Content Menu
● Understanding Surface Mount Technology
>> The Meaning of Surface Mount Technology
● Advantages of Surface Mount Technology
>> Increased Component Density
>> Enhanced Design Flexibility
>> Improved Manufacturing Efficiency
>> Cost-Effectiveness
>> Better Electrical Performance
● Applications of Surface Mount Technology
● Challenges in Implementing Surface Mount Technology
>> Complexity in Design
>> Thermal Management
>> Equipment Costs
● The Future of Surface Mount Technology
● Conclusion
● Related Questions
>> 1. What is the difference between Surface Mount Technology and Through-Hole Technology?
>> 2. How does Surface Mount Technology impact manufacturing costs?
>> 3. What are the common applications of Surface Mount Technology?
>> 4. What challenges are associated with Surface Mount Technology?
>> 5. How can manufacturers ensure the reliability of SMT components?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has transformed the landscape of electronics manufacturing, offering significant advantages in the design and production of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This article explores how SMT enhances PCB design efficiency, delving into its benefits, applications, and the future of electronics manufacturing.
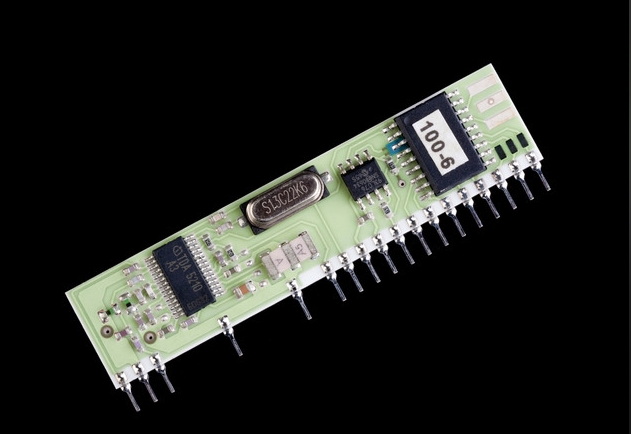
Understanding Surface Mount Technology
Surface Mount Technology refers to a method of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB. Unlike traditional through-hole technology, where components are inserted into holes drilled in the board, SMT allows for a more compact and efficient design. This technology utilizes Surface Mount Devices (SMDs), which are smaller and lighter than their through-hole counterparts, enabling higher component density and improved performance.
The Meaning of Surface Mount Technology
The term "Surface Mount Technology" encompasses various techniques and processes used to attach electronic components to the surface of PCBs. SMT has become the standard in modern electronics due to its ability to facilitate miniaturization and enhance manufacturing efficiency. The adoption of SMT has led to the development of smaller, more powerful devices that meet the demands of today's technology-driven world.
Advantages of Surface Mount Technology
Increased Component Density
One of the primary benefits of SMT is the ability to achieve higher component density on PCBs. This is crucial in an era where devices are becoming increasingly compact. By mounting components directly on the surface, manufacturers can utilize both sides of the PCB, maximizing space and allowing for more complex circuit designs.
Enhanced Design Flexibility
SMT provides designers with greater flexibility in layout and design. The smaller size of SMDs allows for innovative designs that were previously impossible with through-hole components. Designers can create intricate patterns and configurations, leading to more efficient use of space and improved performance.
Improved Manufacturing Efficiency
The automated assembly processes associated with SMT significantly enhance manufacturing efficiency. SMT components can be placed on PCBs using pick-and-place machines, which are faster and more accurate than manual assembly methods. This automation reduces labor costs and minimizes the risk of human error, resulting in higher quality products.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial setup for SMT may be higher due to the need for specialized equipment, the long-term cost savings are substantial. The reduced size and weight of SMT components lead to lower shipping costs, and the efficiency of automated assembly processes decreases production time and labor costs.
Better Electrical Performance
SMT components typically have shorter leads, which reduces the inductance and resistance in the circuit. This leads to better electrical performance, particularly at high frequencies. As a result, devices utilizing SMT can operate more efficiently and reliably, making them ideal for applications in telecommunications, computing, and consumer electronics.
