come in various forms, each with unique characteristics that affect how they should be handled in pick and place machines. Some common types include:
- Pre-taped Components: These parts come with adhesive tape applied to their backs, providing tackiness to hold them in place during assembly. The tape's adhesive strength and thickness can vary, influencing pickup and placement.
- Glue-dotted Components: These parts have small dots of adhesive applied either by the manufacturer or during the assembly process. The glue dots provide temporary adhesion but require careful handling to avoid smearing or excess adhesive.
- Solder Paste Tacky Components: Some components rely on the tackiness of solder paste applied to PCB pads to hold them in place. This method requires precise solder paste application and careful placement to avoid disturbing the paste.
- Sticky Pads or Films: Certain components use sticky pads or films as part of their packaging or mounting method. These can leave residue on nozzles or feeders if not handled properly.
Understanding the type of sticky SMD part you are working with is crucial for selecting the right machine settings and handling techniques.
Preparing Your Pick and Place Machine for Sticky SMD Parts
1. Select the Appropriate Nozzle
The nozzle is the critical interface between the pick and place machine and the SMD parts. For sticky SMD parts, it is essential to use nozzles designed to minimize adhesion issues. Nozzles made from materials that reduce sticking, such as specialized plastics or coated metals, can help prevent components from adhering to the nozzle after pickup.
Adjust nozzle size carefully to match the component dimensions. A nozzle too large may cause vacuum loss or pick up multiple parts, while a nozzle too small may damage the sticky surface or fail to pick the component securely.
2. Optimize Vacuum Pressure
Sticky SMD parts may require fine-tuning of the vacuum pressure. Excessive vacuum can cause parts to stick too firmly to the nozzle, making release difficult and risking damage. Conversely, insufficient vacuum may lead to dropped parts. Adjust vacuum levels to balance secure pickup with easy release.
3. Calibrate Placement Parameters
The placement speed, downward force, and nozzle movement should be calibrated to handle sticky parts delicately. Slow placement speeds and gentle downward pressure help avoid smearing adhesives or dislodging parts from the PCB pads.
4. Use Adhesive Application When Needed
Some sticky SMD parts require additional adhesive application before placement. Integrating a glue-dispensing module or jet dispensing system into the pick and place machine can apply precise adhesive dots on the PCB pads, ensuring parts remain in place during transport and soldering.
5. Advanced Machine Settings
Beyond basic vacuum pressure and nozzle selection, advanced settings can further optimize the handling of sticky SMD parts:
- Vacuum Pulse Control: Some machines offer vacuum pulse or modulation features that can help release sticky parts more smoothly by momentarily reducing suction during placement.
- Nozzle Temperature Control: Heating or cooling nozzles can affect adhesive properties. For example, slightly warming the nozzle may reduce adhesive tackiness, aiding release.
- Placement Angle Adjustment: Adjusting the angle at which parts are placed can minimize adhesive smearing and improve alignment.
- Multi-step Placement: For particularly challenging sticky parts, a multi-step placement process involving initial gentle placement followed by a firmer press can improve results.
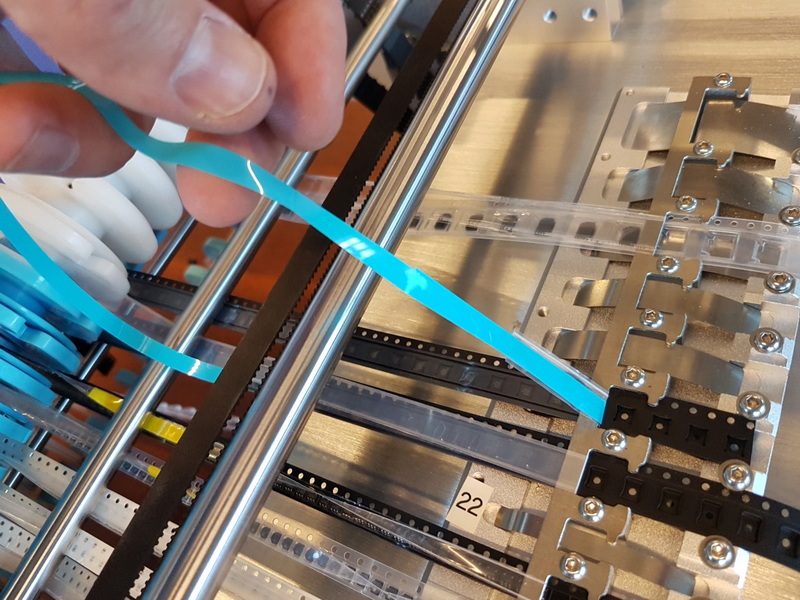

Handling Sticky SMD Parts During Placement
1. Component Feeding and Storage
Store sticky SMD parts in conditions that prevent premature adhesion or contamination. Use proper tape feeders or trays designed for sticky components to avoid jamming or misfeeds. Maintaining clean and dry storage environments is essential to preserve the adhesive properties without causing unwanted stickiness or residue buildup.
