Content Menu
● Understanding SMT Technology
>> The Role of Pick and Place Machines
● Components of an SMT Pick and Place Machine
>> 1. Feeder System
>> 2. Pick and Place Head
>> 3. Vision System
>> 4. Control System
>> 5. Conveyor System
● The PCB Manufacturing Process
>> 1. Design and Layout
>> 2. Printing the PCB
>> 3. Applying Solder Paste
>> 4. Component Placement
>> 5. Reflow Soldering
>> 6. Inspection and Testing
● Advantages of SMT Pick and Place Machines
>> 1. Increased Speed and Efficiency
>> 2. Improved Accuracy
>> 3. Flexibility
>> 4. Reduced Labor Costs
>> 5. Enhanced Quality Control
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is an SMT pick and place machine?
>> 2. How does a pick and place machine work?
>> 3. What are the advantages of using SMT technology?
>> 4. Can pick and place machines handle different types of components?
>> 5. How does the reflow soldering process work?
In the world of electronics manufacturing, the Surface Mount Technology (SMT) pick and place machine plays a crucial role in the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This sophisticated equipment is designed to automate the process of placing electronic components onto PCBs, ensuring precision, speed, and efficiency. In this article, we will explore the workings of SMT pick and place machines, their components, the process of PCB manufacturing, and the advantages they bring to the industry.

Understanding SMT Technology
Surface Mount Technology is a method used to mount electronic components directly onto the surface of PCBs. Unlike traditional through-hole technology, where components are inserted into holes and soldered from the opposite side, SMT allows for a more compact design and higher component density. This technology has revolutionized the electronics industry, enabling the production of smaller, lighter, and more efficient devices.
The Role of Pick and Place Machines
At the heart of SMT assembly is the pick and place machine. This machine is responsible for accurately picking up components from a feeder and placing them onto the PCB in the correct position. The precision of these machines is vital, as even a slight misalignment can lead to defects in the final product.
Components of an SMT Pick and Place Machine
An SMT pick and place machine consists of several key components that work together to ensure efficient operation:
1. Feeder System
The feeder system holds the electronic components in place and delivers them to the pick and place head. There are various types of feeders, including tape feeders, tray feeders, and bulk feeders, each designed for different types of components. The choice of feeder affects the speed and efficiency of the assembly process.
2. Pick and Place Head
The pick and place head is the part of the machine that picks up components and places them onto the PCB. It typically uses vacuum suction to pick up components and can be equipped with multiple nozzles to handle different sizes and types of components simultaneously. The head's movement is controlled by precise motors, allowing for accurate placement.
3. Vision System
A vision system is often integrated into SMT pick and place machines to ensure accurate component placement. This system uses cameras to identify the position and orientation of components and PCBs. It can make real-time adjustments to the placement process, enhancing accuracy and reducing errors.
4. Control System
The control system is the brain of the pick and place machine. It manages the operation of the machine, including the movement of the pick and place head, the activation of the feeders, and the coordination of the vision system. Advanced control systems can optimize the placement process for speed and efficiency.
5. Conveyor System
The conveyor system transports PCBs through the assembly line. It ensures that PCBs are fed into the pick and place machine at the right time and in the correct orientation. The conveyor system can be adjusted to accommodate different PCB sizes and shapes.
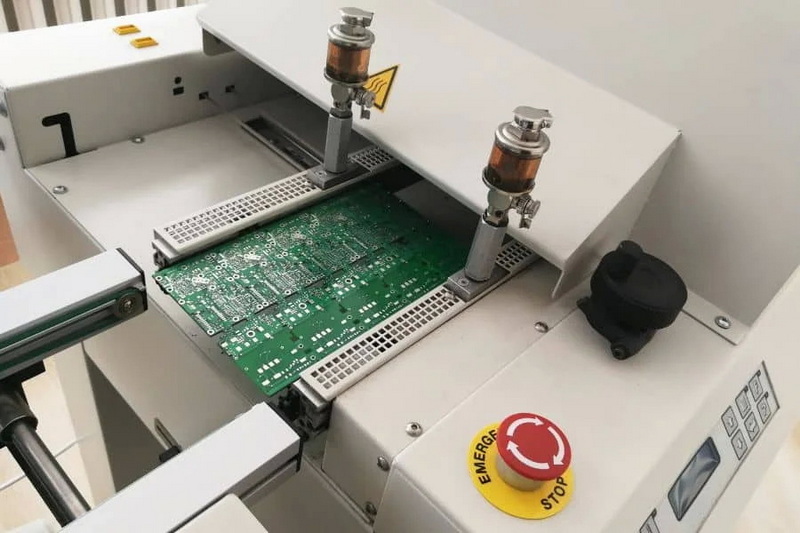

The PCB Manufacturing Process
The process of PCB manufacturing involves several steps, and the SMT pick and place machine plays a critical role in the assembly phase. Here's a breakdown of the typical PCB manufacturing process:
1. Design and Layout
The first step in PCB manufacturing is designing the circuit layout using specialized software. Engineers create a schematic diagram and then convert it into a PCB layout, defining the placement of components and the routing of electrical connections.
