Content Menu
● Understanding the Role of an SMD Resistor Cutting Machine
● Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an SMD Resistor Cutting Machine
>> 1. Compatibility with SMD Resistor Types and Sizes
>> 2. Cutting Precision and Consistency
>> 3. Automation and Control Features
>> 4. Build Quality and Mechanical Design
>> 5. Machine Size and Footprint
>> 6. Power Requirements and Safety Features
>> 7. Cost and After-Sales Support
● Types of SMD Resistor Cutting Machines
>> DIY and Arduino-Based Machines
>> Industrial Automatic Cutting Machines
● Integrating the SMD Resistor Making Machine into Your Workflow
● Additional Tips for Selecting the Best SMD Resistor Making Machine
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is an SMD resistor making machine?
>> 2. Can an Arduino-based resistor cutting machine handle different resistor sizes?
>> 3. How important is the cutting precision in an SMD resistor cutting machine?
>> 4. What maintenance is required for an SMD resistor cutting machine?
>> 5. How does the size of the SMD resistor affect the choice of cutting machine?
Surface Mount Device (SMD) resistors are fundamental components in modern electronics manufacturing. Efficient handling of these tiny components requires specialized equipment, especially when preparing them for assembly lines or prototyping. An SMD resistor making machine, particularly an SMD resistor cutting machine, automates the process of cutting resistor reels into manageable lengths, ensuring precision and productivity.
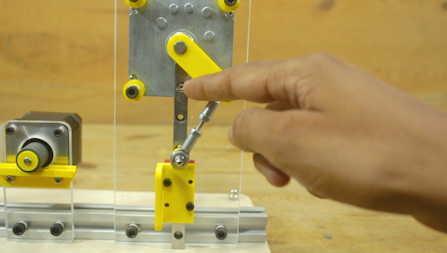
Choosing the right SMD resistor cutting machine can significantly improve your manufacturing workflow by reducing waste, increasing throughput, and maintaining component integrity. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the critical factors to consider when selecting an SMD resistor making machine, with a focus on cutting machines, their features, and how to align them with your specific production needs.
Understanding the Role of an SMD Resistor Cutting Machine
An SMD resistor cutting machine automates the process of cutting resistor tapes or reels into precise lengths. This step is crucial for efficient pick-and-place operations in PCB assembly. Manual cutting is not only labor-intensive but also prone to inconsistency and errors, which can lead to component wastage or assembly line stoppages.
The right cutting machine ensures:
- Accurate cutting length to prevent component wastage
- Consistent feed rate to match production speed
- Compatibility with various reel sizes and component types
- Ease of operation and maintenance
By automating the cutting process, manufacturers can maintain a steady supply of components, reduce human error, and improve overall production efficiency.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an SMD Resistor Cutting Machine
1. Compatibility with SMD Resistor Types and Sizes
SMD resistors come in a variety of standardized sizes, including 0201, 0402, 0603, 0805, 1206, and larger. Each size differs in physical dimensions and power ratings, which affects how the cutting machine must handle them.
- Size Range Support: Ensure the machine supports the full range of resistor sizes you use. Smaller sizes like 0201 require more delicate handling and precise cutting mechanisms.
- Tape Width and Thickness: The machine should accommodate different tape widths and thicknesses, as these vary by manufacturer and resistor type.
- Reel Compatibility: Check if the machine can handle different reel diameters and widths, which is important for flexibility in production.
2. Cutting Precision and Consistency
Precision is paramount to avoid damaging components or creating unusable cuts. Look for machines with:
- High-Precision Motors: Stepper motors or servo motors provide controlled feed and cutting length, ensuring repeatability.
- Sensors and Feedback Systems: Optical or mechanical sensors monitor tape position to guarantee consistent cutting.
- Adjustable Cutting Length: Ability to program or manually adjust cutting lengths to fit different production requirements.
High precision reduces component loss and ensures smooth downstream assembly processes.
