Content Menu
● Introduction
● What is Surface Mount Technology?
● The Advantages of Surface Mount Technology
>> Miniaturization of Devices
>> Increased Manufacturing Efficiency
>> Improved Electrical Performance
>> Cost-Effectiveness
>> Enhanced Reliability
● Challenges of Surface Mount Technology
>> Design Complexity
>> Repair and Rework Difficulties
>> Initial Investment Costs
● The Future of Surface Mount Technology
>> Advanced Materials
>> Integration with Other Technologies
>> Sustainability Considerations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the main difference between Surface Mount Technology and through-hole technology?
>> 2. What are the benefits of using Surface Mount Technology in electronics manufacturing?
>> 3. Are there any challenges associated with Surface Mount Technology?
>> 4. How does Surface Mount Technology impact the future of electronics?
>> 5. Can Surface Mount Technology be used for high-frequency applications?
Introduction
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has transformed the landscape of electronics manufacturing, enabling the production of smaller, lighter, and more efficient devices. This technology allows electronic components to be mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), as opposed to the traditional through-hole method, where components are inserted into holes drilled in the PCB. The evolution of SMT has not only improved manufacturing processes but has also significantly impacted the design and functionality of modern electronic devices. In this article, we will explore how SMT revolutionizes modern electronics, its advantages, challenges, and its future in the industry.
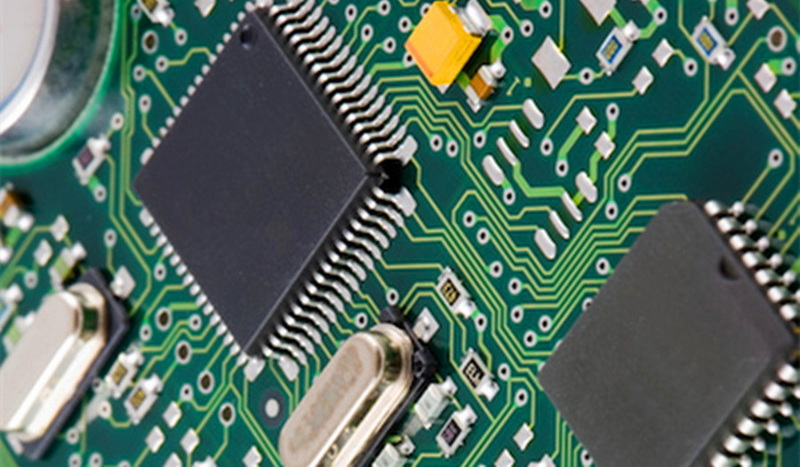

What is Surface Mount Technology?
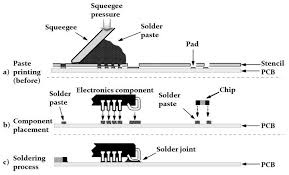
Surface Mount Technology is a method used to mount electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB. This technique contrasts with the older through-hole technology, where components are inserted into holes in the PCB and soldered from the opposite side. SMT components are typically smaller and lighter, allowing for more compact designs. The technology has become the standard in the electronics industry due to its numerous advantages, including reduced manufacturing costs, improved performance, and enhanced reliability.
The Advantages of Surface Mount Technology
Miniaturization of Devices
One of the most significant advantages of SMT is its ability to facilitate the miniaturization of electronic devices. As consumer demand for smaller gadgets increases, manufacturers are turning to SMT to create compact designs. SMT components are generally smaller than their through-hole counterparts, allowing for more components to be placed on a single PCB. This miniaturization is crucial for modern devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology, where space is at a premium.
Increased Manufacturing Efficiency
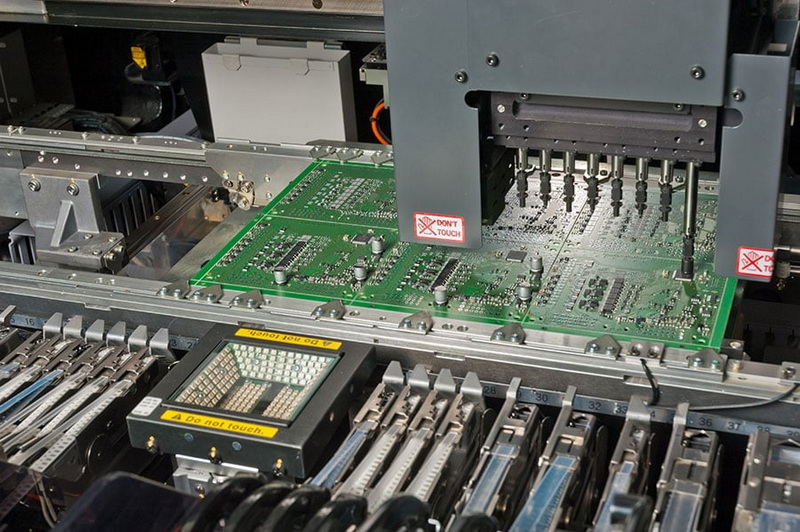
SMT enhances manufacturing efficiency by allowing for automated assembly processes. The use of pick-and-place machines enables manufacturers to quickly and accurately place components on PCBs, significantly reducing assembly time. This automation not only speeds up production but also minimizes human error, leading to higher quality products. Additionally, the ability to place components on both sides of the PCB further optimizes space and reduces the number of required PCBs.
