Content Menu
● Understanding SMT and PCB Assembly
● Key Differences Between SMT Pick and Place Machines and Manual Assembly
>> 1. Speed and Throughput
>> 2. Precision and Accuracy
>> 3. Repeatability and Consistency
>> 4. Component Handling and Damage Risk
>> 5. Scalability and Cost Efficiency
>> 6. Inspection and Quality Control
● Advantages of Using an SMT PCB Pick and Place Machine
● Challenges and Considerations of SMT Pick and Place Machines
● When Manual Assembly is Still Relevant
● Side-by-Side Comparison Table
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is an SMT PCB pick and place machine?
>> 2. Can manual assembly achieve the same precision as SMT pick and place machines?
>> 3. What are the main advantages of SMT pick and place machines over manual assembly?
>> 4. Is manual assembly still used in modern PCB manufacturing?
>> 5. What are the cost implications of using an SMT pick and place machine?
● Citations:
In the world of electronics manufacturing, the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs) is a critical step that directly impacts product quality, production speed, and cost efficiency. Two primary methods dominate this process: manual assembly and automated assembly using an SMT PCB pick and place machine. This article explores in detail how an SMT pick and place machine compares to manual assembly, highlighting the advantages, challenges, and practical considerations of each method.
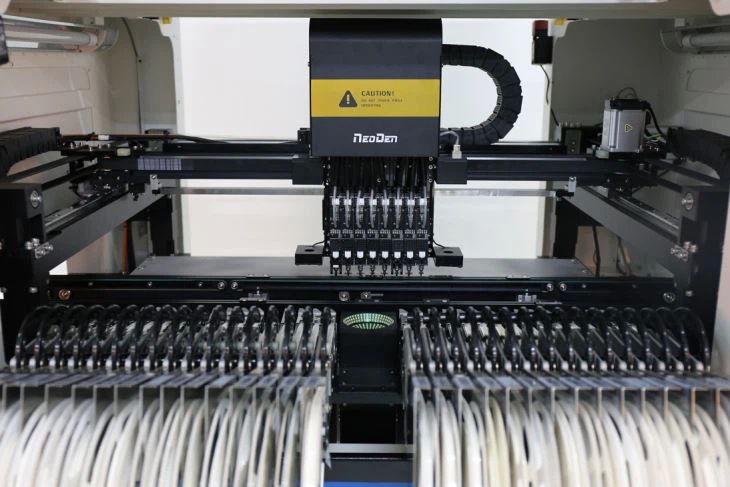

Understanding SMT and PCB Assembly
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a method for producing electronic circuits in which components are mounted directly onto the surface of PCBs. SMT has largely replaced through-hole technology due to its ability to support higher component density, smaller device sizes, and faster production cycles.
An SMT PCB pick and place machine is an automated system that picks electronic components from reels or trays and places them precisely on the PCB pads coated with solder paste. This machine is a core part of the SMT assembly line, which typically involves solder paste printing, component placement, reflow soldering, and inspection.
Manual assembly, by contrast, involves human operators using tools like tweezers and magnifying glasses to place components on the PCB, often followed by hand soldering.
Key Differences Between SMT Pick and Place Machines and Manual Assembly
1. Speed and Throughput
- SMT Pick and Place Machine: Automated machines can place thousands of components per hour with consistent speed, making them ideal for medium to large-scale production runs. The rapid placement reduces the time components spend on the solder paste, minimizing drying issues and improving solder quality[3][8].
- Manual Assembly: Human operators are much slower, especially when dealing with tiny components or high-density boards. Manual placement is typically limited to prototypes, small batches, or repair work[3][6].
2. Precision and Accuracy
- SMT Pick and Place Machine: These machines achieve high precision placement, often within ±0.03 mm, critical for modern miniaturized components like 0201 capacitors and fine-pitch ICs. The machines also handle component rotation and orientation automatically, ensuring correct alignment with PCB pads[3][6].
- Manual Assembly: Human dexterity and eyesight limit precision. Misalignments and incorrect orientations are common, particularly for complex or small components, increasing the risk of soldering defects and rework[3].
3. Repeatability and Consistency
- SMT Pick and Place Machine: Automated systems perform identical placement operations across hundreds or thousands of boards, ensuring uniform quality and reducing variability[3].