3. Automation and Control Features
Automation enhances throughput and reduces labor costs. Consider machines that offer:
- Programmable Settings: Ability to set cutting lengths, batch quantities, and feed speeds.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: LCD touchscreens or software controls simplify operation.
- Integration Capability: Machines that can interface with other manufacturing equipment or production line management systems.
Automation also minimizes human error and allows for unattended operation in high-volume environments.
4. Build Quality and Mechanical Design
Durability and reliability are critical, especially for continuous operation in industrial settings. Important mechanical features include:
- Robust Frame: Aluminum extrusion or steel frames provide stability and reduce vibrations.
- Smooth Feeding Mechanism: Rollers and bearings that prevent tape slippage or damage.
- Modular Parts: Easily replaceable cutting blades and components simplify maintenance and reduce downtime.
A well-built machine will offer consistent performance and a longer service life.
5. Machine Size and Footprint
Depending on your workspace, the physical size of the machine matters:
- Compact Machines: Ideal for small labs, prototyping, or limited workspace.
- Industrial-Scale Machines: Larger footprint but designed for high-volume production.
Consider your available space and production scale when selecting a machine.
6. Power Requirements and Safety Features
- Power Compatibility: Ensure the machine's voltage and power consumption align with your facility's electrical standards.
- Safety Features: Blade guards, emergency stop buttons, and overload protection are essential to protect operators.
Safety compliance is crucial to meet workplace regulations and protect your team.
7. Cost and After-Sales Support
Balancing budget with features and quality is important:
- Initial Cost vs. Long-Term Value: Cheaper machines may save money upfront but could incur higher maintenance costs.
- Technical Support: Availability of customer service, spare parts, and repair services.
- Warranty and Service Agreements: These provide peace of mind and protect your investment.
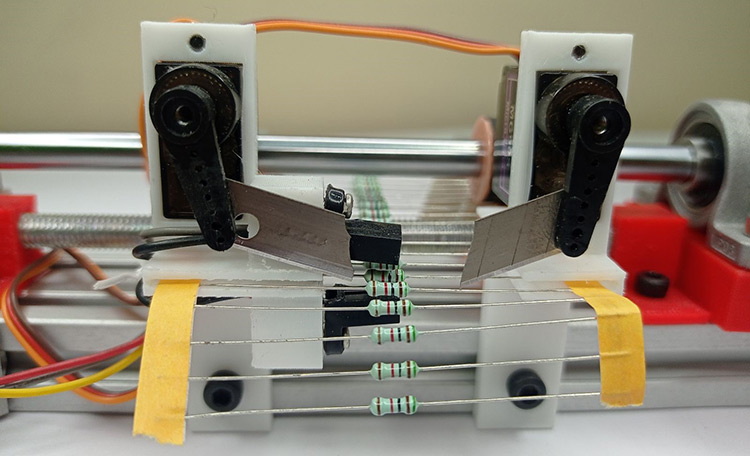
Types of SMD Resistor Cutting Machines
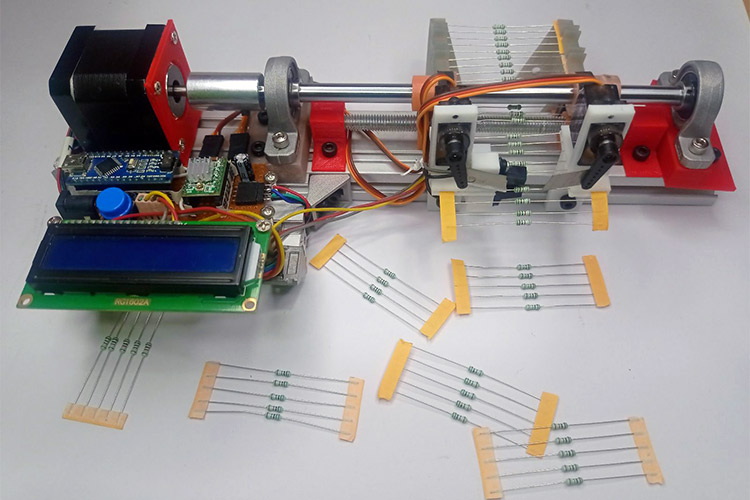
DIY and Arduino-Based Machines
For small-scale or hobbyist use, Arduino-based resistor reel cutting machines offer a cost-effective and customizable solution. These machines typically feature:
- Stepper Motors (e.g., NEMA17): For precise control of feeding and cutting.
