Content Menu
● The Evolution of PCB Manufacturing
● Understanding Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
>> Key Advantages of SMT in PCB Manufacturing
● The Fully Automated PCB Manufacturing Line with SMT
>> Key Components of an Automated SMT Line
● Reducing Human Error through Automation
>> 1. Consistent and Precise Component Placement
>> 2. Improved Quality Control
>> 3. Elimination of Fatigue-Related Errors
>> 4. Reduced Need for Manual Handling
>> 5. Real-Time Error Detection and Correction
● The Impact of Automation on PCB Manufacturing Efficiency
>> Increased Production Speed
>> Enhanced Flexibility
>> Improved Resource Utilization
>> 24/7 Operation Capability
● Challenges and Considerations
>> Initial Investment Costs
>> Maintenance and Upkeep
>> Training Requirements
>> Adapting to New Technologies
● Future Trends in Automated PCB Manufacturing
>> Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
>> Enhanced Traceability and Data Analytics
>> Increased Flexibility for Small-Batch Production
>> Environmental Sustainability
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the main advantage of using fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT?
>> 2. How does SMT contribute to more compact electronic devices?
>> 3. Are there any disadvantages to implementing a fully automated PCB manufacturing line with SMT?
>> 4. How does automated inspection in SMT lines improve quality control?
>> 5. What future developments can we expect in fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT?
● Citations:
In today's rapidly evolving electronics industry, the demand for high-quality, reliable printed circuit boards (PCBs) has never been greater. As technology advances and components become smaller and more complex, the need for precision and accuracy in PCB manufacturing has become paramount. One of the most significant advancements in this field is the implementation of fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with Surface Mount Technology (SMT). These automated systems not only increase production efficiency but also play a crucial role in reducing human error, ultimately leading to higher quality products and improved customer satisfaction.
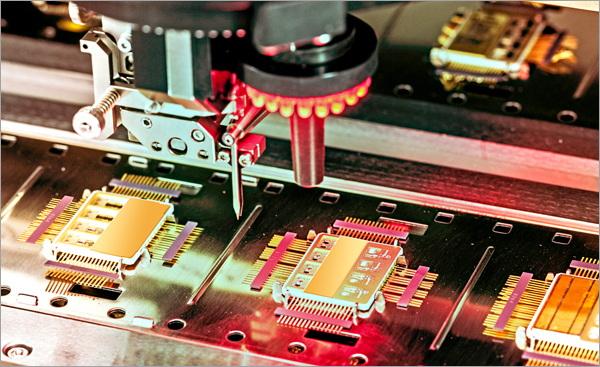
The Evolution of PCB Manufacturing
Traditional PCB manufacturing processes relied heavily on manual labor, which was prone to errors and inconsistencies. As the complexity of electronic devices increased, it became clear that a more efficient and accurate method was needed. This led to the development and widespread adoption of Surface Mount Technology (SMT), which revolutionized the PCB assembly process[1].
Understanding Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
Surface Mount Technology is a method used in PCB manufacturing where electronic components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board[5]. This technique allows for more compact designs, faster assembly, and improved performance compared to traditional through-hole technology.
Key Advantages of SMT in PCB Manufacturing
1. Space-saving: SMT components are significantly smaller than through-hole components, allowing for denser circuitry and smaller PCBs[5].
2. Faster assembly: Automated equipment can place and solder SMT components much more quickly than through-hole components[5].
3. Lower cost: SMT assembly generally requires less manual labor and can be more easily automated, resulting in reduced production costs[5].
4. Higher reliability: SMT components are less susceptible to mechanical stress and vibration due to their direct mounting on the PCB surface[5].
The Fully Automated PCB Manufacturing Line with SMT
A fully automated PCB manufacturing line with SMT integrates various sophisticated machines and processes to create a seamless, efficient production system. This advanced setup minimizes human intervention, thereby reducing the potential for errors and inconsistencies in the manufacturing process.