2. Printing the PCB
Once the design is finalized, the PCB is printed using a process called photolithography. This involves applying a photosensitive material to a substrate, exposing it to light through a mask, and then etching away the unwanted material to create the circuit pattern.
3. Applying Solder Paste
Before components can be placed, solder paste is applied to the PCB. This paste is a mixture of tiny solder balls and flux, which helps the solder flow during the reflow process. The solder paste is typically applied using a stencil printer.
4. Component Placement
This is where the SMT pick and place machine comes into play. The machine picks components from the feeders and places them onto the PCB, aligning them with the solder paste. The accuracy of this step is crucial for ensuring a reliable electrical connection.
5. Reflow Soldering
After all components are placed, the PCB undergoes reflow soldering. The assembled PCB is passed through a reflow oven, where the solder paste is heated to melt the solder, creating a strong bond between the components and the PCB.
6. Inspection and Testing
Once soldering is complete, the PCB is inspected for defects. Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems are often used to check for misaligned components, solder bridges, and other issues. Functional testing may also be performed to ensure the PCB operates as intended.
Advantages of SMT Pick and Place Machines
The use of SMT pick and place machines in PCB manufacturing offers several advantages:
1. Increased Speed and Efficiency
SMT pick and place machines can operate at high speeds, placing thousands of components per hour. This efficiency significantly reduces the time required for PCB assembly, allowing manufacturers to meet tight production deadlines.
2. Improved Accuracy
The precision of pick and place machines minimizes the risk of misalignment and defects. With advanced vision systems and control algorithms, these machines can achieve high levels of accuracy, ensuring reliable electrical connections.
3. Flexibility
Modern SMT pick and place machines are highly flexible and can handle a wide variety of components, from small chip resistors to larger integrated circuits. This adaptability allows manufacturers to produce different types of PCBs without the need for extensive reconfiguration.
4. Reduced Labor Costs
Automation of the component placement process reduces the need for manual labor, leading to lower labor costs. This also allows human operators to focus on more complex tasks, such as quality control and troubleshooting.
5. Enhanced Quality Control
With integrated inspection systems, SMT pick and place machines can detect errors in real-time, allowing for immediate corrections. This proactive approach to quality control helps maintain high standards in PCB manufacturing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SMT pick and place machines are essential tools in the PCB manufacturing process. They automate the placement of electronic components, ensuring speed, accuracy, and efficiency. As technology continues to advance, these machines are becoming even more sophisticated, incorporating features such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to further enhance their capabilities. The benefits they provide, including increased production speed, improved accuracy, and reduced labor costs, make them indispensable in the modern electronics manufacturing landscape.
FAQ
1. What is an SMT pick and place machine?
An SMT pick and place machine is a piece of equipment used in PCB manufacturing to automate the process of placing electronic components onto the surface of printed circuit boards.
2. How does a pick and place machine work?
The machine uses a feeder system to hold components, a pick and place head to pick them up, and a vision system to ensure accurate placement on the PCB.
3. What are the advantages of using SMT technology?
SMT technology allows for higher component density, smaller PCB sizes, and improved performance compared to traditional through-hole technology.
4. Can pick and place machines handle different types of components?
Yes, modern pick and place machines are designed to handle a wide variety of components, including small chip components and larger integrated circuits.
5. How does the reflow soldering process work?
Reflow soldering involves heating the assembled PCB in a reflow oven, melting the solder paste to create strong electrical connections between the components and the PCB.




