Improved Electrical Performance
Surface Mount Technology contributes to improved electrical performance in electronic devices. The shorter leads of SMT components reduce inductance and resistance, which can enhance signal integrity and overall performance. This is particularly important in high-frequency applications, such as telecommunications and data transmission, where signal degradation can lead to performance issues. The compact nature of SMT also allows for better thermal management, which is essential for maintaining the reliability of electronic devices.
Cost-Effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness of SMT is another reason for its widespread adoption in the electronics industry. The reduction in material costs, due to the smaller size of components and the ability to use fewer PCBs, leads to lower overall production costs. Furthermore, the efficiency of automated assembly processes reduces labor costs, making SMT an attractive option for manufacturers looking to optimize their production lines.
Enhanced Reliability
Reliability is a critical factor in the design of electronic devices, and SMT offers several advantages in this area. The solder joints created during the SMT process are generally more robust than those in through-hole technology, as they are less prone to mechanical stress. Additionally, the smaller size of SMT components allows for better heat dissipation, reducing the risk of overheating and failure. This enhanced reliability is particularly important in applications where devices are subjected to harsh conditions, such as automotive and industrial electronics.
Challenges of Surface Mount Technology
Despite its many advantages, Surface Mount Technology is not without its challenges. Manufacturers must navigate several issues to fully leverage the benefits of SMT.
Design Complexity
The design of PCBs for SMT can be more complex than for through-hole technology. Engineers must consider factors such as component placement, thermal management, and signal integrity when designing PCBs. This complexity can lead to longer design cycles and increased costs if not managed properly.
Repair and Rework Difficulties
Repairing and reworking SMT components can be more challenging than with through-hole components. The smaller size and tighter spacing of SMT components make it difficult to access and replace faulty parts. Specialized tools and techniques are often required for rework, which can increase repair costs and time.
Initial Investment Costs
While SMT can lead to long-term cost savings, the initial investment in equipment and training can be significant. Manufacturers may need to purchase advanced pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and other specialized equipment to implement SMT effectively. Additionally, training staff to operate this equipment can add to the initial costs.
The Future of Surface Mount Technology
As technology continues to advance, the future of Surface Mount Technology looks promising. Innovations in materials, processes, and design methodologies are expected to further enhance the capabilities of SMT.
Advanced Materials
The development of new materials for SMT components and PCBs is likely to improve performance and reliability. For example, the use of flexible substrates can enable the creation of bendable electronics, opening up new possibilities for device design.
Integration with Other Technologies
The integration of SMT with other technologies, such as 3D printing and IoT (Internet of Things), will likely lead to new applications and products. As devices become more interconnected, the demand for compact, efficient electronics will continue to grow, driving further innovation in SMT.
Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important consideration in electronics manufacturing. SMT can contribute to more sustainable practices by reducing material waste and energy consumption during production. As manufacturers seek to minimize their environmental impact, SMT will play a crucial role in developing eco-friendly electronics.
Conclusion
Surface Mount Technology has revolutionized modern electronics by enabling the production of smaller, more efficient, and reliable devices. Its advantages, including miniaturization, increased manufacturing efficiency, improved electrical performance, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced reliability, have made it the preferred choice for manufacturers worldwide. While challenges such as design complexity and repair difficulties exist, the future of SMT looks bright, with advancements in materials and integration with other technologies paving the way for continued innovation. As the demand for compact and efficient electronics grows, Surface Mount Technology will remain at the forefront of the electronics industry.
FAQ
1. What is the main difference between Surface Mount Technology and through-hole technology?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) involves mounting components directly onto the surface of a PCB, while through-hole technology requires components to be inserted into holes in the PCB. SMT components are typically smaller and allow for more compact designs.
2. What are the benefits of using Surface Mount Technology in electronics manufacturing?
The benefits of SMT include miniaturization of devices, increased manufacturing efficiency, improved electrical performance, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced reliability.
3. Are there any challenges associated with Surface Mount Technology?
Yes, challenges include design complexity, difficulties in repair and rework, and initial investment costs for specialized equipment and training.
4. How does Surface Mount Technology impact the future of electronics?
SMT is expected to drive innovation in electronics through advanced materials, integration with other technologies, and sustainability considerations, enabling the development of more compact and efficient devices.
5. Can Surface Mount Technology be used for high-frequency applications?
Yes, SMT is particularly beneficial for high-frequency applications due to its ability to reduce inductance and resistance, which enhances signal integrity and overall performance.




