Key Components of an Automated SMT Line
1. PCB Loader: Automatically places bare PCBs into the production line[3].
2. Solder Paste Printing Machine: Applies solder paste to specific areas on the PCB[3].
3. Solder Paste Inspection (SPI) Machine: Checks the quality and placement of solder paste[3].
4. Pick and Place Machines: Accurately place surface mount components onto the PCB[3].
5. Reflow Oven: Melts the solder paste to create permanent connections between components and the PCB[3].
6. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Machine: Inspects the assembled PCB for defects[3].
7. Automated X-ray Inspection (AXI) and Circuit Testing (CT) Equipment: Performs additional quality checks[3].
Reducing Human Error through Automation
The implementation of fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT significantly reduces human error in several ways:
1. Consistent and Precise Component Placement
Automated pick and place machines can work continuously without breaks, leading to higher production throughput compared to manual assembly[1]. These machines operate with extreme precision, placing components accurately and consistently, even when dealing with tiny SMT components that are challenging for human operators to handle.
2. Improved Quality Control
Automated inspection systems, such as SPI, AOI, and AXI, can detect defects that might be missed by human inspectors. These systems can operate 24/7, ensuring that every PCB undergoes thorough quality checks[2]. The accuracy of these automated inspection systems is remarkably high, with some defect recognition models achieving accuracy rates of up to 96.97%[2].
3. Elimination of Fatigue-Related Errors
Unlike human operators, automated systems do not experience fatigue or lapses in concentration. This consistency ensures that the quality of PCB assembly remains high throughout long production runs, eliminating errors that might occur due to human tiredness or boredom[4].
4. Reduced Need for Manual Handling
Automated material handling systems minimize the need for human intervention in moving components and PCBs through the production line. This reduction in manual handling decreases the risk of damage to sensitive components and reduces the likelihood of contamination[4].
5. Real-Time Error Detection and Correction
Advanced SMT lines incorporate real-time monitoring and feedback systems. These systems can detect issues as they occur and make immediate adjustments, preventing the production of defective PCBs. This rapid response capability is far more efficient than relying on human operators to identify and correct problems[6].
The Impact of Automation on PCB Manufacturing Efficiency
The implementation of fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT not only reduces human error but also significantly improves overall production efficiency:
Increased Production Speed
Automated SMT lines can operate at much higher speeds than manual assembly processes. Pick and place machines can place thousands of components per hour with extreme accuracy, far outpacing human capabilities[1].
Enhanced Flexibility
Modern SMT lines are highly flexible and can be quickly reconfigured for different PCB designs. This flexibility allows manufacturers to respond rapidly to changes in demand or product specifications, reducing downtime between production runs[9].
Improved Resource Utilization
Automated systems optimize the use of materials and components, reducing waste and improving cost-effectiveness. Advanced material tracking and management systems ensure that the right components are available at the right time, minimizing production delays[5].
24/7 Operation Capability
Fully automated SMT lines can operate around the clock without the need for breaks or shift changes. This continuous operation capability significantly increases production output and reduces the time-to-market for new products[1].
Challenges and Considerations
While fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT offer numerous advantages in reducing human error, there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
Initial Investment Costs
Implementing a fully automated SMT line requires a significant upfront investment in equipment and software. However, the long-term benefits in terms of increased productivity and reduced errors often justify this initial expense[4].
Maintenance and Upkeep
Automated systems require regular maintenance and occasional repairs to ensure optimal performance. While this may seem like a drawback, proper maintenance actually contributes to consistent quality and reduced errors over time[6].
Training Requirements
Although automated systems reduce the need for manual labor in assembly, they still require skilled operators and technicians to manage and maintain the equipment. Investing in training programs is essential to ensure that staff can effectively operate and troubleshoot the automated systems[7].
Adapting to New Technologies
As SMT and automation technologies continue to evolve, manufacturers must stay up-to-date with the latest advancements. This may require periodic upgrades or replacements of equipment to maintain competitive edge and error reduction capabilities[9].
Future Trends in Automated PCB Manufacturing
The field of automated PCB manufacturing with SMT continues to evolve, with several exciting trends on the horizon:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms are being incorporated into SMT lines to further improve defect detection, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. These technologies have the potential to reduce errors even further by anticipating and preventing issues before they occur[2].