- Manual Assembly: Variability between operators and fatigue-induced errors lead to inconsistent placement quality and increased defect rates[3][6].
4. Component Handling and Damage Risk
- SMT Pick and Place Machine: Specialized nozzles handle components gently, minimizing mechanical stress and damage, especially important for fragile or sensitive parts[3].
- Manual Assembly: Tweezers and manual handling increase the risk of damaging components, particularly tiny or delicate ones[3].
5. Scalability and Cost Efficiency
- SMT Pick and Place Machine: While the initial capital investment is significant, automated assembly reduces labor costs and increases throughput, making it cost-effective for large production volumes. The ability to place components on both sides of the PCB also reduces board size and material costs[1][5][7].
- Manual Assembly: Labor-intensive and slow, manual assembly becomes prohibitively expensive and impractical for high-volume production[3][6].
6. Inspection and Quality Control
- SMT Pick and Place Machine: Often integrated with Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), these machines detect placement defects in real-time, allowing immediate correction and reducing rework[3][4].
- Manual Assembly: Visual inspection is manual, slower, and more prone to missing defects, increasing the risk of faulty boards reaching the next stage[3].
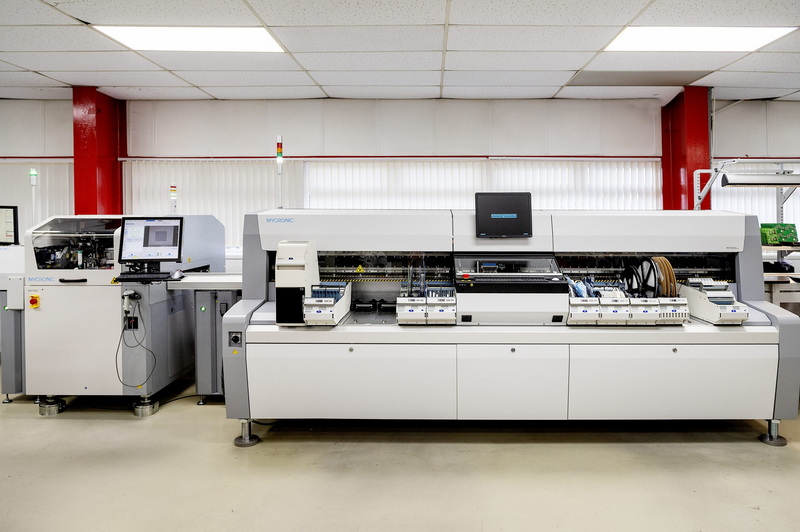

Advantages of Using an SMT PCB Pick and Place Machine
- High-Speed Placement: Machines can place components rapidly, supporting mass production.
- High Accuracy: Precise placement reduces soldering defects.
- Reduced Labor Fatigue: Automation minimizes operator fatigue and errors.
- Consistent Quality: Uniform placement across all boards.
- Integration with Other SMT Processes: Seamless operation with solder paste printing and reflow soldering.
- Advanced Software Control: Optimizes placement paths, manages component libraries, and verifies design files[3][6][8].
- Support for Miniaturized Components: Handles very small components that are difficult to place manually[3][7].
Challenges and Considerations of SMT Pick and Place Machines
- High Initial Cost: The capital investment for machines and supporting equipment is significant.
- Complex Setup: Programming the machine with accurate component data and placement coordinates requires expertise[8].
- Maintenance: Machines require regular maintenance and calibration.
- Limited Flexibility: Small production runs or frequent design changes can reduce efficiency.
- Thermal and Moisture Sensitivity: SMT components and solder joints can be susceptible to damage if not handled properly during assembly[7].
When Manual Assembly is Still Relevant
- Prototyping and Small Batches: For very low-volume projects, manual assembly avoids the high setup cost of machines.
- Complex or Large Components: Through-hole or bulky components that are difficult to handle with pick and place machines.
- Repair and Rework: Manual skills are essential for troubleshooting and fixing assembled boards.
- Limited Budget or Space: Small operations may not afford or have room for automated equipment[2][6].
