Content Menu
● Understanding SMT PCB Services
>> Key Steps in SMT PCB Assembly
● How SMT PCB Services Reduce Production Time
>> 1. Elimination of Drilling Holes
>> 2. High-Speed Automated Component Placement
>> 3. Increased Component Density and Double-Sided Mounting
>> 4. Design Flexibility and Reduced Rework
>> 5. Automated Inspection and Quality Control
● Additional Advantages of SMT PCB Services
>> Smaller and Lighter Components
>> Reduced Manual Labor
>> Improved Reliability
>> Faster Signal Transmission
>> Lower Material Costs
● Challenges and Considerations
● Industry Applications Benefiting from SMT PCB Services
>> Consumer Electronics
>> Automotive Electronics
>> Medical Devices
>> Aerospace and Defense
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
>> 1. What is the main difference between SMT and through-hole PCB assembly?
>> 2. How does SMT PCB assembly speed up production?
>> 3. Can SMT components be mounted on both sides of a PCB?
>> 4. What role does Design for Manufacturing (DFM) play in SMT PCB services?
>> 5. Are SMT PCB services suitable for low-volume production?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) PCB services have revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry by significantly reducing production time while enhancing product quality and design flexibility. This article explores how SMT PCB services contribute to faster production cycles, cost efficiency, and improved manufacturing throughput, making them the preferred choice for modern electronics production.
Understanding SMT PCB Services
SMT PCB services involve mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs) without the need for drilling holes, unlike traditional through-hole technology. This method uses solder paste and automated machinery to place components rapidly and accurately on the board surface. The evolution of SMT has enabled manufacturers to meet the increasing demand for smaller, faster, and more complex electronic devices.
Key Steps in SMT PCB Assembly
1. Solder Paste Printing: A stencil printer applies solder paste precisely on the PCB pads where components will be placed. This step is critical because the quality and accuracy of solder paste deposition directly impact the solder joint reliability.
2. Solder Paste Inspection (SPI): Automated inspection ensures the solder paste is applied correctly, preventing defects early. SPI machines use 3D imaging to detect insufficient or excess solder paste, which can cause short circuits or weak joints.
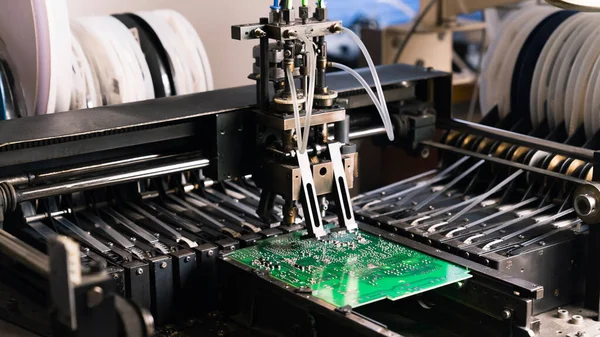
3. Component Placement: Pick-and-place machines position components on the solder paste with high speed and accuracy. These machines can place components as small as 0201 size (0.6mm x 0.3mm) with micron-level precision.
4. Reflow Soldering: The PCB passes through a reflow oven where the solder paste melts and solidifies, securing components. The temperature profile of the oven is carefully controlled to ensure proper solder joint formation without damaging components.
5. Inspection and Testing: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and functional testing verify assembly quality. AOI systems scan the board for missing, misaligned, or incorrectly oriented components, while X-ray inspection is used for hidden solder joints such as Ball Grid Arrays (BGAs).
How SMT PCB Services Reduce Production Time
1. Elimination of Drilling Holes
Traditional through-hole PCB assembly requires drilling thousands of holes on the board, a process that is both time-consuming and costly. SMT eliminates this step by mounting components directly on the surface, which drastically reduces the preparation time of the PCB. Without the need for drilling, manufacturers can move faster from design to production, especially for complex boards with high component counts.
2. High-Speed Automated Component Placement
One of the most significant time-saving aspects of SMT PCB services is the use of automated pick-and-place machines. These machines can place thousands of components per hour with exceptional accuracy, far surpassing manual assembly speeds. Automation reduces human error and fatigue, allowing continuous production runs without downtime. The high throughput of SMT lines is essential for meeting tight deadlines and scaling production volumes.
3. Increased Component Density and Double-Sided Mounting
SMT allows for much smaller components and the ability to mount them on both sides of the PCB. This increased component density means that complex circuits require fewer PCBs, reducing the overall assembly time. Double-sided mounting also optimizes space, enabling more compact device designs. This capability is particularly valuable in industries like smartphones, medical devices, and aerospace where space is at a premium.
4. Design Flexibility and Reduced Rework
Modern SMT PCB services are supported by advanced Design for Manufacturing (DFM) software tools. These tools help engineers optimize PCB layouts for SMT assembly, minimizing potential manufacturing issues such as component placement conflicts or solder bridging. By addressing these problems in the design phase, SMT services reduce costly rework cycles and accelerate the transition from prototype to mass production.