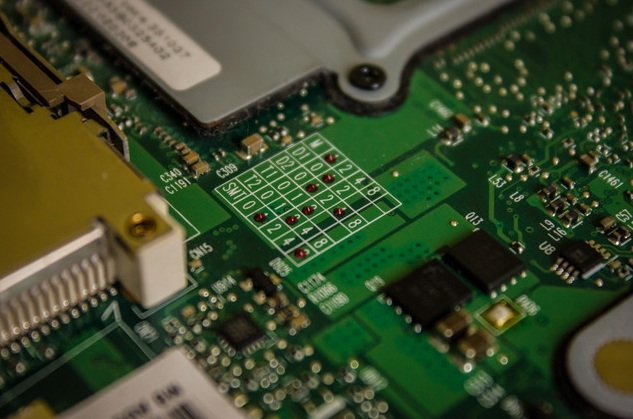

Applications of Surface Mount Technology
SMT is widely used across various industries, including:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, and laptops utilize SMT for their compact designs and high performance.
- Automotive: Modern vehicles incorporate numerous electronic systems that rely on SMT for reliability and efficiency.
- Medical Devices: SMT is crucial in the development of compact and reliable medical equipment, where space and performance are critical.
- Telecommunications: High-frequency applications benefit from the improved electrical performance of SMT components.
Challenges in Implementing Surface Mount Technology
Despite its advantages, SMT also presents challenges that manufacturers must address:
Complexity in Design
The increased density and complexity of SMT designs can make troubleshooting and repair more difficult. Engineers must be well-versed in SMT design principles to avoid potential issues during the manufacturing process.
Thermal Management
SMT components can generate significant heat, which must be managed effectively to prevent damage. Designers need to consider thermal management strategies during the design phase to ensure the longevity and reliability of the final product.
Equipment Costs
The initial investment in SMT equipment can be substantial. However, many manufacturers find that the long-term benefits outweigh these costs, especially as production volumes increase.
The Future of Surface Mount Technology
As technology continues to evolve, SMT will play a crucial role in the development of next-generation electronic devices. Innovations in materials and manufacturing processes will further enhance the capabilities of SMT, allowing for even smaller and more efficient designs. The ongoing trend towards miniaturization and increased functionality will ensure that SMT remains at the forefront of electronics manufacturing.
Conclusion
Surface Mount Technology has revolutionized PCB design and manufacturing, offering numerous advantages that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve performance. As the demand for smaller, more powerful electronic devices continues to grow, SMT will remain a critical component in the evolution of modern electronics. By understanding the benefits and challenges of SMT, manufacturers can leverage this technology to create innovative solutions that meet the needs of today's consumers.
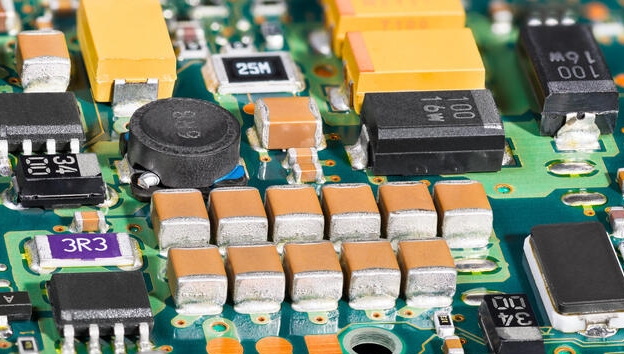
Related Questions
1. What is the difference between Surface Mount Technology and Through-Hole Technology?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) involves mounting components directly onto the surface of a PCB, while Through-Hole Technology requires components to be inserted into holes drilled in the board. SMT allows for higher component density and more compact designs.
2. How does Surface Mount Technology impact manufacturing costs?
While the initial setup for SMT can be expensive, it leads to long-term cost savings through reduced labor, lower shipping costs due to smaller components, and increased manufacturing efficiency.
3. What are the common applications of Surface Mount Technology?
SMT is commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive systems, medical devices, and telecommunications equipment due to its ability to create compact and efficient designs.
4. What challenges are associated with Surface Mount Technology?
Challenges include the complexity of design, thermal management of components, and the high initial costs of SMT equipment. However, these challenges can be mitigated with proper planning and expertise.
5. How can manufacturers ensure the reliability of SMT components?
Manufacturers can ensure reliability by implementing rigorous testing and quality control processes, utilizing proper thermal management techniques, and adhering to best practices in SMT design and assembly.




