2. Pickup and Transport
When the machine picks up sticky parts, ensure the nozzle path is clear of obstacles to prevent collisions that could dislodge or damage parts. Use vision systems to verify component orientation and position before transport. Incorporating real-time feedback from vision sensors can help detect if the part is securely held or if adjustments are necessary.
3. Placement Accuracy
Leverage the machine's optical sensors and fiducial alignment to position sticky SMD parts precisely on the PCB pads. The adhesive or tacky surface should help hold the part in place once placed, but correct alignment is still critical to avoid defects. Adjust placement parameters such as speed and pressure based on component type and adhesive characteristics.
4. Post-Placement Verification
Use onboard cameras or external inspection systems to verify the placement quality of sticky parts. Detecting misalignments early allows for corrective actions before soldering. Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems can be programmed to specifically check for adhesive smearing, residue, or misplacement related to sticky components.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Sticky SMD Parts
Problem: Components Sticking to Nozzle After Pickup
- Solution: Use anti-adhesive nozzle coatings or switch to nozzles made from materials less prone to sticking. Adjust vacuum pressure to reduce suction force. Regular nozzle cleaning is crucial to remove any adhesive buildup that increases stickiness.
Problem: Misplacement Due to Adhesive Smearing
- Solution: Slow down placement speed and reduce downward force. Ensure adhesive application is controlled and not excessive. Use precise adhesive dispensing systems to avoid over-application.
Problem: Feeder Jamming with Sticky Parts
- Solution: Clean feeders regularly and use feeders designed for sticky or adhesive-backed components. Store parts properly to prevent adhesive buildup. Consider using anti-static and low-friction feeder materials.
Problem: Difficulty Releasing Components on PCB
- Solution: Check nozzle condition for wear or contamination. Adjust nozzle height and placement parameters for smooth release. Vacuum pulse control can assist in releasing sticky parts.
Problem: Adhesive Contamination on PCB Pads
- Solution: Use precise adhesive dispensing methods and avoid over-application. Clean PCB pads if necessary before soldering. Use compatible adhesives that do not leave residues harmful to soldering quality.
Best Practices for Using Sticky SMD Parts in Pick and Place Machines
- Always select the right nozzle size and material for sticky parts.
- Regularly maintain and clean nozzles and feeders to prevent adhesive buildup.
- Calibrate vacuum pressure and placement parameters for each sticky component type.
- Use vision systems for accurate component recognition and placement.
- Integrate adhesive dispensing if parts require additional tackiness.
- Conduct thorough post-placement inspection to ensure quality.
- Train operators on handling sticky SMD parts and machine adjustments.
- Monitor environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature to maintain adhesive performance.
Tips for Maintaining Pick and Place Machines When Using Sticky SMD Parts
Maintaining your pick and place machine is critical when working with sticky SMD parts to ensure consistent performance and avoid downtime:
- Regular Cleaning: Adhesive residues can accumulate on nozzles, feeders, and placement heads. Clean these components regularly using appropriate solvents and tools recommended by the machine manufacturer.
- Inspection of Nozzles: Check nozzles for wear, damage, or adhesive buildup. Replace nozzles that show signs of degradation to maintain pickup accuracy.
- Feeder Maintenance: Sticky parts can cause feeders to jam or malfunction. Keep feeders clean and lubricated as per manufacturer guidelines.
- Vacuum System Checks: Inspect vacuum pumps and lines for leaks or blockages that could affect suction power.
- Software Updates: Keep machine software updated to benefit from the latest features and improvements related to sticky part handling.
Case Studies and Examples
Case Study 1: Automotive Electronics Assembly
In automotive electronics, sticky SMD parts such as pre-taped capacitors are common. A manufacturer integrated a glue-dispensing system with their pick and place machine to apply precise adhesive dots on PCB pads. By optimizing vacuum pressure and using anti-adhesive nozzles, they reduced placement errors by a significant margin and improved throughput.
Case Study 2: Consumer Electronics with Glue-dotted Components
A consumer electronics company faced challenges with glue-dotted components sticking to nozzles. They implemented vacuum pulse control and regular nozzle cleaning schedules, which significantly decreased nozzle contamination and improved placement accuracy.