5. Automated Inspection and Quality Control
Quality control is integrated throughout the SMT assembly process using technologies like SPI, AOI, and X-ray inspection. Early detection of defects prevents faulty boards from progressing through the production line, saving time and resources. High first-pass yields mean fewer boards need rework or scrap, which shortens overall production lead time and improves delivery reliability.
Additional Advantages of SMT PCB Services
| Advantage | Impact on Production Time and Cost |
| Smaller and lighter components | Enables compact designs, reducing material use and handling time |
| Reduced manual labor | Automation cuts labor-intensive steps, speeding up assembly |
| Improved reliability | Fewer defects mean less rework and delays |
| Faster signal transmission | Enhances performance, reducing troubleshooting time |
| Lower material costs | Smaller components and less PCB space reduce expenses |
Smaller and Lighter Components
SMT components are significantly smaller and lighter than their through-hole counterparts. This miniaturization reduces the amount of raw material required and simplifies handling during assembly. Smaller components also enable faster heat dissipation and improved electrical performance, which can reduce the need for additional cooling solutions and associated manufacturing steps.
Reduced Manual Labor
By automating critical assembly steps, SMT PCB services reduce the reliance on manual labor, which is slower and prone to errors. Automation not only speeds up production but also improves worker safety by minimizing repetitive tasks and exposure to solder fumes.
Improved Reliability
SMT solder joints are generally more reliable due to the shorter leads and better mechanical support on the PCB surface. This reliability translates to fewer failures during testing and in the field, reducing the time spent on troubleshooting and warranty repairs.
Faster Signal Transmission
The shorter electrical paths in SMT designs improve signal integrity and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). This performance gain reduces the need for extensive debugging and design iterations, accelerating product development cycles.
Lower Material Costs
Because SMT components are smaller and the PCB footprint can be reduced, material costs for both components and boards are lower. These savings contribute to faster production by reducing procurement and handling complexities.
Challenges and Considerations
While SMT PCB services offer many benefits, there are challenges to consider:
- Equipment Investment: SMT assembly requires sophisticated machinery, which can be costly for small manufacturers.
- Component Handling: Very small SMT components require precise handling to avoid damage or misplacement.
- Thermal Management: Reflow soldering profiles must be carefully controlled to prevent component damage.
- Design Complexity: Highly dense SMT boards require meticulous design and testing to ensure manufacturability.
Despite these challenges, the efficiency gains and quality improvements provided by SMT PCB services far outweigh the initial hurdles.
Industry Applications Benefiting from SMT PCB Services
Consumer Electronics
The demand for compact, feature-rich devices like smartphones, tablets, and wearables has driven widespread adoption of SMT PCB services. The ability to place tiny components densely and reliably is critical for these products.
Automotive Electronics
Modern vehicles rely heavily on electronic control units (ECUs) for safety, navigation, and entertainment systems. SMT PCB services ensure these components are produced quickly and meet stringent reliability standards.
Medical Devices
Medical electronics require high precision and reliability. SMT PCB services enable the production of small, complex devices such as pacemakers and diagnostic equipment with fast turnaround times.
Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace industry demands rugged, high-performance electronics. SMT PCB services help meet these requirements while reducing production lead times for critical systems.
Conclusion
SMT PCB services dramatically reduce production time by eliminating the need for drilling, enabling high-speed automated component placement, and supporting high-density, double-sided PCB designs. The integration of advanced inspection technologies and Design for Manufacturing tools further accelerates manufacturing while improving quality. As a result, SMT PCB services are essential for manufacturers aiming to reduce time-to-market, lower costs, and produce reliable, high-performance electronic products. The benefits of SMT extend across various industries, supporting innovation and efficiency in today's fast-paced electronics market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main difference between SMT and through-hole PCB assembly?
SMT mounts components directly on the PCB surface without drilling holes, while through-hole requires inserting component leads through drilled holes. SMT is faster and supports higher component density.
2. How does SMT PCB assembly speed up production?
SMT uses automated machines that place thousands of components per hour and eliminates drilling, significantly reducing assembly time and labor costs.
3. Can SMT components be mounted on both sides of a PCB?
Yes, SMT allows components to be mounted on both sides, increasing component density and reducing the number of PCBs required for complex circuits.
4. What role does Design for Manufacturing (DFM) play in SMT PCB services?
DFM optimizes PCB layouts for manufacturability, reducing errors, rework, and redesigns, which speeds up production and improves first-pass yield.
5. Are SMT PCB services suitable for low-volume production?
While SMT excels in high-volume production due to automation, it can also be beneficial for low-volume runs by reducing manual labor and improving consistency, though setup costs may be higher.




