Enhanced Traceability and Data Analytics
Advanced tracking systems and data analytics tools are being integrated into automated SMT lines. These systems provide manufacturers with detailed insights into every aspect of the production process, allowing for continuous improvement and error reduction[6].
Increased Flexibility for Small-Batch Production
While automated SMT lines excel at high-volume production, new technologies are making them more adaptable to small-batch and customized PCB manufacturing. This flexibility will allow manufacturers to reduce errors across a wider range of production scenarios[9].
Environmental Sustainability
Future automated SMT lines are likely to incorporate more environmentally friendly processes and materials. This trend towards sustainability will not only reduce the environmental impact of PCB manufacturing but may also contribute to error reduction through the use of more stable and consistent eco-friendly materials[6].
Conclusion
Fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT have revolutionized the electronics industry by significantly reducing human error and improving overall production efficiency. By leveraging advanced technologies such as precise pick and place machines, automated inspection systems, and real-time monitoring, these systems ensure consistent quality and accuracy in PCB assembly.
The benefits of automation extend beyond error reduction, encompassing increased production speed, enhanced flexibility, and improved resource utilization. While challenges such as initial investment costs and ongoing maintenance requirements exist, the long-term advantages of automated SMT lines far outweigh these considerations.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even greater improvements in error reduction and efficiency in PCB manufacturing. The integration of AI, machine learning, and advanced data analytics will further enhance the capabilities of automated SMT lines, paving the way for even higher quality standards and more innovative electronic products.
By embracing fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT, electronics manufacturers can stay competitive in an increasingly demanding market, delivering high-quality products with minimal errors and maximum efficiency.

FAQ
1. What is the main advantage of using fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT?
The main advantage of using fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT is the significant reduction in human error. Automated systems can work with extreme precision and consistency, eliminating mistakes that might occur due to human fatigue or lack of concentration. This results in higher quality PCBs and increased production efficiency.
2. How does SMT contribute to more compact electronic devices?
SMT contributes to more compact electronic devices by allowing components to be mounted directly on the surface of the PCB, rather than through holes. This enables the use of smaller components and denser circuit designs, ultimately leading to more compact and lightweight electronic devices.
3. Are there any disadvantages to implementing a fully automated PCB manufacturing line with SMT?
While the benefits are significant, there are some challenges to consider:
- High initial investment costs for equipment and software
- Ongoing maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance
- Need for skilled technicians to operate and maintain the automated systems
- Potential for downtime if a critical component of the line malfunctions
4. How does automated inspection in SMT lines improve quality control?
Automated inspection systems such as SPI, AOI, and AXI can detect defects with high accuracy and consistency. These systems can operate continuously, inspecting every PCB produced, which is often not feasible with human inspectors. This comprehensive inspection process ensures that defects are caught early, reducing waste and improving overall product quality.
5. What future developments can we expect in fully automated PCB manufacturing lines with SMT?
Future developments in automated PCB manufacturing with SMT are likely to include:
- Integration of AI and machine learning for predictive maintenance and process optimization
- Enhanced traceability and data analytics for continuous improvement
- Greater flexibility to handle small-batch and customized production runs
- Implementation of more environmentally sustainable processes and materials
Citations:
[1] https://www.itechsmt.com/products/fully-automatic-smt-pick-and-place-machine-pcb-assembly-line
[2] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9228397/
[3] https://www.grand-tek.com/en/smt-production.aspx
[4] https://blog.isa.org/the-opportunities-and-obstacles-in-using-automation-for-pcb-assembly
[5] https://mermarinc.com/smt-pcb-assembly/
[6] https://www.ourpcb.com/smt-line.html
[7] https://emsginc.com/services/surface-mount-technology-smt/
[8] https://www.allion.com/tech_surface_mount_tech/
[9] https://www.mycronic.com/product-areas/pcb-assembly/smt/




















