Content Menu
● Understanding SMT Products
● Regular Maintenance Practices
>> Establish a Maintenance Schedule
>> Cleaning Protocols
>> Calibration and Testing
● Process Optimization Techniques
>> Automation
>> Lean Manufacturing Principles
>> Quality Control Measures
● Environmental Considerations
>> Temperature and Humidity Control
>> Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection
● Training and Development
>> Continuous Training Programs
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
>> 2. How often should I perform maintenance on my SMT equipment?
>> 3. What are common issues faced during SMT assembly?
>> 4. How can I improve the quality of my SMT assemblies?
>> 5. What environmental conditions are ideal for SMT manufacturing?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry by allowing for more compact, reliable, and efficient assembly of electronic components. However, to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of SMT products, a comprehensive maintenance and optimization strategy is essential. This article explores effective techniques to maintain and optimize SMT products, ensuring they operate efficiently over time.
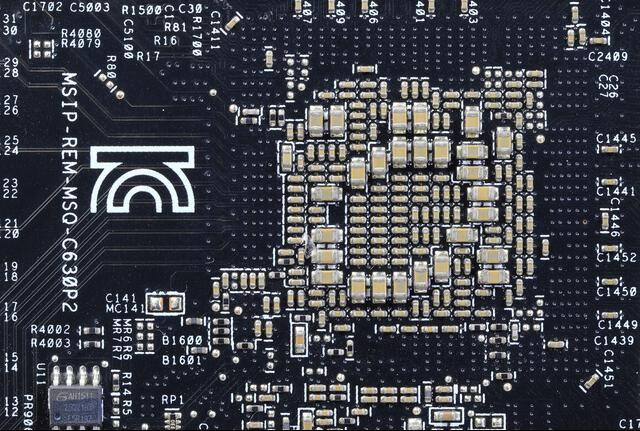

Understanding SMT Products
SMT products are integral to modern electronics, involving the mounting of electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This method contrasts with traditional through-hole technology (THT), where components are inserted into holes in the PCB. The advantages of SMT include:
- Higher Density: SMT allows for more components to be placed on a PCB, facilitating miniaturization.
- Improved Performance: The shorter electrical paths in SMT can lead to better performance and reduced electromagnetic interference.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation in SMT processes reduces labor costs and increases production speed.
To maximize these benefits, manufacturers must focus on maintaining their SMT equipment and processes.
Regular Maintenance Practices
Establish a Maintenance Schedule
Creating a detailed maintenance plan is crucial for the longevity of SMT products. This plan should include:
- Daily Checks: Inspect equipment for cleanliness and functionality. Look for dust accumulation on critical components like nozzles and feeders.
- Weekly Maintenance: Conduct thorough cleaning of machines, including solder paste printers and pick-and-place machines. Check for wear on mechanical parts.
- Monthly Inspections: Review calibration settings for all machines to ensure they meet manufacturer specifications. Replace any worn-out parts as necessary.
Regular maintenance not only extends the lifespan of equipment but also helps prevent unexpected breakdowns that can halt production.
Cleaning Protocols
Keeping SMT equipment clean is foundational to its performance. Dust and solder paste residue can lead to malfunctions. Implement the following cleaning protocols:
- Routine Cleaning: Clean surfaces, nozzles, and feeders regularly to prevent buildup that can affect machine accuracy.
- Use Appropriate Cleaning Solutions: Ensure that the cleaning agents used do not damage sensitive components.
- Scheduled Deep Cleaning: Plan for deeper cleaning sessions that involve disassembling parts of machines to clean hard-to-reach areas.
Calibration and Testing
Calibration is vital for maintaining the precision of SMT equipment. Regularly calibrate machines according to manufacturer guidelines:
- Solder Paste Printers: Ensure that the stencil thickness and printing pressure are optimized for each job.
- Pick-and-Place Machines: Regularly check placement accuracy and adjust settings as needed to maintain high placement rates.
- Reflow Ovens: Monitor temperature profiles closely to ensure consistent soldering quality across all boards.
Implementing a routine calibration schedule helps maintain product quality and reduces defects in assembled boards.
Process Optimization Techniques
Automation
Automation plays a significant role in enhancing efficiency within SMT processes. Automated systems can improve speed while reducing human error:
- Invest in Advanced Machinery: Upgrade to newer models with better diagnostic capabilities that alert operators about potential issues before they escalate.