Example: Using Vision Systems for Sticky Part Placement
Vision systems can detect adhesive residue or misaligned parts before placement. By integrating real-time feedback, machines can adjust placement parameters dynamically, ensuring high-quality assembly even with sticky components.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Handling sticky SMD parts and adhesives requires attention to environmental and safety factors:
- Ventilation: Some adhesives emit fumes that require proper ventilation to protect workers.
- Storage Conditions: Adhesive properties can degrade with temperature and humidity changes, so storage conditions must be controlled.
- Disposal: Adhesive residues and contaminated materials should be disposed of according to environmental regulations.
Common Mistakes When Using Sticky SMD Parts and How to Avoid Them
Working with sticky SMD parts can be challenging, and several common mistakes can lead to defects or machine downtime:
- Using Incorrect Nozzle Types: Using standard nozzles instead of anti-adhesive or coated nozzles can cause parts to stick and misplace.
- Improper Vacuum Settings: Too high or too low vacuum pressure can cause parts to stick to the nozzle or drop prematurely.
- Ignoring Adhesive Compatibility: Using adhesives that are not compatible with the pick and place machine or PCB materials can cause residue buildup or poor adhesion.
- Neglecting Machine Maintenance: Failure to clean and maintain nozzles, feeders, and vacuum systems leads to adhesive buildup and mechanical issues.
- Inadequate Operator Training: Operators unfamiliar with sticky part handling may make errors in setup or troubleshooting.
- Over-application of Adhesive: Excess adhesive can cause smearing, contamination, and placement errors.
- Poor Storage Conditions: Exposure to humidity or temperature extremes can degrade adhesive properties.
Avoiding these mistakes involves careful planning, regular maintenance, and thorough training.
Future Trends in Handling Sticky SMD Parts
The electronics manufacturing industry continues to evolve, and handling sticky SMD parts is no exception. Emerging trends include:
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced vision systems powered by AI can better detect and adapt to sticky part challenges in real-time.
- Improved Adhesive Materials: Development of adhesives that provide strong temporary hold but release cleanly during placement.
- Robotic Enhancements: More precise and flexible robotic arms and nozzles designed specifically for sticky components.
- Integrated Quality Control: Inline inspection systems that automatically adjust machine parameters to optimize placement quality.
Conclusion
Using sticky SMD parts in your pick and place machine requires a combination of proper machine setup, careful handling, and precise process control. Selecting the right nozzles, optimizing vacuum and placement parameters, and applying adhesives correctly are key to achieving high placement accuracy and preventing defects. Regular maintenance and inspection further ensure smooth operation and product quality. By following these guidelines, manufacturers can effectively integrate sticky SMD parts into automated assembly lines, enhancing efficiency and reliability.
By continuously refining your processes and staying informed about the latest technologies and best practices, you can overcome the challenges posed by sticky SMD parts. This proactive approach not only improves assembly quality but also enhances overall manufacturing efficiency and reduces costs.
FAQ
1. How do I prevent sticky SMD parts from adhering to the pick and place nozzle?
To prevent sticky parts from sticking to the nozzle, use nozzles made of anti-adhesive materials or coated with non-stick surfaces. Adjust vacuum pressure to the minimum required for secure pickup, and ensure nozzles are clean and free of residue. Regular cleaning schedules and vacuum pulse control can also help.
2. Can I use the same pick and place machine settings for sticky and non-sticky SMD parts?
No, sticky SMD parts often require different vacuum pressures, nozzle types, and placement speeds compared to non-sticky parts. It is important to calibrate the machine settings specifically for sticky components to avoid placement errors.
3. What types of adhesives are compatible with pick and place machines?
Adhesives used should be compatible with the machine's dispensing system and should not clog nozzles. Common types include UV-curable adhesives, hot melt glues, and solder paste with tacky properties. The adhesive must allow temporary holding without interfering with soldering.
4. How can I improve placement accuracy for sticky SMD parts?
Use vision systems and fiducial alignment to precisely position components. Slow down placement speed and apply gentle downward force to avoid disturbing the adhesive. Regularly inspect and maintain machine calibration.
5. What maintenance is necessary for pick and place machines handling sticky SMD parts?
Regular cleaning of nozzles and feeders to remove adhesive residue is essential. Inspect nozzles for wear or damage and replace them as needed. Maintain vacuum system integrity and ensure adhesive dispensing modules are functioning properly.




