- 3D Printed Components: Feeding rollers, mounts, and blade holders can be custom-made.
- Simple Electronic Controls: LCD displays and buttons for user input.
While these machines are affordable and flexible, they may lack the robustness and speed required for industrial manufacturing. They are best suited for labs, prototyping, or small batch production.
Industrial Automatic Cutting Machines
Designed for high-volume manufacturing, these machines offer:
- High-Torque Motors: For fast and precise feeding and cutting.
- Advanced Sensors: Optical sensors and encoders for real-time feedback.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): For automation and integration with production lines.
- Heavy-Duty Construction: To withstand continuous operation.
Industrial machines can handle a wide range of resistor sizes and tape types, offering superior speed, accuracy, and reliability.
Integrating the SMD Resistor Making Machine into Your Workflow
To maximize the benefits of your SMD resistor cutting machine, consider the following:
- Match Cutting Speed to Assembly Line: Synchronize the cutting machine's feed rate with your pick-and-place machine to avoid bottlenecks.
- Operator Training: Ensure users understand machine settings, safety protocols, and maintenance procedures.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean feeding rollers, replace blades timely, lubricate mechanical parts, and calibrate sensors to maintain precision.
- Use Quality Consumables: High-quality cutting blades and tapes reduce wear and tear and improve cutting quality.
Proper integration leads to smoother production, less downtime, and higher product quality.
Additional Tips for Selecting the Best SMD Resistor Making Machine
- Check Reviews and References: Look for feedback from other users in your industry.
- Request Demonstrations: If possible, test the machine with your specific resistor tapes.
- Consider Future Needs: Choose a machine that can adapt to new resistor sizes or increased production volumes.
- Evaluate Software Features: Advanced software can offer data logging, remote monitoring, and batch tracking.
Conclusion
Selecting the right SMD resistor cutting machine is a vital step in optimizing your electronics manufacturing process. By carefully considering compatibility with resistor sizes, cutting precision, automation capabilities, build quality, and cost, you can find a machine that meets your current and future production needs. Whether you opt for a DIY Arduino-based solution for small-scale operations or invest in a fully automated industrial machine, the right equipment will enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product quality.
Investing time in understanding your requirements and evaluating machine features will pay off in smoother workflows and higher yield in your SMD resistor handling process.
FAQ
1. What is an SMD resistor making machine?
An SMD resistor making machine refers broadly to equipment used in the production or handling of SMD resistors, including cutting machines that automate the process of cutting resistor reels into usable lengths for assembly.
2. Can an Arduino-based resistor cutting machine handle different resistor sizes?
Yes, Arduino-based machines can be designed to handle various resistor sizes by adjusting feeding rollers and cutting lengths. However, they may require manual calibration for different tape widths and thicknesses and are better suited for small-scale or prototyping purposes.
3. How important is the cutting precision in an SMD resistor cutting machine?
Cutting precision is critical to avoid damaging resistors and ensure consistent tape lengths for automated assembly. High-precision motors and sensors help maintain this accuracy, which directly affects production quality and component yield.
4. What maintenance is required for an SMD resistor cutting machine?
Regular cleaning of feeding rollers, timely replacement of cutting blades, lubrication of mechanical parts, and calibration of sensors and motors are essential to maintain machine performance and prolong its service life.
5. How does the size of the SMD resistor affect the choice of cutting machine?
Smaller SMD resistor sizes like 0201 require more delicate handling and precise cutting mechanisms, while larger sizes are easier to handle. Ensuring the machine supports the smallest size you plan to work with is essential to avoid component damage and maintain production efficiency.




