- Integrate Software Solutions: Use software tools for real-time monitoring of production lines, allowing for quick adjustments based on performance data.
Lean Manufacturing Principles
Adopting lean manufacturing principles can help minimize waste and optimize workflows in SMT production:
- Identify Bottlenecks: Regularly analyze production flow to identify areas where delays occur and implement solutions to streamline these processes.
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Foster a culture of continuous improvement where employees are encouraged to suggest enhancements based on their experiences on the line.
Quality Control Measures
Implement robust quality control measures throughout the SMT process:
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Use AOI systems after each assembly stage to detect defects early in the process.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): Monitor critical parameters using SPC techniques to maintain consistency in production quality.
Environmental Considerations
The environment in which SMT products are manufactured significantly impacts their longevity:
Temperature and Humidity Control
Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels is crucial:
- Recommended Conditions: Keep temperatures between 20°C - 26°C (68°F - 79°F) with humidity levels between 30% - 60% RH to avoid moisture-related issues with components.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection
Implement ESD protection measures throughout the production area:
- Grounding Systems: Ensure all equipment is properly grounded to prevent static buildup that can damage sensitive electronic components.
- ESD-Safe Workstations: Use ESD-safe materials in work areas where sensitive components are handled.
Training and Development
Investing in employee training is essential for maintaining high-quality standards in SMT production:
Continuous Training Programs
Regular training sessions help keep employees updated on best practices:
- Skill Development Workshops: Offer workshops focused on machine operation, maintenance techniques, and troubleshooting skills.
- Cross-Training Employees: Encourage cross-training so that employees can operate multiple machines, providing flexibility during peak production times.
Conclusion
Maintaining and optimizing SMT products requires a multifaceted approach that includes regular maintenance, process optimization, environmental control, and employee training. By implementing these strategies, manufacturers can enhance the longevity of their SMT products while ensuring high-quality output. A commitment to continuous improvement will not only extend equipment life but also boost overall productivity in an increasingly competitive market.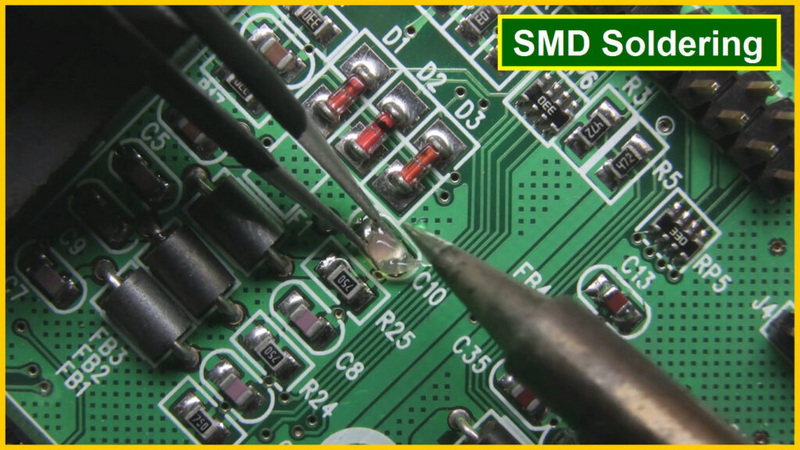
FAQ
1. What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) refers to a method used in electronics manufacturing where components are mounted directly onto the surface of PCBs instead of being inserted into holes as with traditional methods like through-hole technology (THT).
2. How often should I perform maintenance on my SMT equipment?
Maintenance should be performed regularly based on a set schedule—daily checks for cleanliness, weekly maintenance tasks, and monthly inspections for calibration adjustments are recommended practices to ensure optimal performance.
3. What are common issues faced during SMT assembly?
Common issues include misalignment during component placement, solder defects due to improper paste application or reflow profiles, and equipment malfunctions stemming from inadequate maintenance or calibration issues.
4. How can I improve the quality of my SMT assemblies?
To improve quality, focus on optimizing solder paste application techniques, ensuring accurate component placement through regular calibration of pick-and-place machines, and implementing robust inspection processes like AOI after each assembly stage.
5. What environmental conditions are ideal for SMT manufacturing?
The ideal environmental conditions for SMT manufacturing include maintaining temperatures between 20°C - 26°C (68°F - 79°F) and humidity levels between 30% - 60% RH to prevent moisture-related issues with electronic components.




