Side-by-Side Comparison Table
| Feature | Manual Assembly | SMT PCB Pick and Place Machine |
| Speed | Slow, limited by human dexterity | Very fast, thousands of components/hr |
| Precision | Limited, prone to misalignment | High precision, ±0.03 mm accuracy |
| Repeatability | Variable, affected by fatigue | Consistent, uniform across boards |
| Component Handling | Risk of damage with tweezers | Gentle, robotic handling |
| Scalability | Poor for large volumes | Excellent for mass production |
| Inspection | Manual visual inspection | Integrated automated optical inspection |
| Setup Cost | Low initial cost | High initial investment |
| Flexibility | High for small runs and prototyping | Best for stable, large-scale runs |
| Software Integration | Minimal or none | Advanced software for optimization |
| Component Size Handling | Difficult for very small components | Designed for miniaturized components |
Conclusion
The comparison between an SMT PCB pick and place machine and manual assembly clearly favors automation for modern electronics manufacturing. SMT pick and place machines deliver unmatched speed, precision, repeatability, and scalability, making them essential for high-volume production and complex PCB designs. While manual assembly remains relevant for prototyping, small batches, and repair, it cannot compete with the efficiency and consistency of automated SMT assembly.
Investing in an SMT pick and place machine is a strategic decision that can significantly reduce labor costs, improve product quality, and accelerate time-to-market. As electronic devices continue to shrink and demand grows, the role of SMT pick and place machines will only become more critical.
FAQ
1. What is an SMT PCB pick and place machine?
An SMT PCB pick and place machine is an automated device that picks electronic components from feeders and places them accurately on solder-pasted PCBs during the surface mount technology assembly process[3][6].
2. Can manual assembly achieve the same precision as SMT pick and place machines?
No, manual assembly is limited by human dexterity and eyesight, making it difficult to achieve the high precision (±0.03 mm) and consistency provided by SMT pick and place machines[3].
3. What are the main advantages of SMT pick and place machines over manual assembly?
Key advantages include higher speed, accuracy, repeatability, reduced component damage, integration with inspection systems, and scalability for large production volumes[3][7].
4. Is manual assembly still used in modern PCB manufacturing?
Yes, manual assembly is still used for prototyping, small batch production, repair, and assembly of large or complex components not suited for automated placement[2][6].
5. What are the cost implications of using an SMT pick and place machine?
While the initial investment is high, SMT pick and place machines reduce labor costs and improve production efficiency, resulting in overall cost savings for medium to large-scale manufacturing[1][5].
Citations:
[1] https://www.protoexpress.com/blog/good-not-so-good-sides-surface-mount-technology/
[2] https://smtcaddy.com/pages/faq-1
[3] https://www.coloradopcbassembly.com/pick-and-place-vs-hand-assembly-pcb/
[4] https://www.pcbonline.com/blog/pcb-assembly-services.html
[5] https://www.wevolver.com/article/smt-vs-smd-vs-tht-a-comprehensive-guide-to-electronics-assembly-techniques
[6] https://www.ddmnovastar.com/smt-quick-tips-selecting-a-pick-and-place-machine
[7] https://www.macrofab.com/blog/smt-assembly-vs-through-hole/
[8] https://www.elecrow.com/blog/what-is-smt-pcb-assembly-a-must-read-guide.html
[9] https://www.viasion.com/blog/smt-assembly-vs-through-hole-assembly-their-pros-and-cons/
[10] https://www.viasion.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-pcb-smt-assembly-process/
[11] https://www.globalwellpcba.com/difference-between-smt-and-pth-assembly/
[12] https://hackaday.io/project/20260/instructions
[13] https://resources.altium.com/p/complete-guide-diy-smt-assembly-your-office
[14] https://www.pcbunlimited.com/pdf/HW-T4-44_50F_PCBU.pdf
[15] https://www.7pcb.com/blog/assembly-by-hand-vs-machine
[16] https://www.neodensmt.com/news/pros-and-cons-of-manual-and-auto-soldering-71484593.html
[17] https://www.eevblog.com/forum/manufacture/smt-production-line-manual-vs-automatic/
[18] https://ecitech.com/insights/why-manual-soldering-is-still-important-in-smt-assembly-manufacturing-process/
[19] https://community.particle.io/t/manual-smt-pick-and-place-machine/43990
[20] https://forum.pololu.com/t/pcb-assembly-tools-and-equipment-for-smt/2152




















